Difference between revisions of "2006 AMC 12A Problems/Problem 16"
m |
(imgs) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Problem == | == Problem == | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
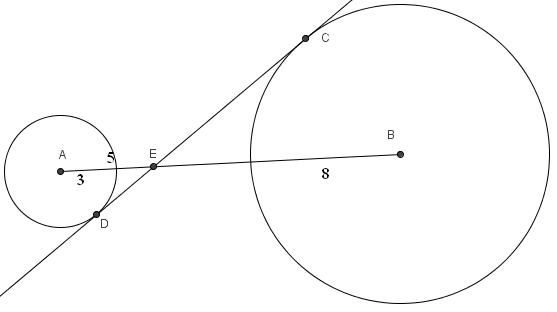
[[Circle]]s with [[center]]s <math>A</math> and <math>B</math> have [[radius |radii]] 3 and 8, respectively. A [[common internal tangent line | common internal tangent]] [[intersect]]s the circles at <math>C</math> and <math>D</math>, respectively. [[Line]]s <math>AB</math> and <math>CD</math> intersect at <math>E</math>, and <math>AE=5</math>. What is <math>CD</math>? | [[Circle]]s with [[center]]s <math>A</math> and <math>B</math> have [[radius |radii]] 3 and 8, respectively. A [[common internal tangent line | common internal tangent]] [[intersect]]s the circles at <math>C</math> and <math>D</math>, respectively. [[Line]]s <math>AB</math> and <math>CD</math> intersect at <math>E</math>, and <math>AE=5</math>. What is <math>CD</math>? | ||
<math>\mathrm{(A) \ } 13\qquad\mathrm{(B) \ } \frac{44}{3}\qquad\mathrm{(C) \ } \sqrt{221}\qquad\mathrm{(D) \ } \sqrt{255}\qquad\mathrm{(E) \ } \frac{55}{3}\qquad</math> | <math>\mathrm{(A) \ } 13\qquad\mathrm{(B) \ } \frac{44}{3}\qquad\mathrm{(C) \ } \sqrt{221}\qquad\mathrm{(D) \ } \sqrt{255}\qquad\mathrm{(E) \ } \frac{55}{3}\qquad</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:2006_AMC12A-16.png]] | ||
| + | |||
== Solution == | == Solution == | ||
| + | [[Image:2006_AMC12A-16a.png]] | ||
| + | |||
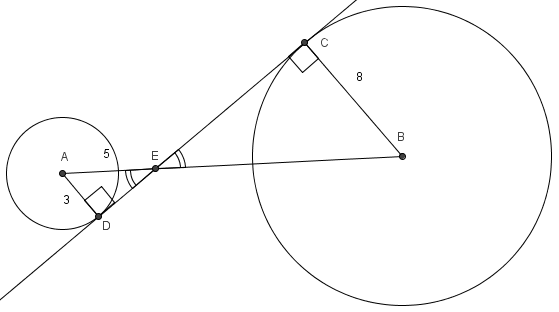
<math>\angle AEC</math> and <math>\angle BED</math> are [[vertical angles]] so they are [[congruent (geometry) | congruent]], as are [[angle]]s <math>\angle ACE</math> and <math>\angle BDE</math> (both are [[right angle]]s because the radius and [[tangent line]] at a point on a circle are always [[perpendicular]]). Thus, <math>\triangle ACE \sim \triangle BDE</math>. | <math>\angle AEC</math> and <math>\angle BED</math> are [[vertical angles]] so they are [[congruent (geometry) | congruent]], as are [[angle]]s <math>\angle ACE</math> and <math>\angle BDE</math> (both are [[right angle]]s because the radius and [[tangent line]] at a point on a circle are always [[perpendicular]]). Thus, <math>\triangle ACE \sim \triangle BDE</math>. | ||
Revision as of 16:55, 15 September 2007
Problem
Circles with centers ![]() and
and ![]() have radii 3 and 8, respectively. A common internal tangent intersects the circles at
have radii 3 and 8, respectively. A common internal tangent intersects the circles at ![]() and
and ![]() , respectively. Lines
, respectively. Lines ![]() and
and ![]() intersect at
intersect at ![]() , and
, and ![]() . What is
. What is ![]() ?
?
![]()
Solution
![]() and
and ![]() are vertical angles so they are congruent, as are angles
are vertical angles so they are congruent, as are angles ![]() and
and ![]() (both are right angles because the radius and tangent line at a point on a circle are always perpendicular). Thus,
(both are right angles because the radius and tangent line at a point on a circle are always perpendicular). Thus, ![]() .
.
By the Pythagorean Theorem, line segment ![]() . The sides are proportional, so
. The sides are proportional, so ![]() . This makes
. This makes ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
See also
| 2006 AMC 12A (Problems • Answer Key • Resources) | |
| Preceded by Problem 15 |
Followed by Problem 17 |
| 1 • 2 • 3 • 4 • 5 • 6 • 7 • 8 • 9 • 10 • 11 • 12 • 13 • 14 • 15 • 16 • 17 • 18 • 19 • 20 • 21 • 22 • 23 • 24 • 25 | |
| All AMC 12 Problems and Solutions | |