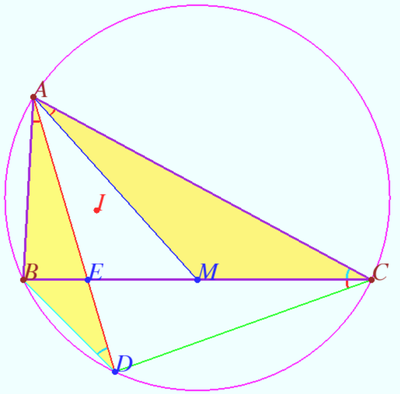
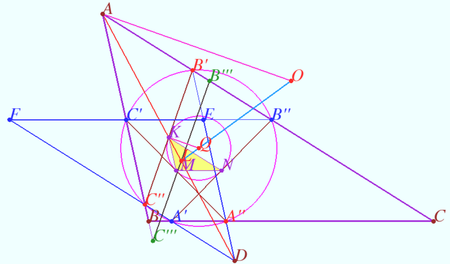
Symmedians, Lemoine point
The reflecting of the median over the corresponding angle bisector is the symmedian. The angle formed by the symmedian and the angle bisector has the same measure as the angle between the median and the angle bisector, but it is on the other side of the angle bisector. The symmedian ![]() is isogonally conjugate to the median
is isogonally conjugate to the median ![]()
There are three symmedians. They are meet at a triangle center called the Lemoine point.
Contents
- 1 Proportions
- 2 Radical axis of circumcircle and Apollonius circle
- 3 Simson line
- 4 Lemoine point of Gergonne triangle
- 5 Symmedian and tangents
- 6 Lemoine point properties
- 7 Parallel lines
- 8 Radical axis
- 9 Construction of symmedian’s point
- 10 Common Lemoine point
- 11 Lemoine point extreme properties
- 12 Lemoine point and perpendicularity
- 13 Lemoine point line
- 14 Antiparallel lines and segments
- 15 Bisectors and antiparallel
- 16 Symmetry of angles
- 17 Three intersecting antiparallel segments
- 18 Three intersecting parallel to sides segments
- 19 Tucker circle
- 20 Tucker circle 2
Proportions
Let ![]() be given.
be given.
Let ![]() be the median,
be the median, ![]()
Prove that iff ![]() is the symmedian than
is the symmedian than ![]()
Proof
1. Let ![]() be the symmedian. So
be the symmedian. So ![]()
![]()
![]() Similarly
Similarly ![]()
![]()
By applying the Law of Sines we get
![]()
![]() Similarly,
Similarly, ![]()
2. ![]()
As point ![]() moves along the fixed arc
moves along the fixed arc ![]() from
from ![]() to
to ![]() , the function
, the function ![]() monotonically increases from zero to infinity. This means that there is exactly one point at which the condition is satisfied. In this case, point
monotonically increases from zero to infinity. This means that there is exactly one point at which the condition is satisfied. In this case, point ![]() lies on the symmedian.
lies on the symmedian.
Similarly for point ![]()
Corollary
Let ![]() be the
be the ![]() symmedian of
symmedian of ![]()
Then ![]() is the
is the ![]() symmedian of
symmedian of ![]() is the
is the ![]() symmedian of
symmedian of ![]() is the
is the ![]() symmedian of
symmedian of ![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
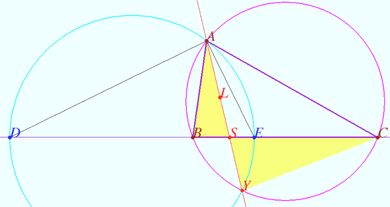
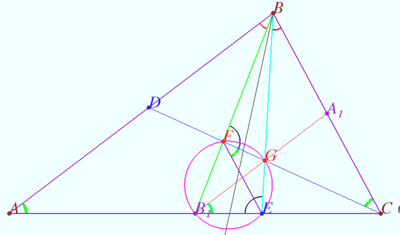
Radical axis of circumcircle and Apollonius circle
The bisectors of the external and internal angles at vertex ![]() of
of ![]() intersect line
intersect line ![]() at points
at points ![]() and
and ![]() The circle
The circle ![]() intersects the circumcircle of
intersects the circumcircle of ![]() at points
at points ![]() and
and ![]() Prove that line
Prove that line ![]() contains the
contains the ![]() symmedian of
symmedian of ![]()
Proof
The circle ![]() is the Apollonius circle for points
is the Apollonius circle for points ![]() and
and ![]()
![]()
![]() is the
is the ![]() symmedian of
symmedian of ![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Simson line
Let triangle ![]() be given,
be given, ![]() Point
Point ![]() lies on arc
lies on arc ![]() of
of ![]()
Let points ![]() and
and ![]() be the the foots from
be the the foots from ![]() to
to ![]() and to
and to ![]() respectively.
respectively.
Prove that ![]() iff
iff ![]() lies on
lies on ![]() symmedian of
symmedian of ![]()
Proof
Points ![]() and
and ![]() lies on Simson line.
lies on Simson line.
![]() is diameter of circle
is diameter of circle ![]()
Similarly, ![]() is diameter of circle
is diameter of circle ![]()
1. Let ![]() lies on
lies on ![]() symmedian of
symmedian of ![]()
![]()
![]() 2. Let
2. Let ![]() lies on
lies on ![]() symmedian of
symmedian of ![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Lemoine point of Gergonne triangle
1. Prove that the Lemoine point of the Gergonne triangle serves as the Gergonne point of the base triangle.
2. The inscribed circle ![]() touches the sides of given triangle
touches the sides of given triangle ![]() at points
at points ![]() Prove that the line
Prove that the line ![]() is
is ![]() symmedian of Gergonne triangle
symmedian of Gergonne triangle ![]()
3. The inscribed circle touches the sides of given triangle ![]() at points
at points ![]() Prove that
Prove that ![]() where
where ![]() is the midpoint
is the midpoint ![]()
Proof
2. Denote ![]()
![]()
Similarly, ![]()
![]() Therefore
Therefore ![]() and
and ![]() is
is ![]() symmedian of Gergonne triangle
symmedian of Gergonne triangle ![]()
1. Similarly, ![]() is
is ![]() symmedian and
symmedian and ![]() is
is ![]() symmedian of Gergonne triangle
symmedian of Gergonne triangle ![]() So the Lemoine point of the Gergonne triangle
So the Lemoine point of the Gergonne triangle ![]() serves as the Gergonne point of the base triangle
serves as the Gergonne point of the base triangle ![]()
3. Let ![]() be the midpoint
be the midpoint ![]() The median
The median ![]() is isogonal conjugate
is isogonal conjugate ![]() with respect
with respect ![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Symmedian and tangents
Let ![]() and it’s circumcircle
and it’s circumcircle ![]() be given.
be given.
Tangents to ![]() at points
at points ![]() and
and ![]() intersect at point
intersect at point ![]()
Prove that ![]() is
is ![]() symmedian of
symmedian of ![]() .
.
Proof
Denote ![]() WLOG,
WLOG, ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() is
is ![]() symmedian of
symmedian of ![]()
Corollary
Let ![]() and it’s circumcircle
and it’s circumcircle ![]() be given.
be given.
Let tangent to ![]() at points
at points ![]() intersect line
intersect line ![]() at point
at point ![]()
Let ![]() be the tangent to
be the tangent to ![]() different from
different from ![]()
Then ![]() is
is ![]() symmedian of
symmedian of ![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Lemoine point properties
Let ![]() be given. Let
be given. Let ![]() be the Lemoine point of
be the Lemoine point of ![]()
![]()
Prove that ![]() is the centroid of
is the centroid of ![]()
Proof
Let ![]() be the centroid of
be the centroid of ![]()
![]()
The double area of ![]() is
is ![]()
Point ![]() is the isogonal conjugate of point
is the isogonal conjugate of point ![]() with respect to
with respect to ![]()
Similarly, one can get ![]()
The double area of ![]() is
is ![]()
Similarly, one can get ![]() is the centroid of
is the centroid of ![]()
Corollary
Vector sum ![]()
Each of these vectors is obtained from the triangle side vectors by rotating by ![]() and multiplying by a constant
and multiplying by a constant ![]()
![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Parallel lines
Let ![]() and it’s Lemoine point
and it’s Lemoine point ![]() be given.
be given.
Let ![]() be an arbitrary point. Let
be an arbitrary point. Let ![]() be the foot from
be the foot from ![]() to line
to line ![]() .
.
Denote ![]() the line through
the line through ![]() and parallel to
and parallel to ![]()
Denote ![]() the line parallel to
the line parallel to ![]() such that distance
such that distance ![]() and points
and points ![]() and
and ![]() are both in the exterior (interior) of
are both in the exterior (interior) of ![]()
Prove that points ![]() and
and ![]() are collinear.
are collinear.
Proof
Denote ![]() the foot from
the foot from ![]() to
to ![]() .
.
![]() Denote
Denote ![]()
![]()
Corollary
If squares ![]() and
and ![]() are constructed in the exterior of
are constructed in the exterior of ![]() then
then ![]() where
where ![]() is the center of circle
is the center of circle ![]() is the symmedian in
is the symmedian in ![]() through
through ![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
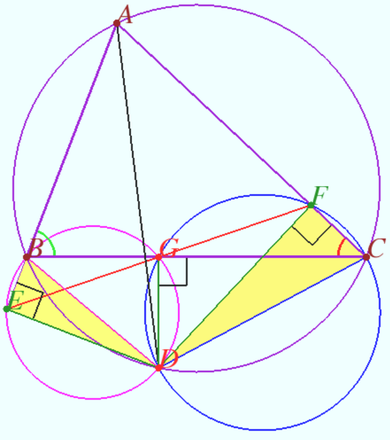
Radical axis
Circle ![]() passes through points
passes through points ![]() and
and ![]() and touches line
and touches line ![]() circle
circle ![]() passes through points
passes through points ![]() and
and ![]() and touches line
and touches line ![]() Let
Let ![]() be the Lemoine point of
be the Lemoine point of ![]()
Prove that the radical axis of these circles contains the symmedian of ![]()
Proof
Denote centers of ![]() and
and ![]() throught
throught ![]() and
and ![]() respectively.
respectively.
Denote ![]() line throught
line throught ![]() parallel to
parallel to ![]() line throught
line throught ![]() parallel to
parallel to ![]()
![]()
The ratio of distance from ![]() to
to ![]() to
to ![]() is equal to the ratio of distance from
is equal to the ratio of distance from ![]() to
to ![]() to
to ![]()
![]()
![]() is the orthocenter of
is the orthocenter of ![]()
the radical axis of these circles contains the ![]() symmedian of
symmedian of ![]()
Corollary
Circumcenter of ![]() Apollonius circle point
Apollonius circle point ![]() circumcenter
circumcenter ![]() the points on
the points on ![]() and
and ![]() opposite
opposite ![]() belong the line perpendicular
belong the line perpendicular ![]() symmedian of
symmedian of ![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
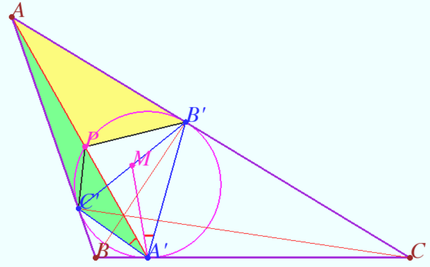
Construction of symmedian’s point
Let triangle ![]() be given.
be given.
Let ![]() be the arbitrary point on sideline
be the arbitrary point on sideline ![]()
The lines ![]() and
and ![]() meet at point
meet at point ![]() The circumcircles of triangles
The circumcircles of triangles ![]() and
and ![]() meet at two distinct points
meet at two distinct points ![]() and
and ![]()
Prove that the line ![]() is the
is the ![]() symmedian of
symmedian of ![]()
Proof
The spiral similarity centered at ![]() with the angle of rotation
with the angle of rotation ![]() maps point
maps point ![]() to point
to point ![]() and point
and point ![]() to point
to point ![]()
So ![]()
![]() is concyclic.
is concyclic.
Let ![]() and
and ![]() be the foot from
be the foot from ![]() to
to ![]() and to
and to ![]() respectively.
respectively.
![]() which means that
which means that ![]() lies on
lies on ![]() symmedian.
symmedian.
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Common Lemoine point
Let ![]() be given,
be given, ![]()
Let ![]() be the Lemoine point of
be the Lemoine point of ![]()
![]()
Prove that the point ![]() is the Lemoine point of
is the Lemoine point of ![]()
Proof
Denote point ![]() so that
so that ![]()
Similarly denote ![]() and
and ![]()
![]() is the centroid of
is the centroid of ![]()
![]() (see Claim).
(see Claim).
Let point ![]() be the centroid of
be the centroid of ![]()
![]()
![]() is cyclic so
is cyclic so ![]() therefore
therefore ![]() and
and ![]() are isogonals with respect
are isogonals with respect ![]()
Similarly ![]() and
and ![]() are isogonals with respect
are isogonals with respect ![]()
![]() is the isogonal conjugate of a point
is the isogonal conjugate of a point ![]() with respect to a triangle
with respect to a triangle ![]()
so ![]() is the Lemoine point of
is the Lemoine point of ![]()
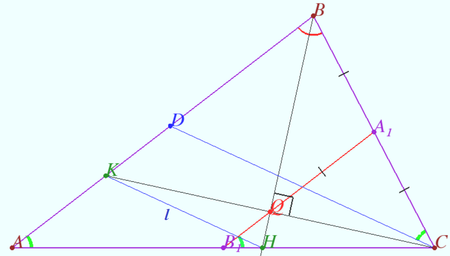
Claim
Lines AP, BP and CP intersect the circumcircle of ![]() at points
at points ![]() and
and ![]()
Points ![]() and
and ![]() are taken on the lines
are taken on the lines ![]() and
and ![]() so that
so that ![]() (see diagram).
(see diagram).
Prove that ![]()
Proof
![]() is cyclic so
is cyclic so ![]()
Similarly, ![]()
![]()
Similarly, ![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Lemoine point extreme properties
Lemoine point ![]() minimizes the sum of the squares of the distances to the sides of the triangle (among all points internal to
minimizes the sum of the squares of the distances to the sides of the triangle (among all points internal to ![]()
Proof
Let us denote the desired point by ![]() Let us imagine that point
Let us imagine that point ![]() is connected to springs of equal stiffness attached to the sides at points
is connected to springs of equal stiffness attached to the sides at points ![]() and
and ![]() and contacts sliding along them without friction. The segments modeling the springs will be perpendicular to the corresponding side. The energy of each spring is proportional to the square of its length. The minimum energy of the system corresponds to the minimum of the sum of the squares of the lengths of these segments, that is, the sum of the squares of the distances from
and contacts sliding along them without friction. The segments modeling the springs will be perpendicular to the corresponding side. The energy of each spring is proportional to the square of its length. The minimum energy of the system corresponds to the minimum of the sum of the squares of the lengths of these segments, that is, the sum of the squares of the distances from ![]() to the sides.
to the sides.
It is known that the minimum spring energy corresponds to the equilibrium position. The condition of equilibrium at a point ![]() is the equality to zero of the vector sum of forces applied from the springs to the point
is the equality to zero of the vector sum of forces applied from the springs to the point ![]() The force developed by each spring is proportional to its length, that is, the equilibrium condition is that the sum of the vectors
The force developed by each spring is proportional to its length, that is, the equilibrium condition is that the sum of the vectors ![]() It is clear that the point
It is clear that the point ![]() corresponds to this condition.
corresponds to this condition.
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Lemoine point and perpendicularity
Let ![]() be given. Let
be given. Let ![]() be the Lemoine point of
be the Lemoine point of ![]()
![]()
![]() is the midpoint
is the midpoint ![]()
Prove that ![]()
Proof
![]() is isogonal conjugated
is isogonal conjugated ![]() with respect
with respect ![]()
![]() is cyclic.
is cyclic.
![]()
![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Lemoine point line
Let ![]() be given. Let
be given. Let ![]() be the Lemoine point of
be the Lemoine point of ![]()
Let ![]() be the height,
be the height, ![]() be the median,
be the median, ![]()
![]() be the midpoint
be the midpoint ![]() .
.
Prove that the points ![]() and
and ![]() are collinear.
are collinear.
Proof
Denote ![]() the circumcenter
the circumcenter ![]()
Denote ![]() the midpoint
the midpoint ![]()
![]() is centroid of
is centroid of ![]() is
is ![]() median of
median of ![]()
Denote ![]() the point symmetric
the point symmetric ![]() with respect
with respect ![]() is the midline of
is the midline of ![]()
![]() is the median of
is the median of ![]()
![]() is the median of
is the median of ![]() the points
the points ![]() and
and ![]() are collinear.
are collinear.
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Antiparallel lines and segments
Two lines ![]() and
and ![]() are said to be antiparallel with respect to the sides of an angle
are said to be antiparallel with respect to the sides of an angle ![]() if they make the same angle in the opposite senses with the bisector of that angle.
if they make the same angle in the opposite senses with the bisector of that angle.
A segment ![]() where points
where points ![]() and
and ![]() lie on rays
lie on rays ![]() and
and ![]() is called antiparallel to side
is called antiparallel to side ![]() if
if ![]() and
and ![]() The points
The points ![]() and
and ![]() are concyclic.
are concyclic.
Prove that the symmedian ![]() bisects any segment
bisects any segment ![]() iff it is antiparallel to side
iff it is antiparallel to side ![]()
Proof
1) Let segment ![]() be the antiparallel to side
be the antiparallel to side ![]() Reflection through the bisector of angle
Reflection through the bisector of angle ![]() maps the segment
maps the segment ![]() into a segment parallel to side
into a segment parallel to side ![]() and maps the symmedian
and maps the symmedian ![]() into the median which bisects image of
into the median which bisects image of ![]()
2) Suppose the symmedian ![]() bisects the segment
bisects the segment ![]() in point
in point ![]() There is a segment
There is a segment ![]() with ends on the sides of angle
with ends on the sides of angle ![]() which contain point
which contain point ![]() and is antiparallel to side
and is antiparallel to side ![]()
![]() is the midpoint
is the midpoint ![]()
![]() is parallelogram, so
is parallelogram, so ![]() contradiction.
contradiction.
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Bisectors and antiparallel
Let ![]() be the antiparallel
be the antiparallel ![]() in the triangle
in the triangle ![]() Prove that
Prove that
1) the bisectors of the angles ![]() and
and ![]() are perpendicular,
are perpendicular,
2) the point ![]() of intersection of bisectors lies on the midline
of intersection of bisectors lies on the midline ![]()
Proof
1) Lines ![]() and
and ![]() are symmetrical with respect to the bisector
are symmetrical with respect to the bisector ![]()
Denote ![]() Line
Line ![]() throught
throught ![]() parallel to
parallel to ![]() is symmetrical to
is symmetrical to ![]() with respect to the bisector
with respect to the bisector ![]()
The axes of symmetry of two lines are perpendicular.
2) Angle ![]() is the midpoint
is the midpoint ![]()
Denote ![]() Bisector
Bisector ![]() is height in
is height in ![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Symmetry of angles
Let ![]() be the antiparallel
be the antiparallel ![]() of the triangle
of the triangle ![]()
Let ![]() crosses the median
crosses the median ![]() of
of ![]() at the point
at the point ![]() and crosses the simedian
and crosses the simedian ![]() at the point
at the point ![]()
Prove that the points ![]() and
and ![]() are concyclic,
are concyclic, ![]()
Proof
Under reflection along a bisector ![]() the median
the median ![]() maps into symmedian
maps into symmedian ![]()
Under reflection along a bisector ![]() antiparallel
antiparallel ![]() maps into the line parallel
maps into the line parallel ![]()
Under reflection along a bisector ![]() the sides of
the sides of ![]() maps into the lines parallel to the sides of the
maps into the lines parallel to the sides of the ![]() so
so ![]() points
points ![]() and
and ![]() are concyclic.
are concyclic.
![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
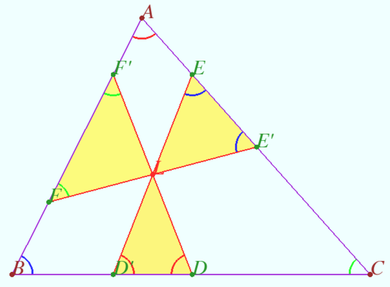
Three intersecting antiparallel segments
Let triangle ![]() and a point
and a point ![]() lying inside it be given. Let
lying inside it be given. Let ![]() and
and ![]() be three segments antiparallel to
be three segments antiparallel to ![]() and
and ![]() respectively.
respectively. ![]()
Prove that ![]() iff
iff ![]() is a Lemoine point.
is a Lemoine point.
Proof
![]() Similarly,
Similarly, ![]()
1. Let ![]() be the Lemoine point. So
be the Lemoine point. So ![]()
2. Let ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() lies on each symmedian.
lies on each symmedian.
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Three intersecting parallel to sides segments
Let triangle ![]() be given.
be given. ![]() is it’s circumcenter,
is it’s circumcenter, ![]() is it’s Lemoine point.
is it’s Lemoine point.
Let ![]() and
and ![]() be three segments parallel to
be three segments parallel to ![]() and
and ![]() respectively.
respectively. ![]()
Prove that points ![]() and
and ![]() lies on the circle centered at midpoint
lies on the circle centered at midpoint ![]() (the first Lemoine circle).
(the first Lemoine circle).
Proof
![]() is the parallelogram.
is the parallelogram.
Denote ![]() is antiparallel to
is antiparallel to ![]()
Similarly, ![]() is antiparallel to
is antiparallel to ![]() is antiparallel to
is antiparallel to ![]()
![]() Denote
Denote ![]()
The coefficient of similarity is
![]()
Therefore ![]() Similarly,
Similarly, ![]()
Denote ![]()
![]() The coefficient of similarity is
The coefficient of similarity is ![]()
Denote ![]() the midpoint
the midpoint ![]() The midline of
The midline of ![]() is
is ![]()
Similarly, ![]() is circumcenter of
is circumcenter of ![]()
![]() is antiparallel to
is antiparallel to ![]() so
so ![]() is tangent to
is tangent to ![]() is the midpoint
is the midpoint ![]()
Similarly, ![]() are tangent to
are tangent to ![]() is the midpoint
is the midpoint ![]() is the midpoint
is the midpoint ![]()
Therefore ![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
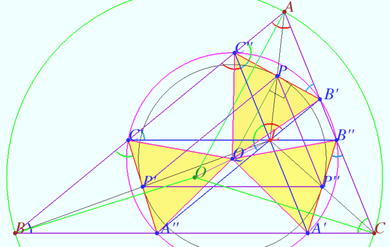
Tucker circle
Let triangle ![]() be given.
be given. ![]() is it’s circumcenter,
is it’s circumcenter, ![]() is it’s Lemoine point.
is it’s Lemoine point.
Let homothety centered at ![]() with factor
with factor ![]() maps
maps ![]() into
into ![]() .
.
Denote the crosspoints of sidelines these triangles as
![]()
![]()
Prove that points ![]() and
and ![]() lies on the circle centered at
lies on the circle centered at ![]() (Tucker circle).
(Tucker circle).
Proof
![]() is the parallelogram.
is the parallelogram.
Denote ![]()
![]() is antiparallel to
is antiparallel to ![]()
Similarly, ![]() is antiparallel to
is antiparallel to ![]() is antiparallel to
is antiparallel to ![]()
![]() is midpoint
is midpoint ![]() is the midpoint
is the midpoint ![]()
![]()
![]()
Similarly, ![]()
Let ![]() be the symmedian
be the symmedian ![]() through
through ![]()
![]()
It is known that three symmedians through ![]() are equal, so
are equal, so ![]()
![]() is homothetic to
is homothetic to ![]() with center
with center ![]() and factor
and factor ![]()
So segments ![]() are tangents to
are tangents to ![]() and points of contact are the midpoints of these segments.
and points of contact are the midpoints of these segments.
Denote ![]() the circumcenter of
the circumcenter of ![]()
Therefore ![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
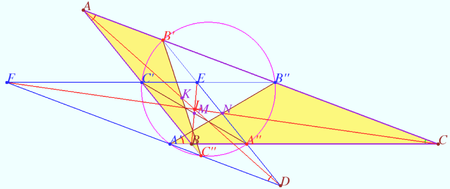
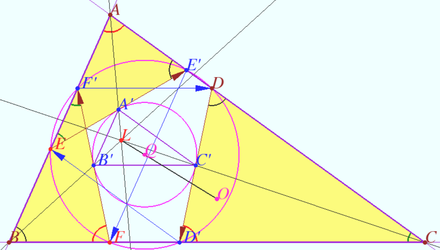
Tucker circle 2
Let triangle ![]() be given. Let
be given. Let ![]() be the arbitrary point on sideline
be the arbitrary point on sideline ![]()
Let ![]() be the antiparallel to side
be the antiparallel to side ![]()
Denote point ![]()
Let ![]() be the antiparallel to side
be the antiparallel to side ![]()
Denote point ![]()
Let ![]() be the antiparallel to side
be the antiparallel to side ![]()
Prove that points ![]() and
and ![]() lies on the circle centered at
lies on the circle centered at ![]() (Tucker circle).
(Tucker circle).
Proof
![]() is isosceles trapezoid.
is isosceles trapezoid.
So ![]()
![]() is isosceles trapezoid.
is isosceles trapezoid.
So ![]()
Denote ![]() the midpoint
the midpoint ![]() the midpoint
the midpoint ![]() the midpoint
the midpoint ![]()
![]() Similarly,
Similarly, ![]()
![]() is the midpoint of antiparallel of
is the midpoint of antiparallel of ![]() is the
is the ![]() symmedian of
symmedian of ![]()
Similarly, ![]() is the
is the ![]() symmedian,
symmedian, ![]() is the
is the ![]() symmedian of
symmedian of ![]()
Therefore Lemoine point ![]() is homothetic to
is homothetic to ![]() with center
with center ![]()
So segments ![]() are tangents to
are tangents to ![]() and points of contact are the midpoints of these segments.
and points of contact are the midpoints of these segments.
Denote ![]() the circumcenter of
the circumcenter of ![]() where
where ![]() is the circumcenter of
is the circumcenter of ![]()
Therefore ![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss