Trigonometry
Trigonometry seeks to find the lengths of a triangle's sides, given 2 angles and a side. Trigonometry is closely related to analytic geometry.
Contents
Basic definitions
Usually we call an angle ![]() , read "theta", but
, read "theta", but ![]() is just a variable. We could just as well call it
is just a variable. We could just as well call it ![]() .
.
For the following definitions, the "opposite side" is the side opposite of angle ![]() , and the "adjacent side" is the side that is part of angle
, and the "adjacent side" is the side that is part of angle ![]() , but is not the hypotenuse.
, but is not the hypotenuse.
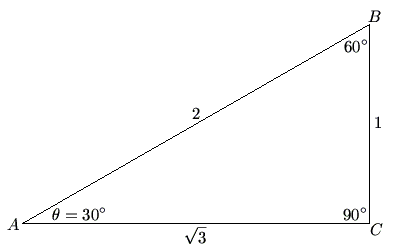
i.e. If ABC is a right triangle with right angle C, and angle A = ![]() , then BC is the "opposite side", AC is the "adjacent side", and AB is the hypotenuse.
, then BC is the "opposite side", AC is the "adjacent side", and AB is the hypotenuse.
Sine
The sine of an angle ![]() , abbreviated
, abbreviated ![]() , is the ratio between the opposite side and the hypotenuse of a triangle. For instance, in the 30-60-90 triangle above,
, is the ratio between the opposite side and the hypotenuse of a triangle. For instance, in the 30-60-90 triangle above, ![]() .
.
Cosine
The cosine of an angle ![]() , abbreviated
, abbreviated ![]() , is the ratio between the adjacent side and the hypotenuse of a triangle. For instance, in the 30-60-90 triangle above,
, is the ratio between the adjacent side and the hypotenuse of a triangle. For instance, in the 30-60-90 triangle above, ![]() .
.
Tangent
The tangent of an angle ![]() , abbreviated
, abbreviated ![]() , is the ratio between the opposite side and the adjacent side of a triangle. For instance, in the 30-60-90 triangle above,
, is the ratio between the opposite side and the adjacent side of a triangle. For instance, in the 30-60-90 triangle above, ![]() . (Note that
. (Note that ![]() .)
.)
Cosecant
The cosecant of an angle ![]() , abbreviated
, abbreviated ![]() , is the ratio between the hypotenuse and the opposite side of a triangle. For instance, in the 30-60-90 triangle above,
, is the ratio between the hypotenuse and the opposite side of a triangle. For instance, in the 30-60-90 triangle above, ![]() . (Note that
. (Note that ![]() .)
.)
Secant
The secant of an angle ![]() , abbreviated
, abbreviated ![]() , is the ratio between the hypotenuse and the adjacent side of a triangle. For instance, in the 30-60-90 triangle above,
, is the ratio between the hypotenuse and the adjacent side of a triangle. For instance, in the 30-60-90 triangle above, ![]() . (Note that
. (Note that ![]() .)
.)
Cotangent
The cotangent of an angle ![]() , abbreviated
, abbreviated ![]() , is the ratio between the adjacent side and the opposite side of a triangle. For instance, in the 30-60-90 triangle above,
, is the ratio between the adjacent side and the opposite side of a triangle. For instance, in the 30-60-90 triangle above, ![]() . (Note that
. (Note that ![]() .)
.)
Trigonometery Definitions for non-acute angles
Consider a unit circle that is centered at the origin. By picking a point on the circle, and dropping a perpendicular line to the x-axis, a right triangle is formed with a hypotenuse 1 unit long. Letting the angle at the origin be ![]() and the coordinates of the point we picked to be
and the coordinates of the point we picked to be ![]() , we have:
, we have:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Note that ![]() is the rectangular coordinates for the point
is the rectangular coordinates for the point ![]() .
.
This is true for all angles, even negative angles and angles greater than 360 degrees. Due to the way trig ratios are defined for non-acute angles, the value of a trig ratio could be positive or negative, or even 0.