Difference between revisions of "2017 AMC 12B Problems/Problem 24"
(→Solution 6) |
(→Solution 6) |
||
| Line 101: | Line 101: | ||
| − | Next, <math>\angle AFE = \frac{\pi}{2} = \angle EGD</math> | + | Next, <math>\angle AFE = \frac{\pi}{2} = \angle EGD</math> because <math>FG \parallel BC</math>. Also, <math>\pi = \angle FEA + \angle AED + \angle DEG = \angle FEA + \angle AED + \angle EAF = \frac{\pi}{2} + \angle AED</math>, so <math>\angle AED = \frac{\pi}{2}</math>. Therefore, <math>\triangle AED \sim \triangle ABC</math> by AA. Since <math>\triangle CED \sim \triangle ABC</math>, <math>\triangle AED \sim \triangle CEB</math>. |
Revision as of 16:56, 31 July 2024
Contents
Problem
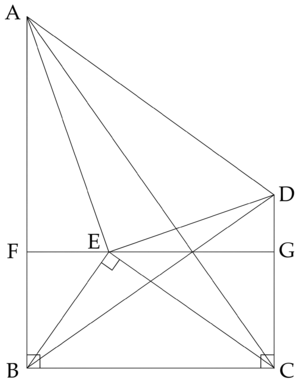
Quadrilateral ![]() has right angles at
has right angles at ![]() and
and ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() . There is a point
. There is a point ![]() in the interior of
in the interior of ![]() such that
such that ![]() and the area of
and the area of ![]() is
is ![]() times the area of
times the area of ![]() . What is
. What is ![]() ?
?
![]()
Solution 1
Let ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() . Note that
. Note that ![]() . By the Pythagorean Theorem,
. By the Pythagorean Theorem, ![]() . Since
. Since ![]() , the ratios of side lengths must be equal. Since
, the ratios of side lengths must be equal. Since ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() . Let F be a point on
. Let F be a point on ![]() such that
such that ![]() is an altitude of triangle
is an altitude of triangle ![]() . Note that
. Note that ![]() . Therefore,
. Therefore, ![]() and
and ![]() . Since
. Since ![]() and
and ![]() form altitudes of triangles
form altitudes of triangles ![]() and
and ![]() , respectively, the areas of these triangles can be calculated. Additionally, the area of triangle
, respectively, the areas of these triangles can be calculated. Additionally, the area of triangle ![]() can be calculated, as it is a right triangle. Solving for each of these yields:
can be calculated, as it is a right triangle. Solving for each of these yields:
\begin{align*} [BEC] &=[CED]=[BEA]=\frac{x^3}{2(x^2+1)} \\ [ABCD] &=[AED]+[DEC]+[CEB]+[BEA] \\ \frac{(BC)(AB+CD)}{2} &= 17*[CEB]+ [CEB] + [CEB] + [CEB] \\ \frac{x^3+x}{2} &= \frac{20x^3}{2(x^2+1)} \\ \frac{x}{x^2+1} &= \frac{20x^3}{x^2+1} \\ (x^2+1)^2 &=20x^2 \\ x^4-18x^2+1 &=0 \implies x^2=9+4\sqrt{5}=4+2(2\sqrt{5})+5 \\ \end{align*}
Therefore, the answer is ![]()
Solution 2
Draw line ![]() through
through ![]() , with
, with ![]() on
on ![]() and
and ![]() on
on ![]() ,
, ![]() . WLOG let
. WLOG let ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() . By weighted average
. By weighted average ![]() .
.
Meanwhile, ![]() . This follows from comparing the ratios of triangle DEG to CFE and triangle AEG to FEB, both pairs in which the two triangles share a height perpendicular to FG, and have base ratio
. This follows from comparing the ratios of triangle DEG to CFE and triangle AEG to FEB, both pairs in which the two triangles share a height perpendicular to FG, and have base ratio ![]() .
.
![]() . We obtain
. We obtain ![]() ,
namely
,
namely ![]() .
.
The rest is the same as Solution 1.
Solution 3
Let ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]()
Note that ![]() cannot be the intersection of
cannot be the intersection of ![]() and
and ![]() , as that would mean
, as that would mean ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![\[\frac{ [ADE] }{ [CEB] } = \frac { \frac{ b(a^2+b^2)^2 - 3a^2b^3 }{ 2a(a^2+b^2) } }{ \frac{ab^3}{2(a^2+b^2)} } = \frac{ (a^2 + b^2)^2 - 3a^2b^2 }{ a^2b^2 } = \frac{ a^4 - a^2b^2 + b^4 }{ a^2b^2 } = 17\]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/b/8/c/b8c90c41b6f6c2741a097ad59143289b465fc935.png)
![]()
Let ![]() ,
,
![]()
![]()
Solution 4
Let ![]() . Then from the similar triangles condition, we compute
. Then from the similar triangles condition, we compute ![]() and
and ![]() . Hence, the
. Hence, the ![]() -coordinate of
-coordinate of ![]() is just
is just ![]() . Since
. Since ![]() lies on the unit circle, we can compute the
lies on the unit circle, we can compute the ![]() coordinate as
coordinate as ![]() . By Shoelace, we want
. By Shoelace, we want ![\[\frac{1}{2}\det\begin{bmatrix} -1 & 4a & 1\\ \frac{1-4a^2}{4a^2+1} & \frac{4a}{4a^2+1} & 1\\ 1 & \frac{1}{a} & 1 \end{bmatrix}=17\cdot\frac{1}{2}\cdot 2 \cdot \frac{4a}{4a^2+1}\]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/e/3/1/e31a4129613c976758006d351f412b52e389f462.png) Factoring out denominators and expanding by minors, this is equivalent to
Factoring out denominators and expanding by minors, this is equivalent to
![]() This factors as
This factors as ![]() , so
, so ![]() and so the answer is
and so the answer is ![]() .
.
Solution 5
Let ![]() where
where ![]() . Because
. Because ![]() . Notice that the diagonals are perpendicular with slopes of
. Notice that the diagonals are perpendicular with slopes of ![]() and
and ![]() . Let the intersection of
. Let the intersection of ![]() and
and ![]() be
be ![]() , then
, then ![]() . However, because
. However, because ![]() is a trapezoid,
is a trapezoid, ![]()
![]() and
and ![]() share the same area, therefore
share the same area, therefore ![]()
![]() is the reflection of
is the reflection of ![]()
![]() over the perpendicular bisector of
over the perpendicular bisector of ![]() , which is
, which is ![]() . We use the linear equations of the diagonals,
. We use the linear equations of the diagonals, ![]() , to find the coordinates of
, to find the coordinates of ![]() .
. ![]()
![]() The y-coordinate of
The y-coordinate of ![]() is simply
is simply ![]() The area of
The area of ![]() is
is ![]() . We apply shoelace theorem to solve for the area of
. We apply shoelace theorem to solve for the area of ![]() . The coordinates of the triangle are
. The coordinates of the triangle are ![]() , so the area is
, so the area is
![]()
![]() Finally, we use the property that the ratio of areas equals
Finally, we use the property that the ratio of areas equals ![]()
![\[\frac{\frac12}{\frac12} \frac{\frac{a^4-a^2+1}{a(a^2+1)}}{\frac{a}{a^2+1}} = 17 \Rightarrow \frac{a^4-a^2+1}{a^2} = 17 \Rightarrow a^4-18a^2+1 = 0\]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/9/2/8/928bb25be3d6759304ecf6ffc5b47bad457d9d31.png)
![]()
~Zeric
Solution 6
This solution involves proving ![]() .
.
Let ![]() be the intersection of
be the intersection of ![]() and
and ![]() . Label points
. Label points ![]() and
and ![]() the same way as
the same way as ![]() .
.
![]() . Additionally,
. Additionally, ![]() , so
, so ![]() by SAS. Therefore,
by SAS. Therefore, ![]() .
.
Next, ![]() because
because ![]() . Also,
. Also, ![]() , so
, so ![]() . Therefore,
. Therefore, ![]() by AA. Since
by AA. Since ![]() ,
, ![]() .
.
Given ![]() , we deduce that the ratio of corresponding side lengths of
, we deduce that the ratio of corresponding side lengths of ![]() to
to ![]() must be
must be ![]() . Now, we set
. Now, we set ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() . Using the Pythagorean Theorem,
. Using the Pythagorean Theorem, ![]() . Thus,
. Thus,  . Solving gives
. Solving gives ![]() .
.
Finally, ![]() .
.
~Zhixing
Video Solution by MOP 2024
~r00tsOfUnity
Notes
1) ![]() is the most relevant answer choice because it shares numbers with the givens of the problem.
is the most relevant answer choice because it shares numbers with the givens of the problem.
2) It's a very good guess to replace finding the area of triangle AED with the area of the triangle DAF, where F is the projection of D onto AB(then find the closest answer choice).
See Also
| 2017 AMC 12B (Problems • Answer Key • Resources) | |
| Preceded by Problem 23 |
Followed by Problem 25 |
| 1 • 2 • 3 • 4 • 5 • 6 • 7 • 8 • 9 • 10 • 11 • 12 • 13 • 14 • 15 • 16 • 17 • 18 • 19 • 20 • 21 • 22 • 23 • 24 • 25 | |
| All AMC 12 Problems and Solutions | |
The problems on this page are copyrighted by the Mathematical Association of America's American Mathematics Competitions.