Difference between revisions of "2016 AIME I Problems/Problem 15"
m |
R00tsofunity (talk | contribs) (new solution + new diagram) |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
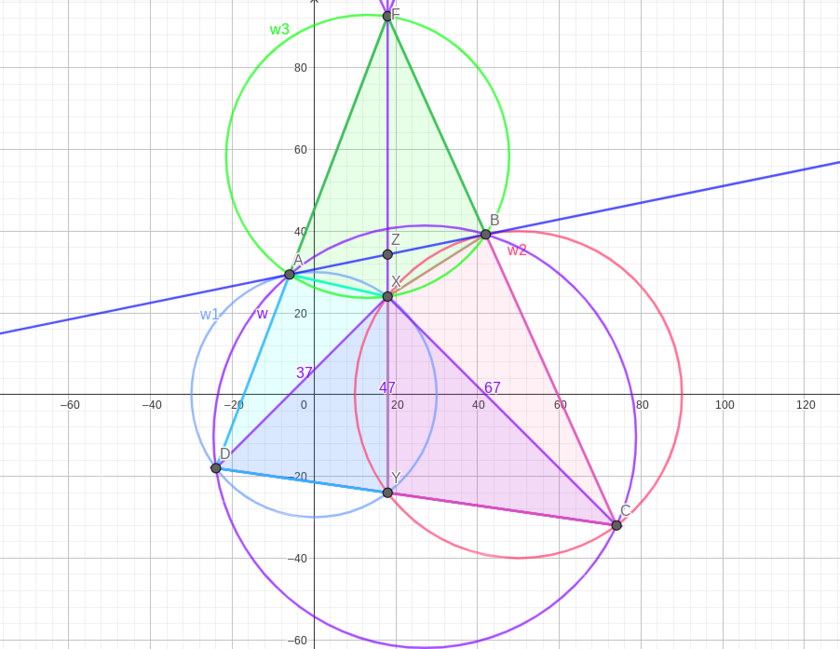
Circles <math>\omega_1</math> and <math>\omega_2</math> intersect at points <math>X</math> and <math>Y</math>. Line <math>\ell</math> is tangent to <math>\omega_1</math> and <math>\omega_2</math> at <math>A</math> and <math>B</math>, respectively, with line <math>AB</math> closer to point <math>X</math> than to <math>Y</math>. Circle <math>\omega</math> passes through <math>A</math> and <math>B</math> intersecting <math>\omega_1</math> again at <math>D \neq A</math> and intersecting <math>\omega_2</math> again at <math>C \neq B</math>. The three points <math>C</math>, <math>Y</math>, <math>D</math> are collinear, <math>XC = 67</math>, <math>XY = 47</math>, and <math>XD = 37</math>. Find <math>AB^2</math>. | Circles <math>\omega_1</math> and <math>\omega_2</math> intersect at points <math>X</math> and <math>Y</math>. Line <math>\ell</math> is tangent to <math>\omega_1</math> and <math>\omega_2</math> at <math>A</math> and <math>B</math>, respectively, with line <math>AB</math> closer to point <math>X</math> than to <math>Y</math>. Circle <math>\omega</math> passes through <math>A</math> and <math>B</math> intersecting <math>\omega_1</math> again at <math>D \neq A</math> and intersecting <math>\omega_2</math> again at <math>C \neq B</math>. The three points <math>C</math>, <math>Y</math>, <math>D</math> are collinear, <math>XC = 67</math>, <math>XY = 47</math>, and <math>XD = 37</math>. Find <math>AB^2</math>. | ||
| + | ==Solution== | ||
| + | Using the radical axis theorem, the lines <math>\overline{AD}, \overline{BC}, \overline{XY}</math> are all concurrent at one point, call it <math>F</math>. Now recall by Miquel's theorem in <math>\triangle FDC</math> the fact that quadrilaterals <math>DAXY</math> and <math>CBXY</math> are cyclic implies <math>FAXB</math> is cyclic as well. Denote <math>\omega_{3}\equiv(FAXB)</math> and <math>Z\equiv\ell\cap\overline{FXY}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Since point <math>Z</math> lies on the radical axis of <math>\omega_{1},\omega_{2}</math>, it has equal power with respect to both circles, thus <cmath>AZ^{2}=\text{Pow}_{\omega_{1}}(Z)=ZX\cdot ZY=\text{Pow}_{\omega_{2}}(Z)=ZB^{2}\implies AZ=ZB.</cmath> Also, notice that <cmath>AZ\cdot ZB=\text{Pow}_{\omega_{3}}(Z)=ZX\cdot ZF\implies ZY=ZF.</cmath> The diagonals of quadrilateral <math>FAYB</math> bisect each other at <math>Z</math>, so we conclude that <math>FAYB</math> is a parallelogram. Let <math>u:=ZX</math>, so that <math>ZY=ZF=u+47</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Because <math>FAYB</math> is a parallelogram and quadrilaterals <math>DAXY, CBXY</math> are cyclic, <cmath>\angle DFX=\angle AFX=\angle BYX=\angle BCX=\angle FCX~~\text{and}~~\angle XDF=\angle XDA=\angle XYA=\angle XFB=\angle XFC</cmath> so we have the pair of similar triangles <math>\triangle DFX~\sim~\triangle FCX</math>. Thus <cmath>\dfrac{37}{2u+47}=\dfrac{2u+47}{67}\implies 2u+47=\sqrt{37\cdot 67}\implies u=\dfrac{1}{2}\left(\sqrt{37\cdot 67}-47\right).</cmath> Now compute <cmath>AB^{2}=4AZ^{2}=4\cdot ZX\cdot ZY=4u(u+47)=37\cdot 67-47^{2}=\textbf{270}.</cmath> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:AIME 2016-I15 Geogebra Diagram.png|840px]] | ||
==Solution 1== | ==Solution 1== | ||
Revision as of 16:47, 14 December 2022
Contents
Problem
Circles ![]() and
and ![]() intersect at points
intersect at points ![]() and
and ![]() . Line
. Line ![]() is tangent to
is tangent to ![]() and
and ![]() at
at ![]() and
and ![]() , respectively, with line
, respectively, with line ![]() closer to point
closer to point ![]() than to
than to ![]() . Circle
. Circle ![]() passes through
passes through ![]() and
and ![]() intersecting
intersecting ![]() again at
again at ![]() and intersecting
and intersecting ![]() again at
again at ![]() . The three points
. The three points ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() are collinear,
are collinear, ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() . Find
. Find ![]() .
.
Solution
Using the radical axis theorem, the lines ![]() are all concurrent at one point, call it
are all concurrent at one point, call it ![]() . Now recall by Miquel's theorem in
. Now recall by Miquel's theorem in ![]() the fact that quadrilaterals
the fact that quadrilaterals ![]() and
and ![]() are cyclic implies
are cyclic implies ![]() is cyclic as well. Denote
is cyclic as well. Denote ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
Since point ![]() lies on the radical axis of
lies on the radical axis of ![]() , it has equal power with respect to both circles, thus
, it has equal power with respect to both circles, thus ![]() Also, notice that
Also, notice that ![]() The diagonals of quadrilateral
The diagonals of quadrilateral ![]() bisect each other at
bisect each other at ![]() , so we conclude that
, so we conclude that ![]() is a parallelogram. Let
is a parallelogram. Let ![]() , so that
, so that ![]() .
.
Because ![]() is a parallelogram and quadrilaterals
is a parallelogram and quadrilaterals ![]() are cyclic,
are cyclic, ![]() so we have the pair of similar triangles
so we have the pair of similar triangles ![]() . Thus
. Thus ![]() Now compute
Now compute ![]()
Solution 1
Let ![]() . By the radical axis theorem
. By the radical axis theorem ![]() are concurrent, say at
are concurrent, say at ![]() . Moreover,
. Moreover, ![]() by simple angle chasing. Let
by simple angle chasing. Let ![]() . Then
. Then ![]() Now,
Now, ![]() , and by power of a point,
, and by power of a point,  Solving, we get
Solving, we get ![]()
![]()
Solution 2
By the Radical Axis Theorem ![]() concur at point
concur at point ![]() .
.
Let ![]() and
and ![]() intersect at
intersect at ![]() . Note that because
. Note that because ![]() and
and ![]() are cyclic, by Miquel's Theorem
are cyclic, by Miquel's Theorem ![]() is cyclic as well. Thus
is cyclic as well. Thus
![]() and
and
![]() Thus
Thus ![]() and
and ![]() , so
, so ![]() is a parallelogram. Hence
is a parallelogram. Hence ![]() and
and ![]() . But notice that
. But notice that ![]() and
and ![]() are similar by
are similar by ![]() Similarity, so
Similarity, so ![]() . But
. But
![]() Hence
Hence ![]()
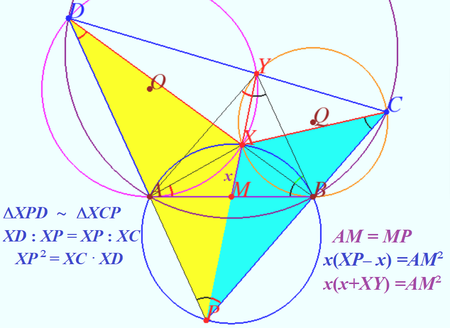
Solution 3
First, we note that as ![]() and
and ![]() have bases along the same line,
have bases along the same line, ![]() . We can also find the ratio of their areas using the circumradius area formula. If
. We can also find the ratio of their areas using the circumradius area formula. If ![]() is the radius of
is the radius of ![]() and if
and if ![]() is the radius of
is the radius of ![]() , then
, then
![]() Since we showed this to be
Since we showed this to be ![]() , we see that
, we see that ![]() .
.
We extend ![]() and
and ![]() to meet at point
to meet at point ![]() , and we extend
, and we extend ![]() and
and ![]() to meet at point
to meet at point ![]() as shown below.
as shown below.
![[asy] size(200); import olympiad; real R1=45,R2=67*R1/37; real m1=sqrt(R1^2-23.5^2); real m2=sqrt(R2^2-23.5^2); pair o1=(0,0),o2=(m1+m2,0),x=(m1,23.5),y=(m1,-23.5); draw(circle(o1,R1)); draw(circle(o2,R2)); pair q=(-R1/(R2-R1)*o2.x,0); pair a=tangent(q,o1,R1,2); pair b=tangent(q,o2,R2,2); pair d=intersectionpoints(circle(o1,R1),q--y+15*(y-q))[0]; pair c=intersectionpoints(circle(o2,R2),q--y+15*(y-q))[1]; pair p=extension(a,d,b,c); dot(q^^a^^b^^x^^y^^c^^d^^p); draw(q--b^^q--c); draw(p--d^^p--c^^x--y); draw(a--y^^b--y); draw(d--x--c); label("$A$",a,NW,fontsize(8)); label("$B$",b,NE,fontsize(8)); label("$C$",c,SE,fontsize(8)); label("$D$",d,SW,fontsize(8)); label("$X$",x,2*WNW,fontsize(8)); label("$Y$",y,3*S,fontsize(8)); label("$P$",p,N,fontsize(8)); label("$Q$",q,W,fontsize(8)); [/asy]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/2/0/0/200feab33999ae63954444617d1c3d67d4a2b23b.png) As
As ![]() is cyclic, we know that
is cyclic, we know that ![]() . But then as
. But then as ![]() is tangent to
is tangent to ![]() at
at ![]() , we see that
, we see that ![]() . Therefore,
. Therefore, ![]() , and
, and ![]() . A similar argument shows
. A similar argument shows ![]() . These parallel lines show
. These parallel lines show ![]() . Also, we showed that
. Also, we showed that ![]() , so the ratio of similarity between
, so the ratio of similarity between ![]() and
and ![]() is
is ![]() , or rather
, or rather
![]() We can now use the parallel lines to find more similar triangles. As
We can now use the parallel lines to find more similar triangles. As ![]() , we know that
, we know that
![]() Setting
Setting ![]() , we see that
, we see that ![]() , hence
, hence ![]() , and the problem simplifies to finding
, and the problem simplifies to finding ![]() . Setting
. Setting ![]() , we also see that
, we also see that ![]() , hence
, hence ![]() . Also, as
. Also, as ![]() , we find that
, we find that
![]() As
As ![]() , we see that
, we see that ![]() , hence
, hence ![]() .
.
Applying Power of a Point to point ![]() with respect to
with respect to ![]() , we find
, we find
![]() or
or ![]() . We wish to find
. We wish to find ![]() .
.
Applying Stewart's Theorem to ![]() , we find
, we find
![]() We can cancel
We can cancel ![]() from both sides, finding
from both sides, finding ![]() . Therefore,
. Therefore,
![]()
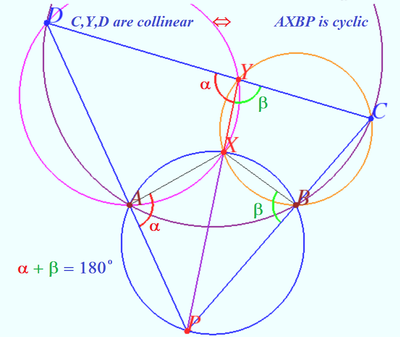
Solution 4
![[asy] size(9cm); import olympiad; real R1=45,R2=67*R1/37; real m1=sqrt(R1^2-23.5^2); real m2=sqrt(R2^2-23.5^2); pair o1=(0,0),o2=(m1+m2,0),x=(m1,23.5),y=(m1,-23.5); draw(circle(o1,R1)); draw(circle(o2,R2)); pair q=(-R1/(R2-R1)*o2.x,0); pair a=tangent(q,o1,R1,2); pair b=tangent(q,o2,R2,2); pair d=intersectionpoints(circle(o1,R1),q--y+15*(y-q))[0]; pair c=intersectionpoints(circle(o2,R2),q--y+15*(y-q))[1]; dot(a^^b^^x^^y^^c^^d); draw(x--y); draw(a--y^^b--y); draw(d--x--c); draw(a--b--c--d--cycle); draw(x--a^^x--b); label("$A$",a,NW,fontsize(9)); label("$B$",b,NE,fontsize(9)); label("$C$",c,SE,fontsize(9)); label("$D$",d,SW,fontsize(9)); label("$X$",x,2*N,fontsize(9)); label("$Y$",y,3*S,fontsize(9)); [/asy]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/9/e/d/9edab2433cc7ad4e4413fc95f45b47d01eae4a00.png) First of all, since quadrilaterals
First of all, since quadrilaterals ![]() and
and ![]() are cyclic, we can let
are cyclic, we can let ![]() , and
, and ![]() , due to the properties of cyclic quadrilaterals. In addition, let
, due to the properties of cyclic quadrilaterals. In addition, let ![]() and
and ![]() . Thus,
. Thus, ![]() and
and ![]() . Then, since quadrilateral
. Then, since quadrilateral ![]() is cyclic as well, we have the following sums:
is cyclic as well, we have the following sums:
![]()
![]() Cancelling out
Cancelling out ![]() in the second equation and isolating
in the second equation and isolating ![]() yields
yields ![]() . Substituting
. Substituting ![]() back into the first equation, we obtain
back into the first equation, we obtain
![]() Since
Since
![]()
![]() we can then imply that
we can then imply that ![]() . Similarly,
. Similarly, ![]() . So then
. So then ![]() , so since we know that
, so since we know that ![]() bisects
bisects ![]() , we can solve for
, we can solve for ![]() and
and ![]() with Stewart’s Theorem. Let
with Stewart’s Theorem. Let ![]() and
and ![]() . Then
. Then
![]()
![]()
![]() Now, since
Now, since ![]() and
and ![]() ,
, ![]() . From there, let
. From there, let ![]() and
and ![]() . From angle chasing we can derive that
. From angle chasing we can derive that ![]() and
and ![]() . From there, since
. From there, since ![]() , it is quite clear that
, it is quite clear that ![]() , and
, and ![]() can be found similarly. From there, since
can be found similarly. From there, since ![]() and
and ![]() , we have
, we have ![]() similarity between
similarity between ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() . Therefore the length of
. Therefore the length of ![]() is the geometric mean of the lengths of
is the geometric mean of the lengths of ![]() and
and ![]() (from
(from ![]() ). However,
). However, ![]() yields the proportion
yields the proportion ![]() ; hence, the length of
; hence, the length of ![]() is the geometric mean of the lengths of
is the geometric mean of the lengths of ![]() and
and ![]() .
We can now simply use arithmetic to calculate
.
We can now simply use arithmetic to calculate ![]() .
.
![]()
![]()
![]()
-Solution by TheBoomBox77
Solution 5 (not too different)
Let ![]() . By Radical Axes,
. By Radical Axes, ![]() lies on
lies on ![]() . Note that
. Note that ![]() is cyclic as
is cyclic as ![]() is the Miquel point of
is the Miquel point of ![]() in this configuration.
in this configuration.
Claim. ![]() Proof. We angle chase.
Proof. We angle chase. ![]() and
and![]()
Let ![]() . Note
. Note ![]() and
and![]() By our claim,
By our claim, ![]() and
and![]() Finally,
Finally, ![]() ~Mathscienceclass
~Mathscienceclass
Solution 6 (No words)
![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Video Solution
~MathProblemSolvingSkills.com
See Also
| 2016 AIME I (Problems • Answer Key • Resources) | ||
| Preceded by Problem 14 |
Followed by Last Question | |
| 1 • 2 • 3 • 4 • 5 • 6 • 7 • 8 • 9 • 10 • 11 • 12 • 13 • 14 • 15 | ||
| All AIME Problems and Solutions | ||
The problems on this page are copyrighted by the Mathematical Association of America's American Mathematics Competitions.