Difference between revisions of "2021 IMO Problems/Problem 4"
(→Solution 3 (Visual)) |
(→Solution 3 (Visual)) |
||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
Therefore <math>\hspace{10mm} TX = ZY.</math> | Therefore <math>\hspace{10mm} TX = ZY.</math> | ||
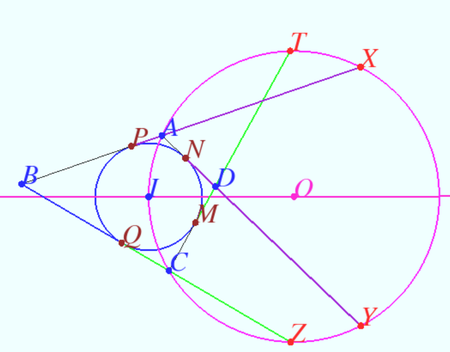
| − | Let <math>P, Q, N</math> and <math>M</math> be the tangency points of <math>\Gamma</math> with <math>AB, BC, CD</math> and <math>DA</math> respectively. | + | Let <math>P, Q, N</math> and <math>M</math> be the tangency points of <math>\Gamma</math> with <math>AB, BC, CD,</math> and <math>DA,</math> respectively. |
| − | Using | + | Using <i><b>Claim 2</b></i> we get <math>TM = QZ, PX = NY.</math> |
<cmath>AD + DT + XA = AN+ND + TM – MD +XP-PA =</cmath> | <cmath>AD + DT + XA = AN+ND + TM – MD +XP-PA =</cmath> | ||
<cmath>= XP + TM = QZ + NY = MC + ZC + MD + DY =</cmath> | <cmath>= XP + TM = QZ + NY = MC + ZC + MD + DY =</cmath> | ||
| − | <cmath>=CD + DY | + | <cmath>=CD + ZC + DY.</cmath> |
<i><b>Claim 1</b></i> | <i><b>Claim 1</b></i> | ||
| Line 71: | Line 71: | ||
<math>\overset{\Large\frown} {IZ}= 2\pi - \overset{\Large\frown} {IT} - \overset{\Large\frown} {TZ}= 2\gamma= \overset{\Large\frown} {IT}\implies</math> symmetry <math>T</math> and <math>Z.</math> | <math>\overset{\Large\frown} {IZ}= 2\pi - \overset{\Large\frown} {IT} - \overset{\Large\frown} {TZ}= 2\gamma= \overset{\Large\frown} {IT}\implies</math> symmetry <math>T</math> and <math>Z.</math> | ||
| − | <i><b> | + | <i><b>Claim 2</b></i> |
Let circles <math>\omega</math> centered at <math>I</math> and <math>\Omega</math> centered at <math>O</math> be given. Let points <math>A</math> and <math>A'</math> lies on <math>\Omega</math> and symmetrical with respect <math>OI.</math> Let <math>AC</math> and <math>A'B</math> be tangents to <math>\omega</math>. Then <math>AC = A'B.</math> | Let circles <math>\omega</math> centered at <math>I</math> and <math>\Omega</math> centered at <math>O</math> be given. Let points <math>A</math> and <math>A'</math> lies on <math>\Omega</math> and symmetrical with respect <math>OI.</math> Let <math>AC</math> and <math>A'B</math> be tangents to <math>\omega</math>. Then <math>AC = A'B.</math> | ||
Revision as of 21:48, 29 August 2022
Problem
Let ![]() be a circle with centre
be a circle with centre ![]() , and
, and ![]() a convex quadrilateral such that each of
the segments
a convex quadrilateral such that each of
the segments ![]() and
and ![]() is tangent to
is tangent to ![]() . Let
. Let ![]() be the circumcircle of the triangle
be the circumcircle of the triangle ![]() .
The extension of
.
The extension of ![]() beyond
beyond ![]() meets
meets ![]() at
at ![]() , and the extension of
, and the extension of ![]() beyond
beyond ![]() meets
meets ![]() at
at ![]() .
The extensions of
.
The extensions of ![]() and
and ![]() beyond
beyond ![]() meet
meet ![]() at
at ![]() and
and ![]() , respectively. Prove that
, respectively. Prove that
![]()
Video Solutions
https://youtu.be/vUftJHRaNx8 [Video contains solutions to all day 2 problems]
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=U95v_xD5fJk
Solution
Let ![]() be the centre of
be the centre of ![]() .
.
For ![]() the result follows simply. By Pitot's Theorem we have
the result follows simply. By Pitot's Theorem we have ![]() so that,
so that, ![]() The configuration becomes symmetric about
The configuration becomes symmetric about ![]() and the result follows immediately.
and the result follows immediately.
Now assume WLOG ![]() . Then
. Then ![]() lies between
lies between ![]() and
and ![]() in the minor arc
in the minor arc ![]() and
and ![]() lies between
lies between ![]() and
and ![]() in the minor arc
in the minor arc ![]() .
Consider the cyclic quadrilateral
.
Consider the cyclic quadrilateral ![]() .
We have
.
We have ![]() and
and ![]() . So that,
. So that, ![]()
![]() Since
Since ![]() is the incenter of quadrilateral
is the incenter of quadrilateral ![]() ,
, ![]() is the angular bisector of
is the angular bisector of ![]() . This gives us,
. This gives us, ![]() Hence the chords
Hence the chords ![]() and
and ![]() are equal.
So
are equal.
So ![]() is the reflection of
is the reflection of ![]() about
about ![]() .
Hence,
.
Hence, ![]() and now it suffices to prove
and now it suffices to prove ![]() Let
Let ![]() and
and ![]() be the tangency points of
be the tangency points of ![]() with
with ![]() and
and ![]() respectively. Then by tangents we have,
respectively. Then by tangents we have, ![]() . So
. So ![]() .
Similarly we get,
.
Similarly we get, ![]() . So it suffices to prove,
. So it suffices to prove, ![]() Consider the tangent
Consider the tangent ![]() to
to ![]() with
with ![]() . Since
. Since ![]() and
and ![]() are reflections about
are reflections about ![]() and
and ![]() is a circle centred at
is a circle centred at ![]() the tangents
the tangents ![]() and
and ![]() are reflections of each other. Hence
are reflections of each other. Hence ![]() By a similar argument on the reflection of
By a similar argument on the reflection of ![]() and
and ![]() we get
we get ![]() and finally,
and finally,
![]() as required.
as required.
![]()
~BUMSTAKA
Solution2
Denote ![]() tangents to the circle
tangents to the circle ![]() at
at ![]() ,
, ![]() tangents to the same circle at
tangents to the same circle at ![]() ;
; ![]() tangents at
tangents at ![]() and
and ![]() tangents at
tangents at ![]() . We can get that
. We can get that ![]() .Since
.Since ![]() Same reason, we can get that
Same reason, we can get that ![]() We can find that
We can find that ![]() . Connect
. Connect ![]() separately, we can create two pairs of congruent triangles. In
separately, we can create two pairs of congruent triangles. In ![]() , since
, since ![]() After getting that
After getting that ![]() , we can find that
, we can find that ![]() . Getting that
. Getting that ![]() , same reason, we can get that
, same reason, we can get that ![]() .
Now the only thing left is that we have to prove
.
Now the only thing left is that we have to prove ![]() . Since
. Since ![]() we can subtract and get that
we can subtract and get that ![]() ,means
,means ![]() and we are done
~bluesoul
and we are done
~bluesoul
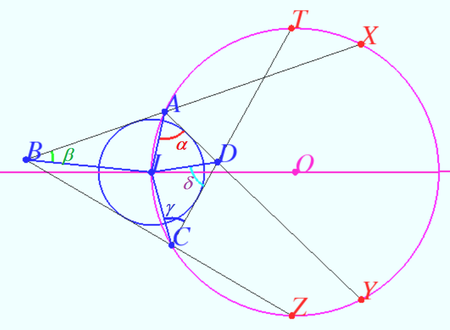
Solution 3 (Visual)
We use the equality of the tangent segments and symmetry.
Using Claim 1 we get ![]() symmetric to
symmetric to ![]() with respect
with respect ![]()
Therefore ![]()
Let ![]() and
and ![]() be the tangency points of
be the tangency points of ![]() with
with ![]() and
and ![]() respectively.
respectively.
Using Claim 2 we get ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() Claim 1
Claim 1
Let ![]() be the center of
be the center of ![]() Then point
Then point ![]() point
point ![]() is symmetryc to
is symmetryc to ![]() with respect
with respect ![]()
Proof
Let ![]()
We find measure of some arcs:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() symmetry
symmetry ![]() and
and ![]()
![]()
![]() symmetry
symmetry ![]() and
and ![]()
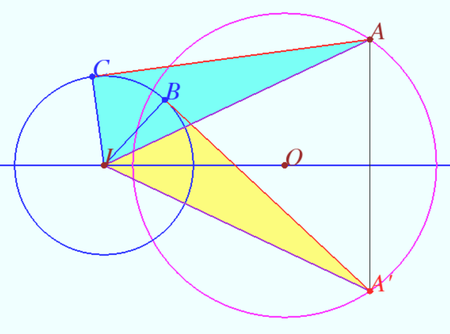
Claim 2
Let circles ![]() centered at
centered at ![]() and
and ![]() centered at
centered at ![]() be given. Let points
be given. Let points ![]() and
and ![]() lies on
lies on ![]() and symmetrical with respect
and symmetrical with respect ![]() Let
Let ![]() and
and ![]() be tangents to
be tangents to ![]() . Then
. Then ![]()
Proof
![]()
![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss