Difference between revisions of "2021 April MIMC 10"
Cellsecret (talk | contribs) (→Problem 20) |
Michael595 (talk | contribs) (→Problem 20) |
||
| Line 151: | Line 151: | ||
[[2021 April MIMC 10 Problems/Problem 20 |Solution]] | [[2021 April MIMC 10 Problems/Problem 20 |Solution]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Problem 21== | ||
| + | How many solutions are there for the equation <math>\Value-\left \lceil{x}\right \rceil=0</math>. (Recall that <math>\left \lfloor{x}\right \rfloor</math> is the largest integer less than <math>x</math>, and <math>\left \lceil{x}\right \rceil</math> is the smallest integer larger than <math>x</math>.) | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\textbf{(A)} ~0 \qquad\textbf{(B)} ~1 \qquad\textbf{(C)} ~2 \qquad\textbf{(D)} ~3 \qquad\textbf{(E)} ~4 \qquad</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[2021 April MIMC 10 Problems/Problem 21 |Solution]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Problem 22== | ||
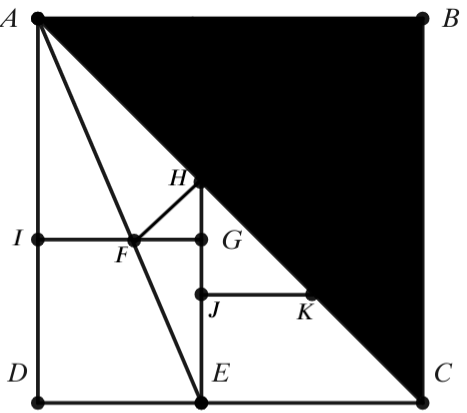
| + | In the diagram, <math>ABCD</math> is a square with area <math>6+4\sqrt{2}</math>. <math>AC</math> is a diagonal of square <math>ABCD</math>. Square <math>IGED</math> has area <math>11-6\sqrt{2}</math>. Given that point <math>J</math> bisects line segment <math>HE</math>, and <math>AE</math> is a line segment. Extend <math>EG</math> to meet diagonal <math>AC</math> and mark the intersection point <math>H</math>. In addition, <math>K</math> is drawn so that <math>JK//EC</math>. <math>FH^2</math> can be represented as <math>\frac{a+b\sqrt{c}}{{d}}</math> where <math>a,b,c,d</math> are not necessarily distinct integers. Given that <math>gcd(a,b,d)=1</math>, and <math>c</math> does not have a perfect square factor. Find <math>a+b+c+d</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:24.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\textbf{(A)} ~5 \qquad\textbf{(B)} ~15 \qquad\textbf{(C)} ~61 \qquad\textbf{(D)} ~349 \qquad\textbf{(E)} ~2009 \qquad</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[2021 April MIMC 10 Problems/Problem 22 |Solution]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Problem 23== | ||
| + | On a coordinate plane, point <math>O</math> denotes the origin which is the center of the diamond shape in the middle of the figure. Point <math>A</math> has coordinate <math>(-12,12)</math>, and point <math>C</math>, <math>E</math>, and <math>G</math> are formed through <math>90\degree</math>, <math>180\degree</math>, and <math>270\degree</math> rotation about the origin <math>O</math>, respectively. Quarter circle <math>BOH</math> (formed by the arc <math>BH</math> and line segments <math>BO</math> and <math>GH</math>) has area <math>25\pi</math>. Furthermore, another quarter circle <math>DOF</math> formed by arc <math>DF</math> and line segments <math>OF</math>, <math>OD</math> is formed through a reflection of sector <math>BOH</math> across the line <math>y=x</math>. The small diamond centered at <math>O</math> is a square, and the area of the little square is <math>2</math>. Let <math>x</math> denote the area of the shaded region, and <math>y</math> denote the sum of the area of the regions <math>ABH</math> (formed by side <math>AB</math>, arc <math>BH</math>, and side <math>HA</math>), <math>DFE</math> (formed by side <math>ED</math>, arc <math>DF</math>, and side <math>FE</math>) and sectors <math>FGH</math> and <math>BCD</math>. Find <math>\frac{x}{y}</math> in the simplest radical form. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:19.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\textbf{(A)} ~\frac{50\pi+1}{280} \qquad\textbf{(B)} ~\frac{50\pi\sqrt{2}+\sqrt{2}}{560} \qquad\textbf{(C)} ~\frac{50\pi+1}{140+100\pi} \qquad\textbf{(D)} ~\frac{50\pi+1}{280+100\pi} \qquad\textbf{(E)} ~\frac{50\pi^2+700\pi\sqrt{2}+3001\pi-70\sqrt{2}+60}{2\pi^2+240\pi+6920}\qquad</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[2021 April MIMC 10 Problems/Problem 23 |Solution]] | ||
Revision as of 16:47, 22 April 2021
Contents
- 1 Problem 1
- 2 Problem 2
- 3 Problem 3
- 4 Problem 4
- 5 Problem 5
- 6 Problem 6
- 7 Problem 7
- 8 Problem 8
- 9 Problem 9
- 10 Problem 10
- 11 Problem 11
- 12 Problem 12
- 13 Problem 13
- 14 Problem 14
- 15 Problem 15
- 16 Problem 16
- 17 Problem 17
- 18 Problem 18
- 19 Problem 19
- 20 Problem 20
- 21 Problem 21
- 22 Problem 22
- 23 Problem 23
Problem 1
What is the sum of ![]() ?
?
![]()
Problem 2
Okestima is reading a ![]() page book. He reads a page every
page book. He reads a page every ![]() minutes, and he pauses
minutes, and he pauses ![]() minutes when he reaches the end of page 90 to take a break. He does not read at all during the break. After, he comes back with food and this slows down his reading speed. He reads one page in
minutes when he reaches the end of page 90 to take a break. He does not read at all during the break. After, he comes back with food and this slows down his reading speed. He reads one page in ![]() minutes. If he starts to read at
minutes. If he starts to read at ![]() , when does he finish the book?
, when does he finish the book?
![]()
Problem 3
Find the number of real solutions that satisfy the equation
![]() .
.
![]()
Problem 4
Stiskwey wrote all the possible permutations of the letters ![]() (
(![]() is different from
is different from ![]() ). How many such permutations are there?
). How many such permutations are there?
![]()
Problem 5
5. Given ![]() , Find
, Find ![]() .
.
![]()
Problem 6
A worker cuts a piece of wire into two pieces. The two pieces, ![]() and
and ![]() , enclose an equilateral triangle and a square with equal area, respectively. The ratio of the length of
, enclose an equilateral triangle and a square with equal area, respectively. The ratio of the length of ![]() to the length of
to the length of ![]() can be expressed as
can be expressed as ![]() in the simplest form. Find
in the simplest form. Find ![]() .
.
![]()
Problem 7
Find the least integer ![]() such that
such that ![]() where
where ![]() denotes
denotes ![]() in base-
in base-![]() .
.
![]()
Problem 8
In the morning, Mr.Gavin always uses his alarm to wake him up. The alarm is special. It always rings in a cycle of ten rings. The first ring lasts ![]() second, and each ring after lasts twice the time than the previous ring. Given that Mr.Gavin has an equal probability of waking up at any time, what is the probability that Mr.Gavin wakes up and end the alarm during the tenth ring?
second, and each ring after lasts twice the time than the previous ring. Given that Mr.Gavin has an equal probability of waking up at any time, what is the probability that Mr.Gavin wakes up and end the alarm during the tenth ring?
![]()
Problem 9
Find the largest number in the choices that divides ![]() .
.
![]()
Problem 10
If ![]() and
and ![]() , find
, find ![]() .
.
![]()
Problem 11
How many factors of ![]() is a perfect cube or a perfect square?
is a perfect cube or a perfect square?
![]()
Problem 12
Given that ![]() , what is
, what is ![]() ?
?
![]()
Problem 13
Given that Giant want to put ![]() green identical balls into
green identical balls into ![]() different boxes such that each box contains at least two balls, and that no box can contain
different boxes such that each box contains at least two balls, and that no box can contain ![]() or more balls. Find the number of ways that Giant can accomplish this.
or more balls. Find the number of ways that Giant can accomplish this.
![]()
Problem 14
James randomly choose an ordered pair ![]() which both
which both ![]() and
and ![]() are elements in the set
are elements in the set ![]() ,
, ![]() and
and ![]() are not necessarily distinct, and all of the equations:
are not necessarily distinct, and all of the equations:
![]()
![]()
![]() are divisible by
are divisible by ![]() . Find the probability that James can do so.
. Find the probability that James can do so.
![]()
Problem 15
Paul wrote all positive integers that's less than ![]() and wrote their base
and wrote their base ![]() representation. He randomly choose a number out the list. Paul insist that he want to choose a number that had only
representation. He randomly choose a number out the list. Paul insist that he want to choose a number that had only ![]() and
and ![]() as its digits, otherwise he will be depressed and relinquishes to do homework. How many numbers can he choose so that he can finish his homework?
as its digits, otherwise he will be depressed and relinquishes to do homework. How many numbers can he choose so that he can finish his homework?
![]()
Problem 16
Find the number of permutations of ![]() such that at exactly two
such that at exactly two ![]() s are adjacent, and the
s are adjacent, and the ![]() s are not adjacent.
s are not adjacent.
![]()
Problem 17
The following expression ![\[\sum_{k=1}^{60} {60 \choose k}+\sum_{k=1}^{59} {59 \choose k}+\sum_{k=1}^{58} {58 \choose k}+\sum_{k=1}^{57} {57 \choose k}+\sum_{k=1}^{56} {56 \choose k}+\sum_{k=1}^{55} {55 \choose k}+\sum_{k=1}^{54} {54 \choose k}+...+\sum_{k=1}^{3} {3 \choose k}-2^{10}\]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/f/3/e/f3ec40504a0dd4366dbbd4b910eb14ab633ae037.png) can be expressed as
can be expressed as ![]() which both
which both ![]() and
and ![]() are relatively prime positive integers. Find
are relatively prime positive integers. Find ![]() .
.
![]()
Problem 18
What can be a description of the set of solutions for this: ![]() ?
?
![]() Two overlapping circles with each area
Two overlapping circles with each area ![]() .
.
![]() Four not overlapping circles with each area
Four not overlapping circles with each area ![]() .
.
![]() There are two overlapping circles on the right of the
There are two overlapping circles on the right of the ![]() -axis with each area
-axis with each area ![]() and the intersection area of two overlapping circles on the left of the
and the intersection area of two overlapping circles on the left of the ![]() -axis with each area
-axis with each area ![]() .
.
![]() Four overlapping circles with each area
Four overlapping circles with each area ![]() .
.
![]() There are two overlapping circles on the right of the
There are two overlapping circles on the right of the ![]() -axis with each area
-axis with each area ![]() and the intersection area of two overlapping circles on the left of the
and the intersection area of two overlapping circles on the left of the ![]() -axis with each area
-axis with each area ![]() .
.
Problem 19
![]() can be expressed as
can be expressed as ![]() in base
in base ![]() which
which ![]() is a positive integer. Find the sum of the digits of
is a positive integer. Find the sum of the digits of ![]() .
.
![]()
Problem 20
Given that ![]() . Given that the product of the even divisors is
. Given that the product of the even divisors is ![]() , and the product of the odd divisors is
, and the product of the odd divisors is ![]() . Find
. Find ![]() .
.
![]()
Problem 21
How many solutions are there for the equation $\Value-\left \lceil{x}\right \rceil=0$ (Error compiling LaTeX. Unknown error_msg). (Recall that ![]() is the largest integer less than
is the largest integer less than ![]() , and
, and ![]() is the smallest integer larger than
is the smallest integer larger than ![]() .)
.)
![]()
Problem 22
In the diagram, ![]() is a square with area
is a square with area ![]() .
. ![]() is a diagonal of square
is a diagonal of square ![]() . Square
. Square ![]() has area
has area ![]() . Given that point
. Given that point ![]() bisects line segment
bisects line segment ![]() , and
, and ![]() is a line segment. Extend
is a line segment. Extend ![]() to meet diagonal
to meet diagonal ![]() and mark the intersection point
and mark the intersection point ![]() . In addition,
. In addition, ![]() is drawn so that
is drawn so that ![]() .
. ![]() can be represented as
can be represented as ![]() where
where ![]() are not necessarily distinct integers. Given that
are not necessarily distinct integers. Given that ![]() , and
, and ![]() does not have a perfect square factor. Find
does not have a perfect square factor. Find ![]() .
.
![]()
Problem 23
On a coordinate plane, point ![]() denotes the origin which is the center of the diamond shape in the middle of the figure. Point
denotes the origin which is the center of the diamond shape in the middle of the figure. Point ![]() has coordinate
has coordinate ![]() , and point
, and point ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() are formed through $90\degree$ (Error compiling LaTeX. Unknown error_msg), $180\degree$ (Error compiling LaTeX. Unknown error_msg), and $270\degree$ (Error compiling LaTeX. Unknown error_msg) rotation about the origin
are formed through $90\degree$ (Error compiling LaTeX. Unknown error_msg), $180\degree$ (Error compiling LaTeX. Unknown error_msg), and $270\degree$ (Error compiling LaTeX. Unknown error_msg) rotation about the origin ![]() , respectively. Quarter circle
, respectively. Quarter circle ![]() (formed by the arc
(formed by the arc ![]() and line segments
and line segments ![]() and
and ![]() ) has area
) has area ![]() . Furthermore, another quarter circle
. Furthermore, another quarter circle ![]() formed by arc
formed by arc ![]() and line segments
and line segments ![]() ,
, ![]() is formed through a reflection of sector
is formed through a reflection of sector ![]() across the line
across the line ![]() . The small diamond centered at
. The small diamond centered at ![]() is a square, and the area of the little square is
is a square, and the area of the little square is ![]() . Let
. Let ![]() denote the area of the shaded region, and
denote the area of the shaded region, and ![]() denote the sum of the area of the regions
denote the sum of the area of the regions ![]() (formed by side
(formed by side ![]() , arc
, arc ![]() , and side
, and side ![]() ),
), ![]() (formed by side
(formed by side ![]() , arc
, arc ![]() , and side
, and side ![]() ) and sectors
) and sectors ![]() and
and ![]() . Find
. Find ![]() in the simplest radical form.
in the simplest radical form.
![]()