Difference between revisions of "2007 AIME I Problems/Problem 13"
Bharatputra (talk | contribs) (→Problem) |
m (→Solution 1) |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Problem == | == Problem == | ||
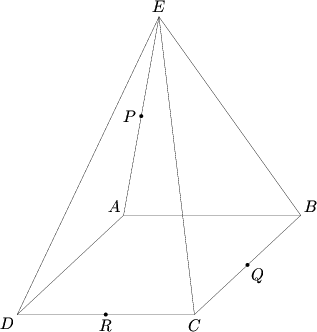
| − | A | + | A square pyramid with base <math>ABCD</math> and vertex <math>E</math> has eight edges of length <math>4</math>. A plane passes through the midpoints of <math>AE</math>, <math>BC</math>, and <math>CD</math>. The plane's intersection with the pyramid has an area that can be expressed as <math>\sqrt{p}</math>. Find <math>p</math>. |
[[Image:AIME I 2007-13.png]] | [[Image:AIME I 2007-13.png]] | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
Note first that the intersection is a [[pentagon]]. | Note first that the intersection is a [[pentagon]]. | ||
| − | Use 3D analytical geometry, setting the origin as the center of the square base and the pyramid’s points oriented as shown above. <math>A(-2,2,0),\ B(2,2,0),\ C(2,-2,0),\ D(-2,-2,0),\ E(0,0,2\sqrt{2})</math>. Using the coordinates of the three points of intersection | + | Use 3D analytical geometry, setting the origin as the center of the square base and the pyramid’s points oriented as shown above. <math>A(-2,2,0),\ B(2,2,0),\ C(2,-2,0),\ D(-2,-2,0),\ E(0,0,2\sqrt{2})</math>. Using the coordinates of the three points of intersection <math>(-1,1,\sqrt{2}),\ (2,0,0),\ (0,-2,0)</math>, it is possible to determine the equation of the plane. The equation of a plane resembles <math>ax + by + cz = d</math>, and using the points we find that <math>2a = d \Longrightarrow d = \frac{a}{2}</math>, <math>-2b = d \Longrightarrow d = \frac{-b}{2}</math>, and <math>-a + b + \sqrt{2}c = d \Longrightarrow -\frac{d}{2} - \frac{d}{2} + \sqrt{2}c = d \Longrightarrow c = d\sqrt{2}</math>. It is then <math>x - y + 2\sqrt{2}z = 2</math>. |
| − | <center> <asy>import three; pointpen = black; pathpen = black+linewidth(0.7); currentprojection = perspective(2.5,-12,4); | + | <center> |
| + | <asy>import three; | ||
| + | pointpen = black; | ||
| + | pathpen = black+linewidth(0.7); | ||
| + | currentprojection = perspective(2.5,-12,4); | ||
triple A=(-2,2,0), B=(2,2,0), C=(2,-2,0), D=(-2,-2,0), E=(0,0,2*2^.5), P=(A+E)/2, Q=(B+C)/2, R=(C+D)/2, Y=(-3/2,-3/2,2^.5/2),X=(3/2,3/2,2^.5/2); | triple A=(-2,2,0), B=(2,2,0), C=(2,-2,0), D=(-2,-2,0), E=(0,0,2*2^.5), P=(A+E)/2, Q=(B+C)/2, R=(C+D)/2, Y=(-3/2,-3/2,2^.5/2),X=(3/2,3/2,2^.5/2); | ||
| − | + | draw(A--B--C--D--A--E--B--E--C--E--D); | |
| − | </asy> | + | label("A",A, SE); |
| + | label("B",B,(1,0,0)); | ||
| + | label("C",C, SE); | ||
| + | label("D",D, W); | ||
| + | label("E",E,N); | ||
| + | label("P",P, NW); | ||
| + | label("Q",Q,(1,0,0)); | ||
| + | label("R",R, S); | ||
| + | label("Y",Y,NW); | ||
| + | label("X",X,NE); | ||
| + | draw(P--X--Q--R--Y--cycle,linetype("6 6")+linewidth(0.7)); | ||
| + | </asy> | ||
| + | <asy> | ||
| + | pointpen = black; | ||
| + | pathpen = black+linewidth(0.7); | ||
pair P = (0, 2.5^.5), X = (3/2^.5,0), Y = (-3/2^.5,0), Q = (2^.5,-2.5^.5), R = (-2^.5,-2.5^.5); | pair P = (0, 2.5^.5), X = (3/2^.5,0), Y = (-3/2^.5,0), Q = (2^.5,-2.5^.5), R = (-2^.5,-2.5^.5); | ||
| − | D(MP("P",P,N)--MP("X",X,NE)--MP("Q",Q)--MP("R",R)--MP("Y",Y,NW)--cycle); D(X--Y,linetype("6 6") + linewidth(0.7)); D(P--(0,-P.y),linetype("6 6") + linewidth(0.7)); | + | D(MP("P",P,N)--MP("X",X,NE)--MP("Q",Q)--MP("R",R)--MP("Y",Y,NW)--cycle); |
| − | MP("3\sqrt{2}",(X+Y)/2); MP("2\sqrt{2}",(Q+R)/2); MP("\sqrt{\frac{5}{2}}",(0,-P.y/2),E); MP("\sqrt{\frac{5}{2}}",(0,2*P.y/5),E); | + | D(X--Y,linetype("6 6") + linewidth(0.7)+blue); D(P--(0,-P.y),linetype("6 6") + linewidth(0.7) + red); |
| + | MP("\color{blue}{3\sqrt{2}}",(X+Y)/2); | ||
| + | MP("2\sqrt{2}",(Q+R)/2); | ||
| + | MP("\color{red}{\sqrt{\frac{5}{2}}}",(0,-P.y/2),E); | ||
| + | MP("\color{red}{\sqrt{\frac{5}{2}}}",(0,2*P.y/5),E); | ||
</asy> | </asy> | ||
| − | |||
</center> | </center> | ||
| Line 27: | Line 48: | ||
Note that the plane determined by <math>\triangle BDE</math> has the equation <math>x=y</math>, and <math>\overline{PQ}</math> can be described by <math>x=2(1-t)-t,\ y=t,\ z=t\sqrt{2}</math>. It intersects the plane when <math>2(1-t)-t=t</math>, or <math>t=\frac{1}{2}</math>. This intersection point has <math>z=\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}</math>. Similarly, the intersection between <math>\overline{PR}</math> and <math>\triangle BDE</math> has <math>z=\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}</math>. So <math>\overline{XY}</math> lies on the plane <math>z=\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}</math>, from which we obtain <math>X=\left( \frac{3}{2},\frac{3}{2},\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\right)</math> and <math>Y=\left( -\frac{3}{2},-\frac{3}{2},\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\right)</math>. The area of the pentagon <math>EXQRY</math> can be computed in the same way as above. | Note that the plane determined by <math>\triangle BDE</math> has the equation <math>x=y</math>, and <math>\overline{PQ}</math> can be described by <math>x=2(1-t)-t,\ y=t,\ z=t\sqrt{2}</math>. It intersects the plane when <math>2(1-t)-t=t</math>, or <math>t=\frac{1}{2}</math>. This intersection point has <math>z=\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}</math>. Similarly, the intersection between <math>\overline{PR}</math> and <math>\triangle BDE</math> has <math>z=\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}</math>. So <math>\overline{XY}</math> lies on the plane <math>z=\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}</math>, from which we obtain <math>X=\left( \frac{3}{2},\frac{3}{2},\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\right)</math> and <math>Y=\left( -\frac{3}{2},-\frac{3}{2},\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}\right)</math>. The area of the pentagon <math>EXQRY</math> can be computed in the same way as above. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Solution 3 === | ||
| + | <center> | ||
| + | <asy>import three; | ||
| + | import math; | ||
| + | pointpen = black; | ||
| + | pathpen = black+linewidth(0.7); | ||
| + | currentprojection = perspective(2.5,-12,4); | ||
| + | triple A=(-2,2,0), B=(2,2,0), C=(2,-2,0), D=(-2,-2,0), E=(0,0,2*2^.5), P=(A+E)/2, Q=(B+C)/2, R=(C+D)/2, Y=(-3/2,-3/2,2^.5/2),X=(3/2,3/2,2^.5/2), H=(4,2,0), I=(-2,-4,0); | ||
| + | draw(A--B--C--D--A--E--B--E--C--E--D); | ||
| + | draw(B--H--Q, linetype("6 6")+linewidth(0.7)+blue); | ||
| + | draw(X--H, linetype("6 6")+linewidth(0.7)+blue); | ||
| + | draw(D--I--R, linetype("6 6")+linewidth(0.7)+blue); | ||
| + | draw(Y--I, linetype("6 6")+linewidth(0.7)+blue); | ||
| + | label("A",A, SE); | ||
| + | label("B",B,NE); | ||
| + | label("C",C, SE); | ||
| + | label("D",D, W); | ||
| + | label("E",E,N); | ||
| + | label("P",P, NW); | ||
| + | label("Q",Q,(1,0,0)); | ||
| + | label("R",R, S); | ||
| + | label("Y",Y,NW); | ||
| + | label("X",X,NE); | ||
| + | label("H",H,NE); | ||
| + | label("I",I,S); | ||
| + | draw(P--X--Q--R--Y--cycle,linetype("6 6")+linewidth(0.7)); | ||
| + | </asy> | ||
| + | </center> | ||
| + | Extend <math>\overline{RQ}</math> and <math>\overline{AB}</math>. The point of intersection is <math>H</math>. Connect <math>\overline{PH}</math>. <math>\overline{EB}</math> intersects <math>\overline{PH}</math> at <math>X</math>. Do the same for <math>\overline{QR}</math> and <math>\overline{AD}</math>, and let the intersections be <math>I</math> and <math>Y</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Because <math>Q</math> is the midpoint of <math>\overline{BC}</math>, and <math>\overline{AB}\parallel\overline{DC}</math>, so <math>\triangle{RQC}\cong\triangle{HQB}</math>. <math>\overline{BH}=2</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Because <math>\overline{BH}=2</math>, we can use mass point geometry to get that <math>\overline{PX}=\overline{XH}</math>. <math>|\triangle{XHQ}|=\frac{\overline{XH}}{\overline{PH}}\cdot\frac{\overline{QH}}{\overline{HI}}\cdot|\triangle{PHI}|=\frac{1}{6}\cdot|\triangle{PHI}|</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Using the same principle, we can get that <math>|\triangle{IYR}|=\frac{1}{6}|\triangle{PHI}|</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Therefore, the area of <math>PYRQX</math> is <math>\frac{2}{3}\cdot|\triangle{PHI}|</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\overline{RQ}=2\sqrt{2}</math>, so <math>\overline{IH}=6\sqrt{2}</math>. Using the law of cosines, <math>\overline{PH}=\sqrt{28}</math>. The area of <math>\triangle{PHI}=\frac{1}{2}\cdot\sqrt{28-18}\cdot6\sqrt{2}=6\sqrt{5}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Using this, we can get the area of <math>PYRQX = \sqrt{80}</math> so the answer is <math>\fbox{080}</math>. | ||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
Latest revision as of 22:30, 18 June 2024
Problem
A square pyramid with base ![]() and vertex
and vertex ![]() has eight edges of length
has eight edges of length ![]() . A plane passes through the midpoints of
. A plane passes through the midpoints of ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() . The plane's intersection with the pyramid has an area that can be expressed as
. The plane's intersection with the pyramid has an area that can be expressed as ![]() . Find
. Find ![]() .
.
Solution
Solution 1
Note first that the intersection is a pentagon.
Use 3D analytical geometry, setting the origin as the center of the square base and the pyramid’s points oriented as shown above. ![]() . Using the coordinates of the three points of intersection
. Using the coordinates of the three points of intersection ![]() , it is possible to determine the equation of the plane. The equation of a plane resembles
, it is possible to determine the equation of the plane. The equation of a plane resembles ![]() , and using the points we find that
, and using the points we find that ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() . It is then
. It is then ![]() .
.
![[asy]import three; pointpen = black; pathpen = black+linewidth(0.7); currentprojection = perspective(2.5,-12,4); triple A=(-2,2,0), B=(2,2,0), C=(2,-2,0), D=(-2,-2,0), E=(0,0,2*2^.5), P=(A+E)/2, Q=(B+C)/2, R=(C+D)/2, Y=(-3/2,-3/2,2^.5/2),X=(3/2,3/2,2^.5/2); draw(A--B--C--D--A--E--B--E--C--E--D); label("A",A, SE); label("B",B,(1,0,0)); label("C",C, SE); label("D",D, W); label("E",E,N); label("P",P, NW); label("Q",Q,(1,0,0)); label("R",R, S); label("Y",Y,NW); label("X",X,NE); draw(P--X--Q--R--Y--cycle,linetype("6 6")+linewidth(0.7)); [/asy]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/6/8/f/68f3fc0eb1abc01bc22e09af946d3d1db6346ffd.png)
![[asy] pointpen = black; pathpen = black+linewidth(0.7); pair P = (0, 2.5^.5), X = (3/2^.5,0), Y = (-3/2^.5,0), Q = (2^.5,-2.5^.5), R = (-2^.5,-2.5^.5); D(MP("P",P,N)--MP("X",X,NE)--MP("Q",Q)--MP("R",R)--MP("Y",Y,NW)--cycle); D(X--Y,linetype("6 6") + linewidth(0.7)+blue); D(P--(0,-P.y),linetype("6 6") + linewidth(0.7) + red); MP("\color{blue}{3\sqrt{2}}",(X+Y)/2); MP("2\sqrt{2}",(Q+R)/2); MP("\color{red}{\sqrt{\frac{5}{2}}}",(0,-P.y/2),E); MP("\color{red}{\sqrt{\frac{5}{2}}}",(0,2*P.y/5),E); [/asy]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/4/6/d/46d70b2b85c7aab344ca28458e1bc95c2e962535.png)
Write the equation of the lines and substitute to find that the other two points of intersection on ![]() ,
, ![]() are
are  . To find the area of the pentagon, break it up into pieces (an isosceles triangle on the top, an isosceles trapezoid on the bottom). Using the distance formula (
. To find the area of the pentagon, break it up into pieces (an isosceles triangle on the top, an isosceles trapezoid on the bottom). Using the distance formula (![]() ), it is possible to find that the area of the triangle is
), it is possible to find that the area of the triangle is ![]() . The trapezoid has area
. The trapezoid has area ![]() . In total, the area is
. In total, the area is ![]() , and the solution is
, and the solution is ![]() .
.
Solution 2
Use the same coordinate system as above, and let the plane determined by ![]() intersect
intersect ![]() at
at ![]() and
and ![]() at
at ![]() . Then the line
. Then the line ![]() is the intersection of the planes determined by
is the intersection of the planes determined by ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
Note that the plane determined by ![]() has the equation
has the equation ![]() , and
, and ![]() can be described by
can be described by ![]() . It intersects the plane when
. It intersects the plane when ![]() , or
, or ![]() . This intersection point has
. This intersection point has ![]() . Similarly, the intersection between
. Similarly, the intersection between ![]() and
and ![]() has
has ![]() . So
. So ![]() lies on the plane
lies on the plane ![]() , from which we obtain
, from which we obtain  and
and  . The area of the pentagon
. The area of the pentagon ![]() can be computed in the same way as above.
can be computed in the same way as above.
Solution 3
![[asy]import three; import math; pointpen = black; pathpen = black+linewidth(0.7); currentprojection = perspective(2.5,-12,4); triple A=(-2,2,0), B=(2,2,0), C=(2,-2,0), D=(-2,-2,0), E=(0,0,2*2^.5), P=(A+E)/2, Q=(B+C)/2, R=(C+D)/2, Y=(-3/2,-3/2,2^.5/2),X=(3/2,3/2,2^.5/2), H=(4,2,0), I=(-2,-4,0); draw(A--B--C--D--A--E--B--E--C--E--D); draw(B--H--Q, linetype("6 6")+linewidth(0.7)+blue); draw(X--H, linetype("6 6")+linewidth(0.7)+blue); draw(D--I--R, linetype("6 6")+linewidth(0.7)+blue); draw(Y--I, linetype("6 6")+linewidth(0.7)+blue); label("A",A, SE); label("B",B,NE); label("C",C, SE); label("D",D, W); label("E",E,N); label("P",P, NW); label("Q",Q,(1,0,0)); label("R",R, S); label("Y",Y,NW); label("X",X,NE); label("H",H,NE); label("I",I,S); draw(P--X--Q--R--Y--cycle,linetype("6 6")+linewidth(0.7)); [/asy]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/0/9/d/09d61a4568c10251fd043fb9f4b5618a47bad002.png)
Extend ![]() and
and ![]() . The point of intersection is
. The point of intersection is ![]() . Connect
. Connect ![]() .
. ![]() intersects
intersects ![]() at
at ![]() . Do the same for
. Do the same for ![]() and
and ![]() , and let the intersections be
, and let the intersections be ![]() and
and ![]()
Because ![]() is the midpoint of
is the midpoint of ![]() , and
, and ![]() , so
, so ![]() .
. ![]() .
.
Because ![]() , we can use mass point geometry to get that
, we can use mass point geometry to get that ![]() .
. ![]()
Using the same principle, we can get that ![]()
Therefore, the area of ![]() is
is ![]()
![]() , so
, so ![]() . Using the law of cosines,
. Using the law of cosines, ![]() . The area of
. The area of ![]()
Using this, we can get the area of ![]() so the answer is
so the answer is ![]() .
.
See also
| 2007 AIME I (Problems • Answer Key • Resources) | ||
| Preceded by Problem 12 |
Followed by Problem 14 | |
| 1 • 2 • 3 • 4 • 5 • 6 • 7 • 8 • 9 • 10 • 11 • 12 • 13 • 14 • 15 | ||
| All AIME Problems and Solutions | ||
The problems on this page are copyrighted by the Mathematical Association of America's American Mathematics Competitions.