Difference between revisions of "Feuerbach point"
(→Sharygin’s prove) |
(→Sharygin’s proof) |
||
| (11 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The incircle and nine-point circle of a triangle are tangent to each other at the Feuerbach point of the triangle. The Feuerbach point is listed as X(11) in Clark Kimberling's Encyclopedia of Triangle Centers and is named after Karl Wilhelm Feuerbach. | The incircle and nine-point circle of a triangle are tangent to each other at the Feuerbach point of the triangle. The Feuerbach point is listed as X(11) in Clark Kimberling's Encyclopedia of Triangle Centers and is named after Karl Wilhelm Feuerbach. | ||
| − | ==Sharygin’s | + | ==Sharygin’s proof== |
<math>1998, 24^{th}</math> Russian math olympiad | <math>1998, 24^{th}</math> Russian math olympiad | ||
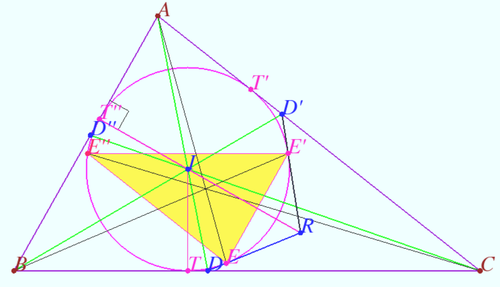
[[File:Feuerbach 1.png|500px|right]] | [[File:Feuerbach 1.png|500px|right]] | ||
| − | + | ===Claim 1=== | |
| − | |||
Let <math>D</math> be the base of the bisector of angle A of scalene triangle <math>\triangle ABC.</math> | Let <math>D</math> be the base of the bisector of angle A of scalene triangle <math>\triangle ABC.</math> | ||
| Line 18: | Line 17: | ||
WLOG, <math>\beta > \gamma.</math> | WLOG, <math>\beta > \gamma.</math> | ||
<cmath>\angle TIT'' = 180^\circ - 2 \beta, \angle ADB = 180^\circ - \alpha - 2 \beta,</cmath> | <cmath>\angle TIT'' = 180^\circ - 2 \beta, \angle ADB = 180^\circ - \alpha - 2 \beta,</cmath> | ||
| − | <cmath>\angle DIT = 90^\circ - \angle ADB = \alpha + 2 \beta | + | <cmath>\angle DIT = 90^\circ - \angle ADB = \alpha + 2 \beta - 90^\circ = \beta -\gamma, \angle EID = \angle TID \implies</cmath> |
<cmath>\angle T''IE = \angle T''IT + 2 \angle TID = 180^\circ - 2 \beta + 2(\beta - \gamma) = 180^\circ - 2 \gamma.</cmath> | <cmath>\angle T''IE = \angle T''IT + 2 \angle TID = 180^\circ - 2 \beta + 2(\beta - \gamma) = 180^\circ - 2 \gamma.</cmath> | ||
Similarly, <math>\angle T''IE' = 180^\circ – 2 \gamma \implies</math> points <math>E</math> and <math>E'</math> are symmetric with respect <math>T''I \perp AB \implies AB || EE'.</math> | Similarly, <math>\angle T''IE' = 180^\circ – 2 \gamma \implies</math> points <math>E</math> and <math>E'</math> are symmetric with respect <math>T''I \perp AB \implies AB || EE'.</math> | ||
| Line 26: | Line 25: | ||
<math>AE, BE', CE''</math> are concurrent at the homothetic center of <math>\triangle ABC</math> and <math>\triangle EE'E''.</math> | <math>AE, BE', CE''</math> are concurrent at the homothetic center of <math>\triangle ABC</math> and <math>\triangle EE'E''.</math> | ||
| − | + | ===Claim 2=== | |
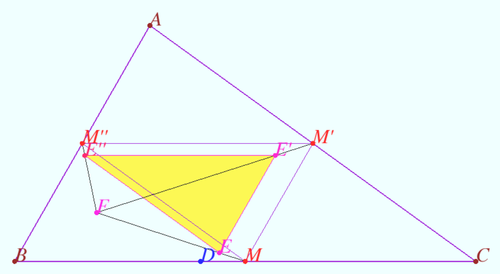
[[File:Feuerbach 2.png|500px|right]] | [[File:Feuerbach 2.png|500px|right]] | ||
Let <math>M, M',</math> and <math>M''</math> be the midpoints <math>BC, AC,</math> and <math>AB,</math> respectively. Points <math>E, E',</math> and <math>E''</math> was defined at Claim 1. | Let <math>M, M',</math> and <math>M''</math> be the midpoints <math>BC, AC,</math> and <math>AB,</math> respectively. Points <math>E, E',</math> and <math>E''</math> was defined at Claim 1. | ||
| Line 37: | Line 36: | ||
<cmath>\triangle MM'M'' \sim \triangle EE'E'' \implies</cmath> | <cmath>\triangle MM'M'' \sim \triangle EE'E'' \implies</cmath> | ||
<math>ME, M'E', M''E''</math> are concurrent at the homothetic center of <math>\triangle MM'M''</math> and <math>\triangle EE'E''.</math> | <math>ME, M'E', M''E''</math> are concurrent at the homothetic center of <math>\triangle MM'M''</math> and <math>\triangle EE'E''.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Claim 3=== | ||
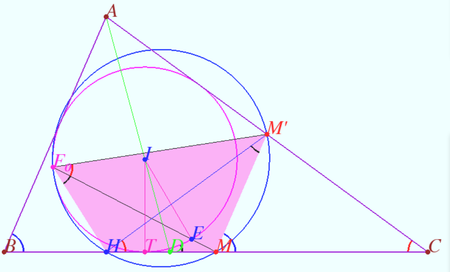
| + | [[File:Feuerbach 3a.png|500px|right]] | ||
| + | Let <math>H</math> be the base of height <math>AH.</math> Let <math>F_0 = ME \cap \omega \ne E.</math> | ||
| + | Prove that points <math>F_0, E, D,</math> and <math>H</math> are concyclic. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <i><b>Proof</b></i> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>MT</math> tangent to <math>\omega \implies MT^2 = ME \cdot MF_0.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Denote <math>a = BC, b = AC, c = AB.</math> | ||
| + | <cmath>BD = \frac {ac}{b+c}, BM = \frac {a}{2} \implies MD = \frac {a(b-c)}{2(b+c)}.</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>BT = \frac {a+c-b}{2} \implies MT = \frac {b-c}{2}.</cmath> | ||
| + | Point <math>H</math> lies on radical axis of circles centered at <math>B</math> and <math>C</math> with the radii <math>c</math> and <math>b,</math> respectively. | ||
| + | <cmath>BH = \frac {a}{2} - \frac {b^2 - c^2}{2a} \implies HM = \frac {b^2 - c^2}{2a}.</cmath> | ||
| + | Therefore <math>MH \cdot MD = MT^2 = ME \cdot MF_0 \implies</math> points <math>F_0, E, D,</math> and <math>H</math> are concyclic. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Claim 4=== | ||
| + | [[File:Feuerbach 4.png|450px|right]] | ||
| + | Prove that points <math>F_0, M, M',</math> and <math>H</math> are concyclic. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <i><b>Proof</b></i> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <cmath>\angle EDM = \angle TIE = 2 \angle TID = 2(\beta - \gamma).</cmath> | ||
| + | <math>F_0, E, D,</math> and <math>H</math> are concyclic <math>\implies</math> | ||
| + | <cmath>\angle EF_0H = \angle EDM = 2(\beta - \gamma) = \angle MF_0H.</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>\angle M'HM = \angle ACB = 2 \gamma.</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>MM'||AB \implies \angle M'MC = 2 \beta.</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>\angle HM'M = \angle CMM' - \angle MHM' = 2\beta - 2 \gamma = \angle MF_0H \implies</cmath> | ||
| + | points <math>F_0, M, M',</math> and <math>H</math> are concyclic. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Sharygin’s proof=== | ||
| + | The incircle <math>\omega</math> and the nine-point circle <math>\Omega</math> of a triangle are tangent to each other. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <i><b>Proof</b></i> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let <math>F_0 = ME \cap \omega \ne E, F' = M'E' \cap \omega \ne E', F'' = M''E'' \cap \omega \ne E''.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | According claim 4, each of this point lyes on <math>\Omega.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\omega</math> and <math>\Omega</math> have not more then two common point, so two of points <math>F_0, F',</math> and <math>F''</math> are coincide. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Therefore these two points coincide with point <math>F</math> witch means that <math>F = \omega \cap \Omega.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>F</math> is the center of similarity of <math>\omega</math> and <math>\Omega,</math> therefore there is no second point of intersection of <math>\omega</math> and <math>\Omega.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | We conclude that these circles are tangent to each other at point <math>F.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | ||
Latest revision as of 09:23, 29 December 2023
The incircle and nine-point circle of a triangle are tangent to each other at the Feuerbach point of the triangle. The Feuerbach point is listed as X(11) in Clark Kimberling's Encyclopedia of Triangle Centers and is named after Karl Wilhelm Feuerbach.
Sharygin’s proof
![]() Russian math olympiad
Russian math olympiad
Claim 1
Let ![]() be the base of the bisector of angle A of scalene triangle
be the base of the bisector of angle A of scalene triangle ![]()
Let ![]() be a tangent different from side
be a tangent different from side ![]() to the incircle of
to the incircle of ![]() is the point of tangency). Similarly, we denote
is the point of tangency). Similarly, we denote ![]() and
and ![]()
Prove that ![]() are concurrent.
are concurrent.
Proof
Let ![]() and
and ![]() be the point of tangency of the incircle
be the point of tangency of the incircle ![]() and
and ![]() and
and ![]()
Let ![]() WLOG,
WLOG, ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() Similarly,
Similarly, ![]() points
points ![]() and
and ![]() are symmetric with respect
are symmetric with respect ![]()
Similarly, ![]()
![]() are concurrent at the homothetic center of
are concurrent at the homothetic center of ![]() and
and ![]()
Claim 2
Let ![]() and
and ![]() be the midpoints
be the midpoints ![]() and
and ![]() respectively. Points
respectively. Points ![]() and
and ![]() was defined at Claim 1.
was defined at Claim 1.
Prove that ![]() and
and ![]() are concurrent.
are concurrent.
Proof
![]()
![]()
![]() are concurrent at the homothetic center of
are concurrent at the homothetic center of ![]() and
and ![]()
Claim 3
Let ![]() be the base of height
be the base of height ![]() Let
Let ![]() Prove that points
Prove that points ![]() and
and ![]() are concyclic.
are concyclic.
Proof
![]() tangent to
tangent to ![]()
Denote ![]()
![]()
![]() Point
Point ![]() lies on radical axis of circles centered at
lies on radical axis of circles centered at ![]() and
and ![]() with the radii
with the radii ![]() and
and ![]() respectively.
respectively.
![]() Therefore
Therefore ![]() points
points ![]() and
and ![]() are concyclic.
are concyclic.
Claim 4
Prove that points ![]() and
and ![]() are concyclic.
are concyclic.
Proof
![]()
![]() and
and ![]() are concyclic
are concyclic ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() points
points ![]() and
and ![]() are concyclic.
are concyclic.
Sharygin’s proof
The incircle ![]() and the nine-point circle
and the nine-point circle ![]() of a triangle are tangent to each other.
of a triangle are tangent to each other.
Proof
Let ![]()
According claim 4, each of this point lyes on ![]()
![]() and
and ![]() have not more then two common point, so two of points
have not more then two common point, so two of points ![]() and
and ![]() are coincide.
are coincide.
Therefore these two points coincide with point ![]() witch means that
witch means that ![]()
![]() is the center of similarity of
is the center of similarity of ![]() and
and ![]() therefore there is no second point of intersection of
therefore there is no second point of intersection of ![]() and
and ![]()
We conclude that these circles are tangent to each other at point ![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss