Difference between revisions of "Isogonal conjugate"
(→Three points) |
(→Ratio for three pairs of isogonal points) |
||
| (137 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
If the abscissa axis coincides with the line <math>\ell</math> and the origin coincides with the point <math>O,</math> then the isogonals define the equations <math>y = \pm kx,</math> and the lines <math>(\frac{1}{x}, \pm k)</math> symmetrical with respect to the line <math>\ell</math> become their images. | If the abscissa axis coincides with the line <math>\ell</math> and the origin coincides with the point <math>O,</math> then the isogonals define the equations <math>y = \pm kx,</math> and the lines <math>(\frac{1}{x}, \pm k)</math> symmetrical with respect to the line <math>\ell</math> become their images. | ||
| − | It is clear that, under the | + | It is clear that, under the converse transformation (also projective), such pairs of lines become isogonals, and the points equidistant from <math>\ell</math> lie on the isogonals. |
<i><b>The isogonal theorem</b></i> | <i><b>The isogonal theorem</b></i> | ||
| − | [[File:Isogonal.png| | + | [[File:Isogonal.png|390px|right]] |
| − | Let two pairs of isogonals <math>OX | + | Let two pairs of isogonals <math>OX - OX'</math> and <math>OY - OY'</math> with respect to the pair <math>(\ell,O)</math> be given. Denote <math>Z = XY \cap X'Y', Z' = X'Y \cap XY'.</math> |
| + | |||
| + | Prove that <math>OZ</math> and <math>OZ'</math> are the isogonals with respect to the pair <math>(\ell,O).</math> | ||
<i><b>Proof</b></i> | <i><b>Proof</b></i> | ||
| − | [[File:Transform isogonal.png| | + | [[File:Transform isogonal.png|390px|right]] |
Let us perform a projective transformation of the plane that maps the point <math>O</math> into a point at infinity and the line <math>\ell</math> maps to itself. In this case, the isogonals turn into a pair of straight lines parallel to <math>\ell</math> and equidistant from <math>\ell.</math> | Let us perform a projective transformation of the plane that maps the point <math>O</math> into a point at infinity and the line <math>\ell</math> maps to itself. In this case, the isogonals turn into a pair of straight lines parallel to <math>\ell</math> and equidistant from <math>\ell.</math> | ||
| − | The | + | The converse (also projective) transformation maps the points equidistant from <math>\ell</math> onto isogonals. We denote the image and the preimage with the same symbols. |
Let the images of isogonals are vertical lines. Let coordinates of images of points be <cmath>X(-a, 0), X'(a,u), Y(-b,v), Y'(b,w).</cmath> | Let the images of isogonals are vertical lines. Let coordinates of images of points be <cmath>X(-a, 0), X'(a,u), Y(-b,v), Y'(b,w).</cmath> | ||
| − | Equation of a straight line <math>XY</math> is <math>\frac{x+a}{a-b} = \frac {y}{v},</math> | + | Equation of a straight line <math>XY</math> is <math>\frac{x + a}{a - b} = \frac {y}{v}.</math> |
| + | |||
| + | Equation of a straight line <math>X'Y'</math> is <math>\frac{x - a}{b - a} = \frac {y - u}{w - u}.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The abscissa <math>Z_x</math> of the point <math>Z</math> is <math>Z_x = \frac {v a - a w + u b}{u - v - w}.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Equation of a straight line <math>XY'</math> is <math>\frac{x + a}{b + a} = \frac {y}{w}.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Equation of a straight line <math>X'Y</math> is <math>\frac{x - a}{- b - a} = \frac {y - u}{v - u}.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The abscissa <math>Z'_x</math> of the point <math>Z'</math> is <math>Z'_x = \frac {v a - a w + u b}{- u + v + w} = - Z_x \implies</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Preimages of the points <math>Z</math> and <math>Z'</math> lie on the isogonals. <math>\blacksquare</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <i><b>The isogonal theorem in the case of parallel lines</b></i> | ||
| + | [[File:Parallels 1.png|330px|right]] | ||
| + | Let <math>OY</math> and <math>OY'</math> are isogonals with respect <math>\angle XOX'.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let lines <math>XY</math> and <math>X'Y'</math> intersect at point <math>Z, X'Y || XY'.</math> | ||
| − | + | Prove that <math>OZ</math> and line <math>l</math> through <math>O</math> parallel to <math>XY'</math> are the isogonals with respect <math>\angle XOX'.</math> | |
| − | + | <i><b>Proof</b></i> | |
| − | + | The preimage of <math>Z'</math> is located at infinity on the line <math>l.</math> | |
| − | + | The equality <math>Z'_x = -Z_x</math> implies the equality the slopes modulo of <math>OZ</math> and <math>l</math> to the bisector of <math>\angle XOX'. \blacksquare</math> | |
| − | + | <i><b>Converse theorem</b></i> | |
| + | [[File:Parallels 2.png|390px|right]] | ||
| + | Let lines <math>XY</math> and <math>X'Y'</math> intersect at point <math>Z, X'Y || XY'.</math> | ||
| − | + | Let <math>OZ</math> and <math>l</math> be the isogonals with respect <math>\angle XOX'.</math> | |
| + | Prove that <math>OY</math> and <math>OY'</math> are isogonals with respect <math>\angle XOX' (\angle XOY' = \angle YOX').</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <i><b>Proof</b></i> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The preimage of <math>Z'</math> is located at infinity on the line <math>l,</math> so the slope of <math>OZ</math> is known. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Suppose that <math>y' \in XY', y' \ne Y', \angle y'OX = \angle YOX'.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The segment <math>XY</math> and the lines <math>XY', OZ</math> are fixed <math>\implies</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>y'X'</math> intersects <math>XY</math> at <math>z \ne Z,</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | but there is the only point where line <math>OZ</math> intersect <math>XY.</math> Сontradiction. <math>\blacksquare</math> | ||
'''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | '''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Parallel segments== | ||
| + | [[File:Parallels.png|350px|right]] | ||
| + | Let triangle <math>ABC</math> be given. Let <math>AD</math> and <math>AE</math> be the isogonals with respect <math>\angle BAC.</math> Let <math>BD ||CE, P = BE \cap CD.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Prove that <math>P</math> lies on bisector of <math>\angle BAC</math> and <math>BD||AP.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <i><b>Proof</b></i> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Both assertions follow from <i><b>The isogonal theorem in the case of parallel lines</b></i> | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | ||
| + | |||
==Perpendicularity== | ==Perpendicularity== | ||
| − | [[File:Right angles.png| | + | [[File:Right angles.png|400px|right]] |
Let triangle <math>ABC</math> be given. Right triangles <math>ABD</math> and <math>ACE</math> with hypotenuses <math>AD</math> and <math>AE</math> are constructed on sides <math>AB</math> and <math>AC</math> to the outer (inner) side of <math>\triangle ABC.</math> Let <math>\angle BAD = \angle CAE, H = CD \cap BE.</math> | Let triangle <math>ABC</math> be given. Right triangles <math>ABD</math> and <math>ACE</math> with hypotenuses <math>AD</math> and <math>AE</math> are constructed on sides <math>AB</math> and <math>AC</math> to the outer (inner) side of <math>\triangle ABC.</math> Let <math>\angle BAD = \angle CAE, H = CD \cap BE.</math> | ||
Prove that <math>AH \perp BC.</math> | Prove that <math>AH \perp BC.</math> | ||
| Line 58: | Line 106: | ||
<math>AH</math> and <math>AF</math> are isogonals with respect to the pair <math>(\ell,A)</math> in accordance with <i><b>The isogonal theorem.</b></i> | <math>AH</math> and <math>AF</math> are isogonals with respect to the pair <math>(\ell,A)</math> in accordance with <i><b>The isogonal theorem.</b></i> | ||
| − | <math>\angle ABD = \angle ACE = 90^\circ \implies | + | <math>\angle ABD = \angle ACE = 90^\circ \implies</math> |
| + | |||
| + | <math>AF</math> is the diameter of circumcircle of <math>\triangle ABC.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Circumradius and altitude are isogonals with respect bisector and vertex of triangle, so <math>AH \perp BC.</math> <math>\blacksquare</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *[[Circumradius]] | ||
'''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | '''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | ||
| + | |||
==Fixed point== | ==Fixed point== | ||
| − | [[File:Fixed point.png| | + | [[File:Fixed point.png|400px|right]] |
| − | Let fixed triangle <math>ABC</math> be given. Let points <math>D</math> and <math>E</math> on sidelines <math>BC</math> and <math>AB</math> respectively be the arbitrary points. | + | Let fixed triangle <math>ABC</math> be given. Let points <math>D</math> and <math>E</math> on sidelines <math>BC</math> and <math>AB,</math> respectively be the arbitrary points. |
| + | |||
| + | Let <math>F</math> be the point on sideline <math>AC</math> such that <math>\angle BDE = \angle CDF.</math> | ||
| − | + | <math>G = BF \cap CE.</math> Prove that line <math>DG</math> pass through the fixed point. | |
| − | |||
| − | Prove that line <math>DG</math> pass through the fixed point. | ||
<i><b>Proof</b></i> | <i><b>Proof</b></i> | ||
| Line 73: | Line 128: | ||
We will prove that point <math>A',</math> symmetric <math>A</math> with respect <math>\ell = BC,</math> lies on <math>DG</math>. | We will prove that point <math>A',</math> symmetric <math>A</math> with respect <math>\ell = BC,</math> lies on <math>DG</math>. | ||
| − | <math>\angle BDE = \angle | + | <math>\angle BDE = \angle CDF \implies DE</math> and <math>DF</math> are isogonals with respect to <math>(\ell, D).</math> |
<math>A = BE \cap CF \implies </math> points <math>A</math> and <math>G</math> lie on isogonals with respect to <math>(\ell, D)</math> in accordance with <i><b>The isogonal theorem.</b></i> | <math>A = BE \cap CF \implies </math> points <math>A</math> and <math>G</math> lie on isogonals with respect to <math>(\ell, D)</math> in accordance with <i><b>The isogonal theorem.</b></i> | ||
| − | Point <math>A'</math> symmetric <math>A</math> with respect <math>\ell</math> lies on isogonal <math>AD</math> with respect to <math>(\ell, D),</math> that is <math>DG.</math> | + | Point <math>A'</math> symmetric <math>A</math> with respect <math>\ell</math> lies on isogonal <math>AD</math> with respect to <math>(\ell, D),</math> that is <math>DG.</math> <math>\blacksquare</math> |
'''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | '''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | ||
==Bisector== | ==Bisector== | ||
| − | [[File:Incircles.png| | + | [[File:Incircles.png|400px|right]] |
| − | Let a convex quadrilateral <math>ABCD</math> be given. Let <math>I</math> and <math>J</math> be the incenters of triangles <math>\triangle ABC</math> and <math>\triangle ADC,</math> respectively. Let <math>I'</math> and <math>J'</math> be the A-excenters of triangles <math>\triangle ABC</math> and <math>\triangle ADC,</math> respectively. <math>E = IJ' \cap I'J.</math> | + | Let a convex quadrilateral <math>ABCD</math> be given. Let <math>I</math> and <math>J</math> be the incenters of triangles <math>\triangle ABC</math> and <math>\triangle ADC,</math> respectively. |
| + | |||
| + | Let <math>I'</math> and <math>J'</math> be the A-excenters of triangles <math>\triangle ABC</math> and <math>\triangle ADC,</math> respectively. <math>E = IJ' \cap I'J.</math> | ||
Prove that <math>CE</math> is the bisector of <math>\angle BCD.</math> | Prove that <math>CE</math> is the bisector of <math>\angle BCD.</math> | ||
| Line 89: | Line 146: | ||
<i><b>Proof</b></i> | <i><b>Proof</b></i> | ||
| − | <math>\angle ICI' = \angle JCJ' = 90^\circ \implies CI'</math> and <math>CJ'</math> are isogonals with respect to the angle <math>\angle ICJ.</math> | + | <math>\angle ICI' = \angle JCJ' = 90^\circ \implies</math> |
| + | |||
| + | <math>CI'</math> and <math>CJ'</math> are isogonals with respect to the angle <math>\angle ICJ.</math> | ||
<math>A = II' \cap JJ' \implies AC</math> and <math>EC</math> are isogonals with respect to the angle <math>\angle ICJ</math> in accordance with <i><b>The isogonal theorem.</b></i> | <math>A = II' \cap JJ' \implies AC</math> and <math>EC</math> are isogonals with respect to the angle <math>\angle ICJ</math> in accordance with <i><b>The isogonal theorem.</b></i> | ||
| Line 97: | Line 156: | ||
WLOG, <math>\beta \ge \alpha.</math> | WLOG, <math>\beta \ge \alpha.</math> | ||
<cmath>\angle ACJ = \angle ACE + \alpha = \beta,</cmath> | <cmath>\angle ACJ = \angle ACE + \alpha = \beta,</cmath> | ||
| − | <cmath>\angle BCE = 2 \alpha + \beta - \alpha = \alpha + \beta = \angle DCE.</cmath> | + | <cmath>\angle BCE = 2 \alpha + \beta - \alpha = \alpha + \beta = \angle DCE. \blacksquare</cmath> |
'''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | '''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | ||
| Line 107: | Line 166: | ||
Let <math>E = AB \cap CD, F = AD \cap BC.</math> | Let <math>E = AB \cap CD, F = AD \cap BC.</math> | ||
| − | Prove that <math>\angle | + | Prove that <math>\angle BPE = \angle DPF.</math> |
<i><b>Proof</b></i> | <i><b>Proof</b></i> | ||
| Line 120: | Line 179: | ||
<math>\ell</math> is the Gauss line of the complete quadrilateral <math>ABCDEF \implies</math> | <math>\ell</math> is the Gauss line of the complete quadrilateral <math>ABCDEF \implies</math> | ||
| + | <math>\ell</math> bisects <math>EF \implies EE_0 = FF_0 \implies</math> | ||
| − | <math> | + | the preimages of the points <math>E</math> and <math>F</math> lie on the isogonals <math>PE</math> and <math>PF. \blacksquare</math> |
| − | + | '''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Isogonals in trapezium== | ==Isogonals in trapezium== | ||
| − | [[File:Trapezium ACFEE.png| | + | [[File:Trapezium ACFEE.png|370px|right]] |
Let the trapezoid <math>AEFC, AC||EF,</math> be given. Denote <cmath>B = AE \cap CF, D = AF \cap CE.</cmath> | Let the trapezoid <math>AEFC, AC||EF,</math> be given. Denote <cmath>B = AE \cap CF, D = AF \cap CE.</cmath> | ||
| Line 138: | Line 195: | ||
<i><b>Proof</b></i> | <i><b>Proof</b></i> | ||
| − | < | + | <cmath>EM = MF \implies </cmath> |
| − | Therefore <math>EM</math> and <math>FM</math> are isogonals. | + | <cmath>\angle AME = \angle MEF = \angle MFE = \angle CMF.</cmath> |
| + | Therefore <math>EM</math> and <math>FM</math> are isogonals with respect <math>(AC,M).</math> | ||
Let us perform a projective transformation of the plane that maps the point <math>M</math> to a point at infinity and the line <math>\ell = AC</math> into itself. | Let us perform a projective transformation of the plane that maps the point <math>M</math> to a point at infinity and the line <math>\ell = AC</math> into itself. | ||
| Line 147: | Line 205: | ||
<math>\ell</math> bisects <math>BD \implies BB_0 = DD_0 \implies</math> | <math>\ell</math> bisects <math>BD \implies BB_0 = DD_0 \implies</math> | ||
| − | The preimages of the points <math>B</math> and <math>D</math> lie on the isogonals <math>MB</math> and <math>MD.</math> | + | The preimages of the points <math>B</math> and <math>D</math> lie on the isogonals <math>MB</math> and <math>MD. \blacksquare</math> |
| + | |||
| + | '''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Isogonals in complete quadrilateral== | ||
| + | [[File:Isogonals in complete quadrilateral.png|400px|right]] | ||
| + | Let complete quadrilateral <math>ABCDEF (E = AB \cap CD, F = AC \cap BD)</math> be given. Let <math>M</math> be the Miquel point of <math>ABCD.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Prove that <math>AM</math> is isogonal to <math>DM</math> and <math>EM</math> is isogonal to <math>FM</math> with respect <math>\angle BMC.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <i><b>Proof</b></i> | ||
| + | <cmath>\angle BME = \angle BDE = \angle CDF = \angle CMF.</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>\angle BMD = \angle BED = \angle AEC = \angle AMC. \blacksquare</cmath> | ||
'''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | '''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | ||
| Line 155: | Line 225: | ||
The triangle <math>ABC</math> be given. The point <math>D</math> chosen on the bisector <math>AA'.</math> | The triangle <math>ABC</math> be given. The point <math>D</math> chosen on the bisector <math>AA'.</math> | ||
| − | Denote < | + | Denote <cmath>B' = BD \cap AC, C' = CD \cap AB,</cmath> |
| − | + | <cmath>E = BB' \cap A'C', F = CC' \cap A'B'.</cmath> | |
Prove that <math>\angle BAE = \angle CAF.</math> | Prove that <math>\angle BAE = \angle CAF.</math> | ||
| Line 165: | Line 235: | ||
In this case, the images of segments <math>BC'</math> and <math>B'C</math> are equidistant from the image of <math>\ell \implies BC' || B'C || \ell.</math> | In this case, the images of segments <math>BC'</math> and <math>B'C</math> are equidistant from the image of <math>\ell \implies BC' || B'C || \ell.</math> | ||
| − | <math>D</math> is midpoint of <math>BB'</math> and midpoint <math>CC' \implies BCB'C'</math> is parallelogramm <math>\implies</math> | + | Image of point <math>D</math> is midpoint of image <math>BB'</math> and midpoint image <math>CC' \implies</math> |
| + | |||
| + | Image <math>BCB'C'</math> is parallelogramm <math>\implies</math> | ||
| − | <math>BC = B'C' \implies \frac {DE}{BD} = \frac {DF}{CD} \implies </math> distances from <math>E</math> and <math>F</math> to <math>\ell</math> are equal | + | <math>BC = B'C' \implies \frac {DE}{BD} = \frac {DF}{CD} \implies </math> distances from <math>E</math> and <math>F</math> to <math>\ell</math> are equal <math>\implies</math> |
| − | <math>\ | + | Preimages <math>AE</math> and <math>AF</math> are isogonals with respect <math>(\ell,A). \blacksquare</math> |
| + | |||
| + | '''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Points on isogonals== | ||
| + | [[File:Points on isogonals.png|400px|right]] | ||
| + | The triangle <math>ABC</math> be given. The point <math>D</math> chosen on <math>BC.</math> | ||
| + | The point <math>E</math> chosen on <math>BC</math> such that <math>AD</math> and <math>AE</math> are isogonals with respect <math>\angle BAC.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Prove that <math>\frac {AB^2}{BD \cdot BE} = \frac{ AC^2}{CD \cdot CE}.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <i><b>Proof</b></i> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Denote <math>\angle BAD = \angle CAE = \varphi,</math> | ||
| + | <math>\angle B = \beta, \angle C = \gamma \implies</math> | ||
| + | <math>\angle ADE = \beta + \varphi, \angle AED = \gamma + \varphi, \angle BAE = \angle CAD = \psi+\varphi.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | We use the Law of Sines and get: | ||
| + | <cmath>\frac {AB}{BD} = \frac {\sin (\beta + \varphi)}{\sin \varphi}, \frac {AB}{BE} = \frac {\sin (\gamma + \varphi)}{\sin (\psi +\varphi)},</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>\frac {AC}{CE} = \frac {\sin (\gamma + \varphi)}{\sin \varphi}, \frac {AC}{CD} = \frac {\sin (\beta + \varphi)}{\sin (\psi +\varphi)} \implies</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>\frac {AB \cdot AB}{BD \cdot BE} = \frac {AC \cdot AC}{CD \cdot CE} = \frac {\sin (\beta + \varphi) \cdot \sin (\gamma +\varphi)} {\sin \varphi \cdot \sin (\psi +\varphi)}.</cmath> | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Trapezoid== | ||
| + | [[File:Trapezoid3.png|370px|right]] | ||
| + | The lateral side <math>CD</math> of the trapezoid <math>ABCD</math> is perpendicular to the bases, point <math>P</math> is the intersection point of the diagonals <math>ABCD</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Point <math>Q</math> is taken on the circumcircle <math>\omega</math> of triangle <math>PCD</math> diametrically opposite to point <math>P.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Prove that <math>\angle BQC = \angle AQD.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <i><b>Proof</b></i> | ||
| + | |||
| + | WLOG, <math>CD</math> is not the diameter of <math>\omega.</math> | ||
| + | Let sidelines <math>AD</math> and <math>BC</math> intersect <math>\omega</math> at points <math>D'</math> and <math>C',</math> respectively. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>DD' \perp CD, CC' \perp CD \implies CDD'C'</math> is rectangle <math>\implies</math> | ||
| + | <math>CC' = DD' \implies \angle CQC' = \angle DQD'.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>QE||BC</math> is isogonal to <math>QO</math> with respect <math>\angle CQD \implies</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>QE||BC</math> is isogonal to <math>QP</math> with respect <math>\angle CQD \implies</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | In accordance with <i><b>The isogonal theorem in case parallel lines</b></i> <math>\angle DQO = \angle CQE.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>QE||BC</math> is isogonal to <math>QP</math> with respect <math>\angle CQD, P = AC \cap BD \implies</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\angle AQD = \angle BQC</math> in accordance with <i><b>Converse theorem for The isogonal theorem in case parallel lines.</b></i> <math>\blacksquare</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==IMO 2007 Short list/G3== | ||
| + | [[File:Trapezoid 17.png|400px|right]] | ||
| + | The diagonals of a trapezoid <math>ABCD</math> intersect at point <math>P.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Point <math>Q</math> lies between the parallel lines <math>BC</math> and <math>AD</math> such that <math>\angle AQD = \angle CQB,</math> and line <math>CD</math> separates points <math>P</math> and <math>Q.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Prove that <math>\angle BQP = \angle DAQ.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <i><b>Proof</b></i> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\angle AQD = \angle CQB \implies</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>BQ</math> and <math>AQ</math> are isogonals with respect <math>\angle CQD.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>P =AC \cap BD, BC || AD \implies</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>QS || AD</math> is isogonal to <math>QP</math> with respect <math>\angle CQD.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | From the converse of <i><b>The isogonal theorem</b></i> we get | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\angle BQP = \angle SQA = \angle DAQ \blacksquare</math> | ||
'''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | '''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | ||
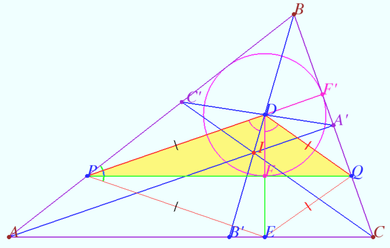
== Definition of isogonal conjugate of a point == | == Definition of isogonal conjugate of a point == | ||
| − | [[File:Definitin 1.png| | + | [[File:Definitin 1.png|390px|right]] |
| − | Let <math>P</math> be | + | Let triangle <math>\triangle ABC</math> be given. Let <math>\omega</math> be the circumcircle of <math>ABC.</math> Let point <math>P</math> be in the plane of <math>\triangle ABC, P \notin AB, P \notin BC, P \notin AC, P \notin \omega.</math> |
| + | Denote by <math>a,b,c</math> the lines <math>BC, CA, AB,</math> respectively. Denote by <math>p_a, p_b, p_c</math> the lines <math>PA</math>, <math>PB</math>, <math>PC</math>, respectively. | ||
| + | Denote by <math>q_a</math>, <math>q_b</math>, <math>q_c</math> the reflections of <math>p_a</math>, <math>p_b</math>, <math>p_c</math> over the angle bisectors of angles <math>A</math>, <math>B</math>, <math>C</math>, respectively. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Prove that lines <math>q_a</math>, <math>q_b</math>, <math>q_c</math> [[concurrence | concur]] at a point <math>Q.</math> | ||
| + | This point is called the isogonal conjugate of <math>P</math> with respect to triangle <math>ABC</math>. | ||
<i><b>Proof</b></i> | <i><b>Proof</b></i> | ||
| Line 188: | Line 337: | ||
Then these points lie on isogonals with respect angle <math>\angle A.</math> | Then these points lie on isogonals with respect angle <math>\angle A.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <i><b>Corollary 2</b></i> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let point <math>P</math> be in the sideline <math>BC</math> of <math>\triangle ABC, P \ne B, P \ne C.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Then the isogonal conjugate of a point <math>P</math> is a point <math>A.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Points <math>A,B,</math> and <math>C</math> do not have an isogonally conjugate point. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | ||
| + | |||
==Three points== | ==Three points== | ||
| − | [[File:3 points.png| | + | [[File:3 points.png|400px|right]] |
Let fixed triangle <math>ABC</math> be given. Let the arbitrary point <math>D</math> not be on sidelines of <math>\triangle ABC.</math> Let <math>E</math> be the point on isogonal of <math>CD</math> with respect angle <math>\angle ACB.</math> | Let fixed triangle <math>ABC</math> be given. Let the arbitrary point <math>D</math> not be on sidelines of <math>\triangle ABC.</math> Let <math>E</math> be the point on isogonal of <math>CD</math> with respect angle <math>\angle ACB.</math> | ||
Let <math>F</math> be the crosspoint of isogonal of <math>BD</math> with respect angle <math>\angle ABC</math> and isogonal of <math>AE</math> with respect angle <math>\angle BAC.</math> | Let <math>F</math> be the crosspoint of isogonal of <math>BD</math> with respect angle <math>\angle ABC</math> and isogonal of <math>AE</math> with respect angle <math>\angle BAC.</math> | ||
| Line 199: | Line 359: | ||
Denote <math>D' = BF \cap CE, S = CF \cap BE.</math> | Denote <math>D' = BF \cap CE, S = CF \cap BE.</math> | ||
| − | <math>AE</math> and <math>AF</math> are isogonals with respect <math>\angle BAC \implies | + | <math>AE</math> and <math>AF</math> are isogonals with respect <math>\angle BAC \implies</math> |
| − | <math>\angle DBC = \angle D'BA, \angle DCB = \angle D'CA \implies D'</math> is isogonal conjugated of <math>D</math> with respect <math>\triangle ABC \implies D'</math> and <math>D</math> lie on isogonals of <math>\angle BAC.</math> Therefore points <math>A, S</math> and <math>D</math> lie on the same line which is isogonal to <math>AD' | + | <math>D'</math> and S lie on isogonals of <math>\angle BAC.</math> |
| + | |||
| + | <math>\angle DBC = \angle D'BA, \angle DCB = \angle D'CA \implies</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>D'</math> is isogonal conjugated of <math>D</math> with respect <math>\triangle ABC \implies</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>D'</math> and <math>D</math> lie on isogonals of <math>\angle BAC.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Therefore points <math>A, S</math> and <math>D</math> lie on the same line which is isogonal to <math>AD'</math> with respect <math>\angle BAC. \blacksquare</math> | ||
'''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | '''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | ||
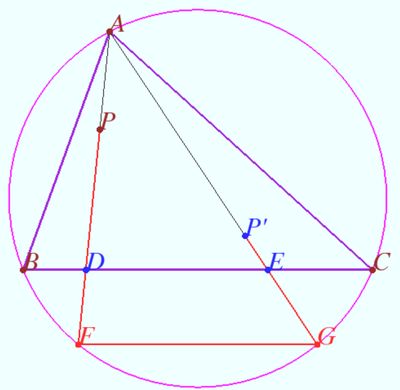
== Second definition == | == Second definition == | ||
| − | [[File:Definition 2.png| | + | [[File:Definition 2.png|370px|right]] |
Let triangle <math>\triangle ABC</math> be given. Let point <math>P</math> lies in the plane of <math>\triangle ABC,</math> | Let triangle <math>\triangle ABC</math> be given. Let point <math>P</math> lies in the plane of <math>\triangle ABC,</math> | ||
<cmath>P \notin AB, P \notin BC, P \notin AC.</cmath> | <cmath>P \notin AB, P \notin BC, P \notin AC.</cmath> | ||
| Line 221: | Line 389: | ||
<cmath>\angle ACQ = \angle BCP_1 \implies \angle QCP_1 = \angle ACB.</cmath> | <cmath>\angle ACQ = \angle BCP_1 \implies \angle QCP_1 = \angle ACB.</cmath> | ||
<cmath>\angle BCQ = \angle ACP_2 \implies \angle QCP_2 = \angle ACB.</cmath> | <cmath>\angle BCQ = \angle ACP_2 \implies \angle QCP_2 = \angle ACB.</cmath> | ||
| − | <math>\angle QCP_1 = \angle QCP_2, CP_1 = CP_2, QC</math> common | + | <math>\angle QCP_1 = \angle QCP_2, CP_1 = CP_2, QC</math> is common therefore |
<cmath>\triangle QCP_1 = \triangle QCP_2 \implies QP_1 = QP_2.</cmath> | <cmath>\triangle QCP_1 = \triangle QCP_2 \implies QP_1 = QP_2.</cmath> | ||
Similarly <math>QP_1 = QP_3 \implies Q</math> is the circumcenter of the <math>\triangle P_1P_2P_3.</math> <math>\blacksquare</math> | Similarly <math>QP_1 = QP_3 \implies Q</math> is the circumcenter of the <math>\triangle P_1P_2P_3.</math> <math>\blacksquare</math> | ||
| Line 230: | Line 398: | ||
Let point <math>P</math> be the point with barycentric coordinates <math>(p : q : r),</math> | Let point <math>P</math> be the point with barycentric coordinates <math>(p : q : r),</math> | ||
| − | <cmath>p = [(P-B),(P-C)], q = [(P-C),(P-A)], r = [(P-A),(P-B)].</cmath> | + | <cmath>p = [(P - B),(P - C)], q = [(P - C),(P - A)], r = [(P - A),(P - B)].</cmath> |
Then <math>Q</math> has barycentric coordinates <cmath>(p' : q' : r'), p' = \frac {|B - C|^2}{p}, q' = \frac {|A-C|^2}{q}, r' = \frac {|A - B|^2}{r}.</cmath> | Then <math>Q</math> has barycentric coordinates <cmath>(p' : q' : r'), p' = \frac {|B - C|^2}{p}, q' = \frac {|A-C|^2}{q}, r' = \frac {|A - B|^2}{r}.</cmath> | ||
| Line 248: | Line 416: | ||
Let <math>\theta = \angle ACP = \angle BCQ, \Theta = \angle ACQ = \angle BCP.</math> | Let <math>\theta = \angle ACP = \angle BCQ, \Theta = \angle ACQ = \angle BCP.</math> | ||
| − | <cmath>\frac {PE}{PD} = \frac {PC \sin \theta}{PC \sin \Theta} = \frac {QC \sin \theta}{QC \sin \Theta} = \frac {QD'}{QE'}.</cmath> | + | <cmath>\frac {PE}{PD} = \frac {PC \sin \theta}{PC \sin \Theta} = \frac {QC \sin \theta}{QC \sin \Theta} = \frac {QD'}{QE'}. \blacksquare</cmath> |
'''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | '''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | ||
==Sign of isogonally conjugate points== | ==Sign of isogonally conjugate points== | ||
| − | [[File:Isog dist.png| | + | [[File:Isog dist.png|350px|right]] |
| − | [[File:Isog distance.png| | + | [[File:Isog distance.png|350px|right]] |
Let triangle <math>\triangle ABC</math> and points <math>P</math> and <math>Q</math> inside it be given. | Let triangle <math>\triangle ABC</math> and points <math>P</math> and <math>Q</math> inside it be given. | ||
| Line 262: | Line 430: | ||
Let <math>\frac {PE}{PD} = \frac{QD'}{QE'}, \frac {PF}{PD} = \frac{QD'}{QF'}.</math> Prove that point <math>Q</math> is the isogonal conjugate of a point <math>P</math> with respect to a triangle <math>\triangle ABC.</math> | Let <math>\frac {PE}{PD} = \frac{QD'}{QE'}, \frac {PF}{PD} = \frac{QD'}{QF'}.</math> Prove that point <math>Q</math> is the isogonal conjugate of a point <math>P</math> with respect to a triangle <math>\triangle ABC.</math> | ||
| − | One can prove similar theorem in the case <math>P</math> outside <math>\triangle ABC.</math> | + | One can prove a similar theorem in the case <math>P</math> outside <math>\triangle ABC.</math> |
<i><b>Proof</b></i> | <i><b>Proof</b></i> | ||
| Line 272: | Line 440: | ||
<cmath>\sin \varphi \cdot \sin (\gamma - \psi) = \sin \psi \cdot \sin (\gamma - \varphi) \implies</cmath> | <cmath>\sin \varphi \cdot \sin (\gamma - \psi) = \sin \psi \cdot \sin (\gamma - \varphi) \implies</cmath> | ||
<cmath>\cos (\varphi - \gamma + \psi) - \cos(\varphi + \gamma - \psi) = \cos (\psi - \gamma + \varphi) - \cos(\psi + \gamma - \varphi)</cmath> | <cmath>\cos (\varphi - \gamma + \psi) - \cos(\varphi + \gamma - \psi) = \cos (\psi - \gamma + \varphi) - \cos(\psi + \gamma - \varphi)</cmath> | ||
| − | <cmath>\cos (\gamma + \varphi -\psi) = \cos(\gamma - \psi + \varphi) \implies</cmath> | + | <cmath>\cos (\gamma + \varphi - \psi) = \cos(\gamma - \psi + \varphi) \implies</cmath> |
<cmath>\cos \gamma \cos (\varphi - \psi) - \sin \gamma \sin (\varphi - \psi) = \cos \gamma \cos (\varphi - \psi) + \sin \gamma \sin (\varphi - \psi)</cmath> | <cmath>\cos \gamma \cos (\varphi - \psi) - \sin \gamma \sin (\varphi - \psi) = \cos \gamma \cos (\varphi - \psi) + \sin \gamma \sin (\varphi - \psi)</cmath> | ||
<cmath>2 \sin \gamma \cdot \sin (\varphi - \psi) = 0, \varphi + \psi < 180^\circ \implies \varphi = \psi.</cmath> | <cmath>2 \sin \gamma \cdot \sin (\varphi - \psi) = 0, \varphi + \psi < 180^\circ \implies \varphi = \psi.</cmath> | ||
| − | Similarly <math>\angle ABP = \angle CBQ | + | Similarly <math>\angle ABP = \angle CBQ.</math> |
| − | point <math>Q</math> is the isogonal conjugate of a point <math>P</math> with respect to a triangle <math>\triangle ABC.</math> | + | Hence point <math>Q</math> is the isogonal conjugate of a point <math>P</math> with respect to a triangle <math>\triangle ABC. \blacksquare</math> |
'''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | '''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | ||
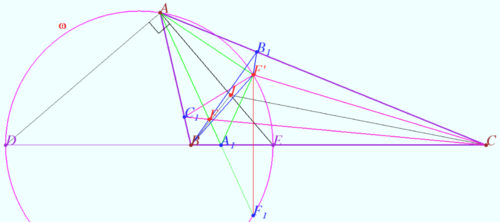
==Circumcircle of pedal triangles== | ==Circumcircle of pedal triangles== | ||
| − | [[File:Common circle.png| | + | [[File:Common circle.png|330px|right]] |
Let <math>Q</math> be the isogonal conjugate of a point <math>P</math> with respect to a triangle <math>\triangle ABC.</math> | Let <math>Q</math> be the isogonal conjugate of a point <math>P</math> with respect to a triangle <math>\triangle ABC.</math> | ||
| + | |||
Let <math>E, D, F</math> be the projection <math>P</math> on sides <math>AC, BC, AB,</math> respectively. | Let <math>E, D, F</math> be the projection <math>P</math> on sides <math>AC, BC, AB,</math> respectively. | ||
Let <math>E', D', F'</math> be the projection <math>Q</math> on sides <math>AC, BC, AB,</math> respectively. | Let <math>E', D', F'</math> be the projection <math>Q</math> on sides <math>AC, BC, AB,</math> respectively. | ||
| − | + | Prove that points <math>D, D', E, E', F, F'</math> are concyclic. | |
The midpoint <math>PQ</math> is circumcenter of <math>DD'EE'FF'.</math> | The midpoint <math>PQ</math> is circumcenter of <math>DD'EE'FF'.</math> | ||
| Line 294: | Line 463: | ||
Let <math>\theta = \angle ACP = \angle BCQ, \Theta = \angle ACQ = \angle BCP.</math> | Let <math>\theta = \angle ACP = \angle BCQ, \Theta = \angle ACQ = \angle BCP.</math> | ||
| − | <math>CE \cdot CE' = PC \cos \theta \cdot QC \cos \Theta = PC \cos \Theta \cdot QC \cos \theta = CD \cdot CD'.</math> | + | <math>CE \cdot CE' = PC \cos \theta \cdot QC \cos \Theta = PC \cos \Theta \cdot QC \cos \theta = CD \cdot CD'.</math> |
| + | |||
Hence points <math>D, D', E, E'</math> are concyclic. | Hence points <math>D, D', E, E'</math> are concyclic. | ||
| Line 316: | Line 486: | ||
This follows from the uniqueness of the conjugate point and the fact that the line intersects the circle in at most two points. | This follows from the uniqueness of the conjugate point and the fact that the line intersects the circle in at most two points. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | ||
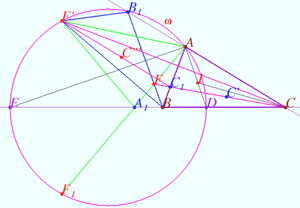
| + | ==Two pares of isogonally conjugate points== | ||
| + | [[File:3 pare of points.png|400px|right]] | ||
| + | Let triangle <math>\triangle ABC</math> and points <math>X</math> and <math>Y</math> be given. Let points <math>X'</math> and <math>Y'</math> be the isogonal conjugate of a points <math>X</math> and <math>Y</math> with respect to a triangle <math>\triangle ABC,</math> respectively. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let <math>XY</math> cross <math>X'Y'</math> at <math>Z</math> and <math>XY'</math> cross <math>X'Y</math> at <math>Z'.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Prove that point <math>Z'</math> is the isogonal conjugate of a point <math>Z</math> with respect to <math>\triangle ABC.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <i><b>Proof</b></i> | ||
| + | |||
| + | There are two pairs of isogonals <math>CX - CX'</math> and <math>CY - CY'</math> with respect to the angle <math>\angle ACB \implies</math> | ||
| + | <math>CZ - CZ'</math> are isogonals with respect to the <math>\angle ACB</math> in accordance with <i><b>The isogonal theorem</b></i>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Similarly <math>AZ - AZ'</math> are the isogonals with respect to the <math>\angle BAC.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Therefore the point <math>Z'</math> is the isogonal conjugate of a point <math>Z</math> with respect to <math>\triangle ABC.</math> | ||
'''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | '''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | ||
==Circles== | ==Circles== | ||
| − | [[File:2 points isogon.png| | + | [[File:2 points isogon.png|300px|right]] |
| − | Let <math>Q</math> be the isogonal conjugate of a point <math>P</math> with respect to a triangle <math>\triangle ABC.</math> | + | Let <math>Q</math> be the isogonal conjugate of a point <math>P</math> with respect to a triangle <math>\triangle ABC.</math> |
| + | |||
Let <math>D</math> be the circumcenter of <math>\triangle BCP.</math> | Let <math>D</math> be the circumcenter of <math>\triangle BCP.</math> | ||
| + | |||
Let <math>E</math> be the circumcenter of <math>\triangle BCQ.</math> | Let <math>E</math> be the circumcenter of <math>\triangle BCQ.</math> | ||
| + | |||
Prove that points <math>D</math> and <math>E</math> are inverses with respect to the circumcircle of <math>\triangle ABC.</math> | Prove that points <math>D</math> and <math>E</math> are inverses with respect to the circumcircle of <math>\triangle ABC.</math> | ||
| Line 330: | Line 521: | ||
The circumcenter of <math>\triangle ABC</math> point <math>O,</math> and points <math>D</math> and <math>E</math> lies on the perpendicular bisector of <math>BC.</math> | The circumcenter of <math>\triangle ABC</math> point <math>O,</math> and points <math>D</math> and <math>E</math> lies on the perpendicular bisector of <math>BC.</math> | ||
<cmath>\angle BOD = \angle COE = \angle BAC.</cmath> | <cmath>\angle BOD = \angle COE = \angle BAC.</cmath> | ||
| − | <cmath>2 \angle BDO = \angle BDC = \overset{\Large\frown} {BC} = 360^\circ - \overset{\Large\frown} {CB} = 360^\circ - 2 \angle BPC.</cmath> | + | <cmath>2 \angle BDO = \angle BDC = \overset{\Large\frown} {BC} =</cmath> |
| + | <cmath>= 360^\circ - \overset{\Large\frown} {CB} = 360^\circ - 2 \angle BPC.</cmath> | ||
<cmath>\angle BDO = 180^\circ - \angle BPC = \angle PBC + \angle PCB.</cmath> | <cmath>\angle BDO = 180^\circ - \angle BPC = \angle PBC + \angle PCB.</cmath> | ||
Similarly <math>\angle CEO = 180^\circ - \angle BQC = \angle QBC + \angle QCB.</math> | Similarly <math>\angle CEO = 180^\circ - \angle BQC = \angle QBC + \angle QCB.</math> | ||
| Line 342: | Line 534: | ||
'''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | '''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | ||
| − | == Problems == | + | ==Equidistant isogonal conjugate points== |
| + | [[File:Equal distances.png|330px|right]] | ||
| + | [[File:Equidistant points.png|330px|right]] | ||
| + | Let triangle <math>ABC</math> with incenter <math>I</math> be given. | ||
| + | Denote <math>\omega = \odot BIC.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let point <math>P'</math> be the isogonal conjugate of the point <math>P</math> with respect to <math>\triangle ABC.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Prove that <math>AP = AP'</math> iff <math>P \in \omega.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <i><b>Proof</b></i> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 1. Let <math>P \in \omega.</math> WLOG, <math>P \in \angle BAI.</math> | ||
| + | Point <math>P \in \omega \implies \angle PBI = \angle PCI.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Point <math>P'</math> is the isogonal conjugate of the point <math>P</math> with respect to <math>\triangle ABC \implies</math> | ||
| + | <cmath>\angle PBI = \angle P'BI, \angle PCI = \angle P'CI \implies \angle P'BI = \angle P'CI.</cmath> | ||
| + | So points <math>B,C,I, P,</math> and <math>P'</math> are concyclic. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let <math>E = AI \cap \odot ABC.</math> Then <math>E</math> is the center of <math>\omega \implies</math> | ||
| + | <cmath>EP = EP', \angle IEP = \angle IEP' = 2 \angle PBI.</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>\triangle AEP = \triangle AEP' \implies AP = AP'.</cmath> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | 2. Let <math>AP = AP'.</math> | ||
| + | <math>\angle PAI = \angle PAE = \angle P'AI = \angle P'AE \implies</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Points <math>P</math> and <math>P'</math> are symmetric with respect <math>AI \implies PE = P'E.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Suppose that <math>P \notin \odot BIC.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let <math>O</math> be the center of <math>\odot BPC, O'</math> be the center of <math>\odot BP'C.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | It is known that points <math>O</math> and <math>O'</math> are inverted with respect to the circumcircle of <math>\triangle ABC.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Points <math>O, O',</math> and <math>E</math> belong to bisector <math>BC, E \in \odot ABC.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Therefore <math>\overset{\Large\frown} {BIC}</math> divide <math>\overset{\Large\frown} {BPC}</math> and <math>\overset{\Large\frown} {BP'C}.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | WLOG (see diagram) <math>PE > IE > P'E,</math> contradiction. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==1995 USAMO Problems/Problem 3== | ||
| + | [[File:1995 USAMO 3.png|300px|right]] | ||
| + | Given a nonisosceles, nonright triangle <math>ABC,</math> let <math>O</math> denote the center of its circumscribed circle, and let <math>A_1, \, B_1,</math> and <math>C_1</math> be the midpoints of sides <math>BC, \, CA,</math> and <math>AB,</math> respectively. Point <math>A_2</math> is located on the ray <math>OA_1</math> so that <math>\triangle OAA_1</math> is similar to <math>\triangle OA_2A</math>. Points <math>B_2</math> and <math>C_2</math> on rays <math>OB_1</math> and <math>OC_1,</math> respectively, are defined similarly. Prove that lines <math>AA_2, \, BB_2,</math> and <math>CC_2</math> are concurrent. | ||
| − | === | + | <i><b>Solution</b></i> |
| + | |||
| + | Let <math>AH</math> be the altitude of <math>\triangle ABC \implies</math> | ||
| + | <cmath>\angle BAH = 90^\circ - \angle ABC, \angle OAC = \angle OCA =</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>= \frac{180^\circ - \angle AOC}{2} = \frac{180^\circ - 2\angle ABC}{2} = \angle BAH.</cmath> | ||
| + | Hence <math>AH</math> and <math>AO</math> are isogonals with respect to the angle <math>\angle BAC.</math> | ||
| + | <cmath>\triangle OAA_1 \sim \triangle OA_2A, AH || A_1O \implies \angle AA_1O = \angle A_2AO = \angle A_1AH.</cmath> | ||
| + | <math>AA_2</math> and <math>AA_1</math> are isogonals with respect to the angle <math>\angle BAC.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Similarly <math>BB_2</math> and <math>BB_1</math> are isogonals with respect to <math>\angle ABC.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Similarly <math>CC_2</math> and <math>CC_1</math> are isogonals with respect to <math>\angle ACB.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let <math>G = AA_1 \cap BB_1</math> be the centroid of <math>\triangle ABC, L = AA_2 \cap BB_2.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>L</math> is the isogonal conjugate of a point <math>G</math> with respect to a triangle <math>\triangle ABC.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <cmath>G \in CC_1 \implies L \in CC_2.</cmath> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <i><b>Corollary</b></i> | ||
| + | |||
| + | If median and symmedian start from any vertex of the triangle, then the angle formed by the symmedian and the angle side has the same measure as the angle between the median and the other side of the angle. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>AA_1, BB_1, CC_1</math> are medians, therefore <math>AA_2, BB_2, CC_2</math> are symmedians, so the three symmedians meet at a point which is triangle center called the Lemoine point. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==2011 USAMO Problems/Problem 5== | ||
| + | [[File:2011 USAMO 5.png|400px|right]] | ||
| + | Let <math>P</math> be a given point inside quadrilateral <math>ABCD</math>. Points <math>Q_1</math> and <math>Q_2</math> are located within <math>ABCD</math> such that <math>\angle Q_1 BC = \angle ABP</math>, <math>\angle Q_1 CB = \angle DCP</math>, <math>\angle Q_2 AD = \angle BAP</math>, <math>\angle Q_2 DA = \angle CDP</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Prove that <math>\overline{Q_1 Q_2} \parallel \overline{AB}</math> if and only if <math>\overline{Q_1 Q_2} \parallel \overline{CD}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <i><b>Solution</b></i> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <i><b>Case 1</b></i> The lines <math>AB</math> and <math>CD</math> are not parallel. Denote <math>E = AB \cap CD.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <cmath>\angle Q_1 BC = \angle ABP, \angle Q_1 CB = \angle DCP \implies</cmath> | ||
| + | Point <math>Q_1</math> isogonal conjugate of a point <math>P</math> with respect to a triangle <math>\triangle EBC \implies</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>EP</math> and <math>EQ_1</math> are isogonals with respect to <math>\angle BEC.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Similarly point <math>Q_2</math> isogonal conjugate of a point <math>P</math> with respect to a triangle <math>\triangle EAD \implies</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>EP</math> and <math>EQ_2</math> are isogonals with respect to <math>\angle BEC.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Therefore points <math>E, Q_1, Q_2</math> lies on the isogonal <math>EP</math> with respect to <math>\angle BEC \implies</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>Q_1Q_2</math> is not parallel to <math>AB</math> or <math>CD.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <i><b>Case 2</b></i> <math>AB||CD.</math> We use <i><b>The isogonal theorem in case parallel lines</b></i> and get | ||
| + | <cmath>AB||Q_1Q_2 || CD. \blacksquare</cmath> | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | ||
| + | ==2024 Sharygin olimpiad Problem 16== | ||
| + | [[File:2024 16.png|390px|right]] | ||
| + | Let <math>AA', BB',</math> and <math>CC'</math> be the bisectors of a triangle <math>\triangle ABC.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The segments <math>BB'</math> and <math>A'C'</math> meet at point <math>D.</math> Let <math>E</math> be the projection of <math>D</math> to <math>AC.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Points <math>P</math> and <math>Q</math> on the sides <math>AB</math> and <math>BC,</math> respectively, are such that <math>EP = PD, EQ = QD.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Prove that <math>\angle PDB' = \angle EDQ.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <i><b>Proof</b></i> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\triangle PDQ = \triangle PEQ (DQ = EQ, DP = PF, PQ</math> is the common side) <math>\implies</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>PQ \perp DE, F = PQ \cap DE</math> is the midpoint <math>DE.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Denote <math>r</math> the inradius of <math>\triangle ABC, F'</math> is the base of perpendicular from <math>D</math> to <math>BC.</math> | ||
| + | <cmath>\frac {DF'}{r} = \frac {BD}{BI}, \frac {DE}{r} = \frac {B'D}{B'I},</cmath> | ||
| + | It is known that <cmath>\frac {B'D}{BD} = 2\frac {B'I}{BI} \implies \frac {DE}{r} = 2 \frac {DF'}{r}</cmath> | ||
| + | (see [[Bisector | Division of bisector]] for details.) | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>DF = DF' \implies D</math> is incenter of <math>\triangle BPQ \implies</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\angle BPD = \angle QPD = \angle QPE, \angle BQD = \angle PQD = \angle PQE \implies</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>B</math> is isogonal conjugate of E with respect <math>\triangle PDQ \implies \angle PDB' = \angle EDQ.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Another solution see [[Sharygin_Olympiads,_the_best | 2024.2C_Problem_16]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Simplified distance formula for isogonal points== | ||
| + | [[File:1 pare and.png|370px|right]] | ||
| + | Let triangle <math>\triangle ABC,</math> points <math>P</math> and <math>P',</math> and <math>\odot ABC = \Omega</math> be given. Let point <math>P'</math> be the isogonal conjugate of a point <math>P</math> with respect to a triangle <math>\triangle ABC.</math> | ||
| + | <cmath>D = AP \cap BC, E = AP' \cap BC, F = AP \cap \Omega, G = AP' \cap \Omega.</cmath> | ||
| + | Prove that <math>PF \cdot P'G= AF \cdot EG.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <i><b>Proof</b></i> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\angle AFC</math> and <math>\angle AGC</math> are both subtended by arc <math>\overset{\Large\frown} {AC} \implies \angle AFC = \angle AGC.</math> | ||
| + | <cmath>\angle PCF = \angle PCB + \angle BCF = \angle P'CA + \angle BAF = \angle P'CA + \angle P'AC=</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>= \angle GP'C \implies \triangle CPF \sim \triangle P'CG \implies PF \cdot P'G = FC \cdot CG.</cmath> | ||
| + | Similarly <cmath>\triangle CAF \sim \triangle ECG \implies AF \cdot EG = FC \cdot CG.</cmath> | ||
| + | [[Barycentric coordinates | Product of isogonal segments]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Point on circumcircle== | ||
| + | [[File:RADAX.png|350px|right]] | ||
| + | Let triangle <math>\triangle ABC,</math> points <math>D \in BC</math> and <math>E \in BC</math> be given. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Denote <math>\Omega = \odot ABC, \omega = \odot AED, G = \omega \cap \Omega \ne A, F = AG \cap BC,</math> | ||
| + | <cmath>K = AE \cap \Omega \ne A, L = GD \cap \Omega \ne G.</cmath> | ||
| + | Prove that <math>KL || BC.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <i><b>Proof</b></i> | ||
| + | |||
| + | WLOG, the order of the points is <math>B,E,F,C,D,</math> as shown on diagram. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The spiral symilarity centered at <math>A</math> maps <math>\Omega</math> to <math>\omega</math> and point <math>L \in \Omega</math> to point <math>D \in \omega \implies \overset{\Large\frown} {AL} = \overset{\Large\frown} {AD} \implies \angle ABL = \angle AED.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\angle AED</math> is the external angle of <math>\triangle AEB \implies \angle AED = \angle ABC + \angle BAE \implies</math> | ||
| + | <cmath>\angle CBL = \angle BAK \implies \overset{\Large\frown} {BK} = \overset{\Large\frown} {CL} \implies BC ||KL. \blacksquare</cmath> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <i><b>Corollary</b></i> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>AL</math> is the isogonal conjugate to <math>AK</math> with respect <math>\angle BAC.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Fixed point on circumcircle== | ||
| + | [[File:Fixed point 2.png|280px|right]] | ||
| + | [[File:Fixed point 3.png|280px|right]] | ||
| + | [[File:Fixed point 4.png|280px|right]] | ||
| + | [[File:Fixed point 5.png|280px|right]] | ||
| + | Let triangle <math>\triangle ABC,</math> point <math>G \ne A</math> on circumcircle <math>\Omega = \odot ABC,</math> and point <math>D \in BC</math> be given. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Point <math>P</math> lies on <math>AG,</math> point <math>P'</math> be the isogonal conjugate of a point <math>P</math> with respect to a triangle <math>\triangle ABC, Q = DP' \cap AP, F = \odot DPQ \cap \Omega.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Prove that <math>F</math> is fixed point and not depends from position of <math>P.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <i><b>Proof</b></i> | ||
| + | |||
| + | WLOG, the order of points on sideline is <math>B, C, D,</math> point <math>B</math> is closer to <math>AP</math> than to <math>AP'.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Denote <math>Y = AP \cap BC, Z = AP' \cap BC,\omega = \odot ADY,</math> | ||
| + | <cmath>F' = \omega \cap \Omega \ne A, H = \Omega \cap F'D \ne F'.</cmath> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Spiral similarity centered at <math>A</math> which maps <math>\Omega</math> into <math>\odot AYD</math> transform point <math>H</math> into point <math>D \implies</math> | ||
| + | <cmath>\overset{\Large\frown} {ACH} = \overset{\Large\frown} {AD} \implies \angle AGH = \angle AYD \implies GH||BC \implies</cmath> <cmath>\overset{\Large\frown} {CH} = \overset{\Large\frown} {BG} \implies \angle BAG = \angle CAH \implies H \in AP'.</cmath> | ||
| + | Points <math>F', H,</math> and <math>D</math> are collinear. | ||
| + | |||
| + | It is known ([[Barycentric coordinates | Ratio of isogonal segments]]) that <math>\frac {AP'}{P'Z} \cdot \frac {AP}{PY} = \frac {AH}{HZ}.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | We use the ratio of the areas and get: | ||
| + | <cmath>\frac {[AQD]}{[QYD]} = \frac{AQ}{QY}, \frac {[ZQD]}{[YQD]} = \frac{ZD}{YD},</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>\frac {[AQD]}{[ZQD]} = \frac{AP'}{P'Z} \implies</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath> \frac{AQ}{QY} = \frac {[AQD]}{[QYD]} = \frac {[AQD]}{[ZQD]} \cdot \frac {[ZQD]}{[YQD]} = \frac{AP'}{P'Z} \cdot \frac{ZD}{YD}.</cmath> | ||
| + | Denote <math>X = AP \cap DH.</math> | ||
| + | <cmath>\frac {[AXD]}{[YXD]} = \frac{AX}{XY}, \frac {[XZD]}{[XYD]} = \frac{ZD}{YD},</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>\frac {[AXD]}{[XZD]} = \frac{AH}{HZ} \implies</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath> \frac{AX}{XY} = \frac {[AXD]}{[YXD]} = \frac {[AXD]}{[XZD]} \cdot \frac {[XZD]}{[YXD]} = \frac{AH}{HZ} \cdot \frac{ZD}{YD}.</cmath> | ||
| + | Therefore <math>\frac{AX}{XY} = \frac{AQ}{QY} \cdot \frac{AP}{PY}</math> which means ([[Radical axis | Problems | Simple]]) that <math>DX</math> is the radical axes of <math>\omega</math> and <math>\odot DPQ \implies</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>F = F'</math> and not depends from position of <math>P.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Barycentric coordinates | Fixed point on circumcircle]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Distance formula for isogonal points== | ||
| + | [[File:Isogonal formulas.png|400px|right]] | ||
| + | Let triangle <math>\triangle ABC</math> and point <math>P</math> be given. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let point <math>P'</math> be the isogonal conjugate of a point <math>P</math> with respect to a triangle <math>\triangle ABC.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let lines <math>AP</math> and <math>AP'</math> cross sideline <math>BC</math> at <math>D</math> and <math>E</math> and circumcircle of <math>\triangle ABC</math> at <math>F</math> and <math>G,</math> respectively. | ||
| + | |||
| + | We apply the Isogonal’s property and get <math>\frac {BD}{DC} \cdot \frac{BE}{EC} = \frac {AB^2}{AC^2}.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>EF || BC.</math> We apply the Ptolemy's theorem to <math>BCGF</math> and get <cmath>BC \cdot FG = BG^2 – BF^2.</cmath> | ||
| + | |||
| + | We apply the barycentric coordinates and get | ||
| + | <cmath>\left| \frac{BE}{EC} - \frac {BD}{DC} \right| = \frac {AB \cdot BC \cdot FG}{AC \cdot PF \cdot P'G}.</cmath> | ||
| + | *[[Barycentric coordinates]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Miquel point for isogonal conjugate points== | ||
| + | [[File:Miquel of one pare.png|370px|right]] | ||
| + | [[File:Miquel 1 pare.png|370px|right]] | ||
| + | Let triangle <math>\triangle ABC,</math> points <math>Q \in BC</math> and <math>P</math> be given. Let point <math>P'</math> be the isogonal conjugate of a point <math>P</math> with respect to a triangle <math>\triangle ABC.</math> | ||
| + | <cmath>D = QP \cap AP', E = AP \cap QP'.</cmath> | ||
| + | Let <math>M</math> be the Miquel point of a complete quadrilateral <math>PDP'E.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Prove that <math>M</math> lies on the circumcircle of <math>\triangle ABC.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <i><b>Proof</b></i> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Point <math>A</math> is the isogonal conjugate of a point <math>Q</math> with respect to a triangle <math>\triangle ABC,</math> so point <math>D</math> is the isogonal conjugate of a point <math>E</math> with respect to a triangle <math>\triangle ABC.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Points <math>P</math> and <math>E</math> lies on the same line, therefore <cmath>PF \cdot P'G = EF \cdot DG \implies</cmath> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <cmath>\frac {PF-EP}{PF} = \frac{DG-DP'}{DG} \implies \frac {EP}{PF} = \frac{DP'}{DG}.</cmath> | ||
| + | Point <math>M</math> lies on circles <math>APD</math> and <math>AEP' \implies </math> spiral similarity centered at <math>M</math> transform triangle <math>\triangle MPE</math> to <math>\triangle MDP' \implies</math> | ||
| + | <cmath>\angle MPE = \angle MDP', \frac {MP}{MD} = \frac {PE}{DP'} = \frac{PF}{DG} \implies</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>\triangle MPF \sim \triangle MDG \implies</cmath> <cmath>\angle AFM = \angle AGM \implies M \in \odot ABC.</cmath> | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | ||
| + | ==Point on circumcircle== | ||
| + | [[File:Point on circumcircle 0.png|400px|right]] | ||
| + | Let triangle <math>\triangle ABC,</math> and points <math>D \in BC</math> and <math>E \in \odot ABC = \Omega</math> be given. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let <math>\odot ADE = \omega, F = BC \cap \omega \ne D.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let lines <math>AF</math> and <math>AG (G \in BC)</math> be the isogonals with respect to the angle <math>\angle BAC, \odot AGD = \theta.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let <math>P</math> be an arbitrary point on <math>AF, Q = DP \cap AG, H = \theta \cap \Omega.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Prove that <math>X = EP \cap HQ</math> lies on <math>\Omega.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Simplified problem=== | ||
| + | Let <math>\triangle ABC,</math> and points <math>D \in BC</math> and <math>E \in \odot ABC = \Omega</math> be given, <math>\omega = \odot ADE, F = \omega \cap BC \ne D.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let lines <math>AF</math> and <math>AG (G \in BC)</math> be the isogonals with respect to <math>\angle BAC, \theta = \odot AGD, H = \theta \cap \Omega.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Prove that <math>X = EF \cap HG \in \Omega.</math> | ||
| + | [[File:Point on circumcircle 1.png|400px|right]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <i><b>Proof, Simplified problem</b></i> | ||
| + | <cmath>\angle CGH = \angle DAH = \frac{1}{2} \overset{\Large\frown} {HD} (\theta),</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>\angle DFE = \angle DAE = \frac{1}{2} \overset{\Large\frown} {ED} (\omega),</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>\angle EAH = \angle DAE - \angle DAH = \frac{1}{2} \overset{\Large\frown} {EH}(\Omega),</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>\angle EXH = \angle DFE - \angle DGH = \angle EAH \implies</cmath> | ||
| + | |||
| + | points <math>A, H, E, X</math> are concyclic on <math>\Omega.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <i><b>Proof</b></i> | ||
| + | [[File:Point on circumcircle 2.png|400px|right]] | ||
| + | Let points <math>P'</math> and <math>Q'</math> be the isogonal conjugate of a points <math>P</math> and <math>Q</math> with respect to a triangle <math>\triangle ABC, \omega' = \odot Q'PD, \theta' = \odot P'QD.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | It is known that <math>E \in \omega', H \in \theta', \omega' \cap \theta' \cap \Omega = M.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <cmath>\angle DQH = \angle DMH = \frac{1}{2} \overset{\Large\frown} {HD} (\theta'),</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>\angle DPE = \angle DME = \frac{1}{2} \overset{\Large\frown} {ED} (\omega'),</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>\angle EMH = \angle DME - \angle DMH = \frac{1}{2} \overset{\Large\frown} {EH}(\Omega),</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>\angle EXH = \angle DPE - \angle DQH = \angle EMH \implies</cmath> | ||
| + | points <math>M, H, E, X</math> are concyclic on <math>\Omega.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Isogonal of line BC with respect to angle BAC== | ||
| + | [[File:Isogonal of BC.png|350px|right]] | ||
| + | Let triangle <math>\triangle ABC</math> be given, <math>\Omega = \odot ABC, AD || BC.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let lines <math>AE</math> and <math>AD</math> be the isogonals with respect to <math>\angle BAC.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Prove that <math>AE</math> is tangent to <math>\Omega.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <i><b>Proof</b></i> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let <math>O</math> and <math>H</math> be the circumcenter and the orthocenter of <math>\triangle ABC,</math> respectively. | ||
| + | <cmath>AH \perp BC, AD || BC \implies AH \perp AD.</cmath> | ||
| + | <math>AH</math> is isogonal to <math>AO</math> with respect to <math>\angle BAC \implies AE \perp AO \implies AE</math> is tangent to <math>\Omega.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Isogonal bijection lines and points== | ||
| + | [[File:Isogonal of l.png|350px|right]] | ||
| + | Let triangle <math>\triangle ABC</math> and line <math>\ell, P \in \ell</math> be given, <math>\Omega = \odot ABC.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Define <math>G \in \Omega</math> the point with property <math>G' \in \ell.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Prove that <math>\angle ABG</math> is equal the angle <math>\theta</math> between <math>\ell</math> and <math>BC.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <i><b>Proof</b></i> | ||
| + | |||
| + | WLOG, the configuration is the same as shown on diagram, <math>F = \ell \cap BC, AD' || \ell, \theta = \angle PFB, AD || BC, AE</math> is the tangent to <math>\Omega.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>AD</math> is isogonal to <math>AE, AD'</math> is isogonal to <math>AG</math> with respect to <math>\angle BAC \implies</math> | ||
| + | <cmath>\theta = \angle PFB = \angle D'AD = \angle GAE = \angle GBA.</cmath> | ||
| + | A bijection has been established between the set of lines parallel to a given one and the set of points of the circumcircle. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Miquel point for two pare isogonal points== | ||
| + | [[File:2 pare Miquel o.png|400px|right]] | ||
| + | Let triangle <math>\triangle ABC</math> and points <math>P</math> and <math>Q</math> be given. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let points <math>P'</math> and <math>Q'</math> be the isogonal conjugate of the points <math>P</math> and <math>Q</math> with respect to <math>\triangle ABC, \Omega = \odot ABC, M</math> is the Miquel point of quadrilateral <math>PQP'Q'.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Prove that <math>M \in \Omega.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <i><b>Proof</b></i> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Denote <math>R = PQ \cap P'Q', \Theta = \odot P'QR, \theta = \odot PQ'R.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Then <math>M = \theta \cap \Theta</math> is the Miquel point of quadrilateral <math>PQP'Q'.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Denote <math>E = \theta \cap \Omega \notin \Theta, F = \Theta \cap \Omega \notin \theta.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let <math>D \in \Omega</math> be the point with property <math>D' \in PQ.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | WLOG, configuration is similar as shown in diagram. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>P' \in DF, Q' \in DE</math> ([[Isogonal_conjugate | Isogonal_bijection_lines_and_points]]). | ||
| + | <cmath>\angle EMF = \angle RME - \angle RMF = \angle RQ'E - \angle RP'F = \angle P'Q'E - \angle DP'Q' = \angle P'DQ' = \angle EDF \implies M \in \odot DEF \blacksquare</cmath> | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Isogonic center’s conjugate point== | ||
| + | [[File:Fermat 1.png|500px|right]] | ||
| + | [[File:Fermat 2.png|300px|right]] | ||
| + | Let triangle <math>ABC</math> with isogonic center <math>F (X(13)</math> or <math>X(14))</math> be given. Denote <math>\omega = \odot BIC.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let line <math>\ell_A</math> be the axial symmetry of line <math>AF</math> according to the sideline <math>BC.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Define lines <math>\ell_B</math> and <math>\ell_C</math> similarly. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Prove that the lines <math>\ell_A, \ell_B,</math> and <math>\ell_C</math> are concurrent. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <i><b>Proof</b></i> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let <math>I</math> be the incenter of <math>\triangle ABC, F =X(13).</math> | ||
| + | <cmath>A_1 = AF \cup BC, E = AI \cup BC, D \in BC, AD \perp AE, \omega = \odot AED.</cmath> | ||
| + | Let <math>F_1 = AF \cup \omega, F'</math> is simmetric to <math>F_1</math> with respect <math>BC \implies A_1F' = \ell_A.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The diameter <math>DE</math> of <math>\omega</math> lies on <math>BC \implies F_1 \in \omega, \overset{\Large\frown} {EF_1} = \overset{\Large\frown} {EF'} \implies \angle EAF_1 = \angle EAF'.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Therefore <math>AF'</math> is the isogonal conjugate of <math>AF</math> with respect to <math>\angle BAC.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Similarly <math>\ell_B</math> and <math>\ell_C</math> are the isogonal conjugate of <math>BF</math> and <math>CF,</math> so point <math>F'</math> is the isogonal conjugate of point <math>F</math> with respect to <math>\triangle ABC.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The second diagram show construction in the case <math>F =X(14).</math> The proof is similar. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | ||
| + | |||
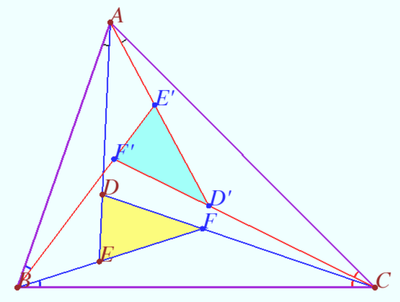
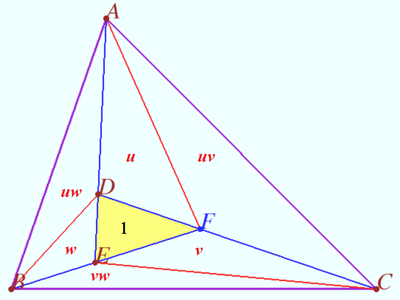
| + | ==Three pairs isogonal points== | ||
| + | [[File:Shar 2024 20.png|400px|right]] | ||
| + | Let a triangle <math>ABC,</math> points <math>D</math> and <math>E \in AD</math> be given, <math>F = CD \cap BE.</math> | ||
| + | Points <math>D', E'</math> and <math>F'</math> are the isogonal conjugate of the points <math>D, E,</math> and <math>F,</math> respectively, with respect to <math>\triangle ABC.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Prove that <math>\frac {AD}{AE} \cdot \frac {BE}{BF} \cdot \frac {CF}{CD} = \frac {AE'}{AD'} \cdot \frac {BF'}{BE'} \cdot \frac {CD'}{CF'}.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <i><b>Proof</b></i> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Denote <math>\angle BAC = \alpha, \angle ABC = \beta, \angle ACB = \gamma,</math> | ||
| + | <cmath>\angle BAD = \varphi_A, \angle CBE = \varphi_B, \angle ACD = \varphi_C.</cmath> | ||
| + | We use isogonal properties and get | ||
| + | <cmath>\angle CAD' = \varphi_A, \angle ABE' = \varphi_B, \angle BCD' = \varphi_C.</cmath> | ||
| + | By applying the Law of Sines, we get <cmath>\frac {BE}{AE} = \frac {\sin \varphi_A}{\sin (\beta - \varphi_B)}, \frac {CF}{BF} = \frac {\sin \varphi_B}{\sin (\gamma - \varphi_C)}, \frac {AD}{CD} = \frac {\sin \varphi_C}{\sin (\alpha - \varphi_A)}.</cmath> | ||
| + | Symilarly, <cmath>\frac {AE'}{BE'} = \frac {\sin \varphi_B}{\sin (\alpha - \varphi_A)}, \frac {BF'}{CF'} = \frac {\sin \varphi_C}{\sin (\beta - \varphi_B)}, \frac {CD'}{AD'} = \frac {\sin \varphi_A}{\sin (\gamma - \varphi_C)}.</cmath> | ||
| + | We multiply these equations and get | ||
| + | <cmath>\frac {AE \cdot BF \cdot CD}{AD \cdot BE \cdot CF} = \frac{AD' \cdot BE' \cdot CF'}{AE' \cdot BF' \cdot CD'} = \frac {\sin \varphi_A \cdot \sin \varphi_B \cdot \sin \varphi_C}{\sin (\alpha - \varphi_A) \cdot \sin (\beta - \varphi_B) \cdot \sin (\gamma - \varphi_C)}.</cmath> | ||
| + | '''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | ||
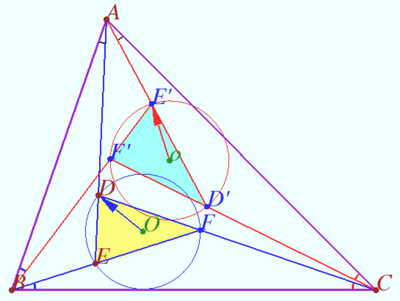
| + | ==Ratio for three pairs of isogonal points== | ||
| + | [[File:Shar 2024 20 1.png|400px|right]] | ||
| + | [[File:Shar 2024 20 2.png|400px|right]] | ||
| + | Let a triangle <math>ABC,</math> points <math>D</math> and <math>E \in AD</math> be given, <math>F = CD \cap BE.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Points <math>D', E'</math> and <math>F'</math> are the isogonal conjugate of the points <math>D, E,</math> and <math>F,</math> respectively, with respect to <math>\triangle ABC.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Denote <math>R</math> and <math>R'</math> the circumradii of triangles <math>\triangle DEF</math> and <math>\triangle D'E'F',</math> respectively. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Prove that <math>\frac {AD \cdot BE \cdot CF}{R} = \frac {AE' \cdot BF' \cdot CD'}{R'}.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <i><b>Proof</b></i> | ||
| − | + | Denote <math>\frac {AD}{DE} = u, \frac {BE}{EF} = w, \frac {CF}{FD} = v.</math> | |
| − | + | <math>[DEF] = 1,</math> where <math>[X]</math> is the area of the figure <math>X.</math> | |
| + | <cmath>\frac {[ADF]}{[DEF]} = \frac {AD}{DE} = u, \frac {[ACF]}{[DEF]} = \frac {[ACF]}{[ADF]} \cdot \frac {[ADF]}{[DEF]} = uv.</cmath> | ||
| + | Similarly, <cmath>\frac {[CFE]}{[DEF]} = v, \frac {[BCE]}{[DEF]} = vw, \frac {[BDE]}{[DEF]} = w, \frac {[ABD]}{[DEF]} = uw.</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>\frac {[ABC]}{[DEF]} = 1 + u + v + w + uv + uw + vw = (1 + u)(1 + v)(1 + w) - uvw,</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>\frac {[ABC]}{[DEF]} = \frac {AE \cdot BF \cdot CD}{DE \cdot DF \cdot EF} - \frac {AD \cdot BE \cdot CF}{DE \cdot DF \cdot EF}.</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>\frac {DE \cdot DF \cdot EF}{4R} = [DEF] \implies</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>[ABC] = \frac {AD \cdot BE \cdot CF}{4R} \cdot \left ( \frac {AE \cdot BF \cdot CD}{BE \cdot CF \cdot AD}-1 \right).</cmath> | ||
| + | Similarly, <cmath>[ABC] = \frac {AE' \cdot BF' \cdot CD'}{4R'} \cdot \left ( \frac {AD' \cdot BE' \cdot CD}{AE' \cdot BF' \cdot CD'}-1 \right).</cmath> | ||
| + | It is known that <math>\frac {AD}{AE} \cdot \frac {BE}{BF} \cdot \frac {CF}{CD} = \frac {AE'}{AD'} \cdot \frac {BF'}{BE'} \cdot \frac {CD'}{CF'}</math> ([[Isogonal_conjugate | Three pairs isogonal points]]), therefore | ||
| + | <cmath>\frac {AD \cdot BE \cdot CF}{4R} = \frac {AE' \cdot BF' \cdot CD'}{4R'}.</cmath> | ||
| + | Comment: The main idea of the proof was found by Leonid Shatunov. | ||
| + | '''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | ||
[[Category:Geometry]] | [[Category:Geometry]] | ||
Latest revision as of 07:40, 18 April 2024
Isogonal conjugates are pairs of points in the plane with respect to a certain triangle.
Contents
- 1 The isogonal theorem
- 2 Parallel segments
- 3 Perpendicularity
- 4 Fixed point
- 5 Bisector
- 6 Isogonal of the diagonal of a quadrilateral
- 7 Isogonals in trapezium
- 8 Isogonals in complete quadrilateral
- 9 Isogonal of the bisector of the triangle
- 10 Points on isogonals
- 11 Trapezoid
- 12 IMO 2007 Short list/G3
- 13 Definition of isogonal conjugate of a point
- 14 Three points
- 15 Second definition
- 16 Distance to the sides of the triangle
- 17 Sign of isogonally conjugate points
- 18 Circumcircle of pedal triangles
- 19 Common circumcircle of the pedal triangles as the sign of isogonally conjugate points
- 20 Two pares of isogonally conjugate points
- 21 Circles
- 22 Equidistant isogonal conjugate points
- 23 1995 USAMO Problems/Problem 3
- 24 2011 USAMO Problems/Problem 5
- 25 2024 Sharygin olimpiad Problem 16
- 26 Simplified distance formula for isogonal points
- 27 Point on circumcircle
- 28 Fixed point on circumcircle
- 29 Distance formula for isogonal points
- 30 Miquel point for isogonal conjugate points
- 31 Point on circumcircle
- 32 Isogonal of line BC with respect to angle BAC
- 33 Isogonal bijection lines and points
- 34 Miquel point for two pare isogonal points
- 35 Isogonic center’s conjugate point
- 36 Three pairs isogonal points
- 37 Ratio for three pairs of isogonal points
The isogonal theorem
Isogonal lines definition
Let a line ![]() and a point
and a point ![]() lying on
lying on ![]() be given. A pair of lines symmetric with respect to
be given. A pair of lines symmetric with respect to ![]() and containing the point
and containing the point ![]() be called isogonals with respect to the pair
be called isogonals with respect to the pair ![]()
Sometimes it is convenient to take one pair of isogonals as the base one, for example, ![]() and
and ![]() are the base pair. Then we call the remaining pairs as isogonals with respect to the angle
are the base pair. Then we call the remaining pairs as isogonals with respect to the angle ![]()
Projective transformation
It is known that the transformation that maps a point with coordinates ![]() into a point with coordinates
into a point with coordinates ![]() is projective.
is projective.
If the abscissa axis coincides with the line ![]() and the origin coincides with the point
and the origin coincides with the point ![]() then the isogonals define the equations
then the isogonals define the equations ![]() and the lines
and the lines ![]() symmetrical with respect to the line
symmetrical with respect to the line ![]() become their images.
become their images.
It is clear that, under the converse transformation (also projective), such pairs of lines become isogonals, and the points equidistant from ![]() lie on the isogonals.
lie on the isogonals.
The isogonal theorem
Let two pairs of isogonals ![]() and
and ![]() with respect to the pair
with respect to the pair ![]() be given. Denote
be given. Denote ![]()
Prove that ![]() and
and ![]() are the isogonals with respect to the pair
are the isogonals with respect to the pair ![]()
Proof
Let us perform a projective transformation of the plane that maps the point ![]() into a point at infinity and the line
into a point at infinity and the line ![]() maps to itself. In this case, the isogonals turn into a pair of straight lines parallel to
maps to itself. In this case, the isogonals turn into a pair of straight lines parallel to ![]() and equidistant from
and equidistant from ![]()
The converse (also projective) transformation maps the points equidistant from ![]() onto isogonals. We denote the image and the preimage with the same symbols.
onto isogonals. We denote the image and the preimage with the same symbols.
Let the images of isogonals are vertical lines. Let coordinates of images of points be ![]() Equation of a straight line
Equation of a straight line ![]() is
is ![]()
Equation of a straight line ![]() is
is ![]()
The abscissa ![]() of the point
of the point ![]() is
is ![]()
Equation of a straight line ![]() is
is ![]()
Equation of a straight line ![]() is
is ![]()
The abscissa ![]() of the point
of the point ![]() is
is ![]()
Preimages of the points ![]() and
and ![]() lie on the isogonals.
lie on the isogonals. ![]()
The isogonal theorem in the case of parallel lines
Let ![]() and
and ![]() are isogonals with respect
are isogonals with respect ![]()
Let lines ![]() and
and ![]() intersect at point
intersect at point ![]()
Prove that ![]() and line
and line ![]() through
through ![]() parallel to
parallel to ![]() are the isogonals with respect
are the isogonals with respect ![]()
Proof
The preimage of ![]() is located at infinity on the line
is located at infinity on the line ![]()
The equality ![]() implies the equality the slopes modulo of
implies the equality the slopes modulo of ![]() and
and ![]() to the bisector of
to the bisector of ![]()
Converse theorem
Let lines ![]() and
and ![]() intersect at point
intersect at point ![]()
Let ![]() and
and ![]() be the isogonals with respect
be the isogonals with respect ![]()
Prove that ![]() and
and ![]() are isogonals with respect
are isogonals with respect ![]()
Proof
The preimage of ![]() is located at infinity on the line
is located at infinity on the line ![]() so the slope of
so the slope of ![]() is known.
is known.
Suppose that ![]()
The segment ![]() and the lines
and the lines ![]() are fixed
are fixed ![]()
![]() intersects
intersects ![]() at
at ![]()
but there is the only point where line ![]() intersect
intersect ![]() Сontradiction.
Сontradiction. ![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Parallel segments
Let triangle ![]() be given. Let
be given. Let ![]() and
and ![]() be the isogonals with respect
be the isogonals with respect ![]() Let
Let ![]()
Prove that ![]() lies on bisector of
lies on bisector of ![]() and
and ![]()
Proof
Both assertions follow from The isogonal theorem in the case of parallel lines
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Perpendicularity
Let triangle ![]() be given. Right triangles
be given. Right triangles ![]() and
and ![]() with hypotenuses
with hypotenuses ![]() and
and ![]() are constructed on sides
are constructed on sides ![]() and
and ![]() to the outer (inner) side of
to the outer (inner) side of ![]() Let
Let ![]() Prove that
Prove that ![]()
Proof
Let ![]() be the bisector of
be the bisector of ![]()
![]() and
and ![]() are isogonals with respect to the pair
are isogonals with respect to the pair ![]()
![]() and
and ![]() are isogonals with respect to the pair
are isogonals with respect to the pair ![]()
![]() and
and ![]() are isogonals with respect to the pair
are isogonals with respect to the pair ![]() in accordance with The isogonal theorem.
in accordance with The isogonal theorem.
![]()
![]() is the diameter of circumcircle of
is the diameter of circumcircle of ![]()
Circumradius and altitude are isogonals with respect bisector and vertex of triangle, so ![]()
![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Fixed point
Let fixed triangle ![]() be given. Let points
be given. Let points ![]() and
and ![]() on sidelines
on sidelines ![]() and
and ![]() respectively be the arbitrary points.
respectively be the arbitrary points.
Let ![]() be the point on sideline
be the point on sideline ![]() such that
such that ![]()
![]() Prove that line
Prove that line ![]() pass through the fixed point.
pass through the fixed point.
Proof
We will prove that point ![]() symmetric
symmetric ![]() with respect
with respect ![]() lies on
lies on ![]() .
.
![]() and
and ![]() are isogonals with respect to
are isogonals with respect to ![]()
![]() points
points ![]() and
and ![]() lie on isogonals with respect to
lie on isogonals with respect to ![]() in accordance with The isogonal theorem.
in accordance with The isogonal theorem.
Point ![]() symmetric
symmetric ![]() with respect
with respect ![]() lies on isogonal
lies on isogonal ![]() with respect to
with respect to ![]() that is
that is ![]()
![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Bisector
Let a convex quadrilateral ![]() be given. Let
be given. Let ![]() and
and ![]() be the incenters of triangles
be the incenters of triangles ![]() and
and ![]() respectively.
respectively.
Let ![]() and
and ![]() be the A-excenters of triangles
be the A-excenters of triangles ![]() and
and ![]() respectively.
respectively. ![]()
Prove that ![]() is the bisector of
is the bisector of ![]()
Proof
![]()
![]() and
and ![]() are isogonals with respect to the angle
are isogonals with respect to the angle ![]()
![]() and
and ![]() are isogonals with respect to the angle
are isogonals with respect to the angle ![]() in accordance with The isogonal theorem.
in accordance with The isogonal theorem.
Denote ![]()
WLOG, ![]()
![]()
![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Isogonal of the diagonal of a quadrilateral
Given a quadrilateral ![]() and a point
and a point ![]() on its diagonal such that
on its diagonal such that ![]()
Let ![]()
Prove that ![]()
Proof
Let us perform a projective transformation of the plane that maps the point ![]() to a point at infinity and the line
to a point at infinity and the line ![]() into itself.
into itself.
In this case, the images of points ![]() and
and ![]() are equidistant from the image of
are equidistant from the image of ![]()
the point ![]() (midpoint of
(midpoint of ![]() lies on
lies on ![]()
![]() contains the midpoints of
contains the midpoints of ![]() and
and ![]()
![]() is the Gauss line of the complete quadrilateral
is the Gauss line of the complete quadrilateral ![]()
![]() bisects
bisects ![]()
the preimages of the points ![]() and
and ![]() lie on the isogonals
lie on the isogonals ![]() and
and ![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Isogonals in trapezium
Let the trapezoid ![]() be given. Denote
be given. Denote ![]()
The point ![]() on the smaller base
on the smaller base ![]() is such that
is such that ![]()
Prove that ![]()
Proof
![]()
![]() Therefore
Therefore ![]() and
and ![]() are isogonals with respect
are isogonals with respect ![]()
Let us perform a projective transformation of the plane that maps the point ![]() to a point at infinity and the line
to a point at infinity and the line ![]() into itself.
into itself.
In this case, the images of points ![]() and
and ![]() are equidistant from the image of
are equidistant from the image of ![]() contains the midpoints of
contains the midpoints of ![]() and
and ![]() , that is,
, that is, ![]() is the Gauss line of the complete quadrilateral
is the Gauss line of the complete quadrilateral ![]()
![]() bisects
bisects ![]()
The preimages of the points ![]() and
and ![]() lie on the isogonals
lie on the isogonals ![]() and
and ![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Isogonals in complete quadrilateral
Let complete quadrilateral ![]() be given. Let
be given. Let ![]() be the Miquel point of
be the Miquel point of ![]()
Prove that ![]() is isogonal to
is isogonal to ![]() and
and ![]() is isogonal to
is isogonal to ![]() with respect
with respect ![]()
Proof
![]()
![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Isogonal of the bisector of the triangle
The triangle ![]() be given. The point
be given. The point ![]() chosen on the bisector
chosen on the bisector ![]()
Denote ![]()
![]() Prove that
Prove that ![]()
Proof
Let us perform a projective transformation of the plane that maps the point ![]() to a point at infinity and the line
to a point at infinity and the line ![]() into itself.
into itself.
In this case, the images of segments ![]() and
and ![]() are equidistant from the image of
are equidistant from the image of ![]()
Image of point ![]() is midpoint of image
is midpoint of image ![]() and midpoint image
and midpoint image ![]()
Image ![]() is parallelogramm
is parallelogramm ![]()
![]() distances from
distances from ![]() and
and ![]() to
to ![]() are equal
are equal ![]()
Preimages ![]() and
and ![]() are isogonals with respect
are isogonals with respect ![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Points on isogonals
The triangle ![]() be given. The point
be given. The point ![]() chosen on
chosen on ![]() The point
The point ![]() chosen on
chosen on ![]() such that
such that ![]() and
and ![]() are isogonals with respect
are isogonals with respect ![]()
Prove that ![]()
Proof
Denote ![]()
![]()
![]()
We use the Law of Sines and get:
![]()
![]()
![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Trapezoid
The lateral side ![]() of the trapezoid
of the trapezoid ![]() is perpendicular to the bases, point
is perpendicular to the bases, point ![]() is the intersection point of the diagonals
is the intersection point of the diagonals ![]() .
.
Point ![]() is taken on the circumcircle
is taken on the circumcircle ![]() of triangle
of triangle ![]() diametrically opposite to point
diametrically opposite to point ![]()
Prove that ![]()
Proof
WLOG, ![]() is not the diameter of
is not the diameter of ![]() Let sidelines
Let sidelines ![]() and
and ![]() intersect
intersect ![]() at points
at points ![]() and
and ![]() respectively.
respectively.
![]() is rectangle
is rectangle ![]()
![]()
![]() is isogonal to
is isogonal to ![]() with respect
with respect ![]()
![]() is isogonal to
is isogonal to ![]() with respect
with respect ![]()
In accordance with The isogonal theorem in case parallel lines ![]()
![]() is isogonal to
is isogonal to ![]() with respect
with respect ![]()
![]() in accordance with Converse theorem for The isogonal theorem in case parallel lines.
in accordance with Converse theorem for The isogonal theorem in case parallel lines. ![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
IMO 2007 Short list/G3
The diagonals of a trapezoid ![]() intersect at point
intersect at point ![]()
Point ![]() lies between the parallel lines
lies between the parallel lines ![]() and
and ![]() such that
such that ![]() and line
and line ![]() separates points
separates points ![]() and
and ![]()
Prove that ![]()
Proof
![]()
![]() and
and ![]() are isogonals with respect
are isogonals with respect ![]()
![]()
![]() is isogonal to
is isogonal to ![]() with respect
with respect ![]()
From the converse of The isogonal theorem we get
![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Definition of isogonal conjugate of a point
Let triangle ![]() be given. Let
be given. Let ![]() be the circumcircle of
be the circumcircle of ![]() Let point
Let point ![]() be in the plane of
be in the plane of ![]() Denote by
Denote by ![]() the lines
the lines ![]() respectively. Denote by
respectively. Denote by ![]() the lines
the lines ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() , respectively.
Denote by
, respectively.
Denote by ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() the reflections of
the reflections of ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() over the angle bisectors of angles
over the angle bisectors of angles ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() , respectively.
, respectively.
Prove that lines ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() concur at a point
concur at a point ![]() This point is called the isogonal conjugate of
This point is called the isogonal conjugate of ![]() with respect to triangle
with respect to triangle ![]() .
.
Proof
By our constructions of the lines ![]() ,
, ![]() , and this statement remains true after permuting
, and this statement remains true after permuting ![]() . Therefore by the trigonometric form of Ceva's Theorem
. Therefore by the trigonometric form of Ceva's Theorem
![]() so again by the trigonometric form of Ceva, the lines
so again by the trigonometric form of Ceva, the lines ![]() concur, as was to be proven.
concur, as was to be proven. ![]()
Corollary
Let points P and Q lie on the isogonals with respect angles ![]() and
and ![]() of triangle
of triangle ![]()
Then these points lie on isogonals with respect angle ![]()
Corollary 2
Let point ![]() be in the sideline
be in the sideline ![]() of
of ![]()
Then the isogonal conjugate of a point ![]() is a point
is a point ![]()
Points ![]() and
and ![]() do not have an isogonally conjugate point.
do not have an isogonally conjugate point.
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Three points
Let fixed triangle ![]() be given. Let the arbitrary point
be given. Let the arbitrary point ![]() not be on sidelines of
not be on sidelines of ![]() Let
Let ![]() be the point on isogonal of
be the point on isogonal of ![]() with respect angle
with respect angle ![]() Let
Let ![]() be the crosspoint of isogonal of
be the crosspoint of isogonal of ![]() with respect angle
with respect angle ![]() and isogonal of
and isogonal of ![]() with respect angle
with respect angle ![]()
Prove that lines ![]() and
and ![]() are concurrent.
are concurrent.
Proof
Denote ![]()
![]() and
and ![]() are isogonals with respect
are isogonals with respect ![]()
![]() and S lie on isogonals of
and S lie on isogonals of ![]()
![]()
![]() is isogonal conjugated of
is isogonal conjugated of ![]() with respect
with respect ![]()
![]() and
and ![]() lie on isogonals of
lie on isogonals of ![]()
Therefore points ![]() and
and ![]() lie on the same line which is isogonal to
lie on the same line which is isogonal to ![]() with respect
with respect ![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Second definition
Let triangle ![]() be given. Let point
be given. Let point ![]() lies in the plane of
lies in the plane of ![]()
![]() Let the reflections of
Let the reflections of ![]() in the sidelines
in the sidelines ![]() be
be ![]()
Then the circumcenter ![]() of the
of the ![]() is the isogonal conjugate of
is the isogonal conjugate of ![]()
Points ![]() and
and ![]() have not isogonal conjugate points.
have not isogonal conjugate points.
Another points of sidelines ![]() have points
have points ![]() respectively as isogonal conjugate points.
respectively as isogonal conjugate points.
Proof
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() is common therefore
is common therefore
![]() Similarly
Similarly ![]() is the circumcenter of the
is the circumcenter of the ![]()
![]()
From definition 1 we get that ![]() is the isogonal conjugate of
is the isogonal conjugate of ![]()
It is clear that each point ![]() has the unique isogonal conjugate point.
has the unique isogonal conjugate point.
Let point ![]() be the point with barycentric coordinates
be the point with barycentric coordinates ![]()
![]() Then
Then ![]() has barycentric coordinates
has barycentric coordinates ![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Distance to the sides of the triangle
Let ![]() be the isogonal conjugate of a point
be the isogonal conjugate of a point ![]() with respect to a triangle
with respect to a triangle ![]()
Let ![]() and
and ![]() be the projection
be the projection ![]() on sides
on sides ![]() and
and ![]() respectively.
respectively.
Let ![]() and
and ![]() be the projection
be the projection ![]() on sides
on sides ![]() and
and ![]() respectively.
respectively.
Then ![]()
Proof
Let ![]()
![]() vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Sign of isogonally conjugate points
Let triangle ![]() and points
and points ![]() and
and ![]() inside it be given.
inside it be given.
Let ![]() be the projections
be the projections ![]() on sides
on sides ![]() respectively.
respectively.
Let ![]() be the projections
be the projections ![]() on sides
on sides ![]() respectively.
respectively.
Let ![]() Prove that point
Prove that point ![]() is the isogonal conjugate of a point
is the isogonal conjugate of a point ![]() with respect to a triangle
with respect to a triangle ![]()
One can prove a similar theorem in the case ![]() outside
outside ![]()
Proof
![]()
![]()
Denote ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() Similarly
Similarly ![]() Hence point
Hence point ![]() is the isogonal conjugate of a point
is the isogonal conjugate of a point ![]() with respect to a triangle
with respect to a triangle ![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Circumcircle of pedal triangles
Let ![]() be the isogonal conjugate of a point
be the isogonal conjugate of a point ![]() with respect to a triangle
with respect to a triangle ![]()
Let ![]() be the projection
be the projection ![]() on sides
on sides ![]() respectively.
respectively.
Let ![]() be the projection
be the projection ![]() on sides
on sides ![]() respectively.
respectively.
Prove that points ![]() are concyclic.
are concyclic.
The midpoint ![]() is circumcenter of
is circumcenter of ![]()
Proof
Let ![]()
![]()
Hence points ![]() are concyclic.
are concyclic.
![]() is trapezoid,
is trapezoid, ![]()
the midpoint ![]() is circumcenter of
is circumcenter of ![]()
Similarly points ![]() are concyclic and points
are concyclic and points ![]() are concyclic.
are concyclic.
Therefore points ![]() are concyclic, so the midpoint
are concyclic, so the midpoint ![]() is circumcenter of
is circumcenter of ![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Common circumcircle of the pedal triangles as the sign of isogonally conjugate points
Let triangle ![]() and points
and points ![]() and
and ![]() inside it be given. Let
inside it be given. Let ![]() be the projections
be the projections ![]() on sides
on sides ![]() respectively.
Let
respectively.
Let ![]() be the projections
be the projections ![]() on sides
on sides ![]() respectively.
respectively.
Let points ![]() be concyclic and none of them lies on the sidelines of
be concyclic and none of them lies on the sidelines of ![]()
Then point ![]() is the isogonal conjugate of a point
is the isogonal conjugate of a point ![]() with respect to a triangle
with respect to a triangle ![]()
This follows from the uniqueness of the conjugate point and the fact that the line intersects the circle in at most two points.
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Two pares of isogonally conjugate points
Let triangle ![]() and points
and points ![]() and
and ![]() be given. Let points
be given. Let points ![]() and
and ![]() be the isogonal conjugate of a points
be the isogonal conjugate of a points ![]() and
and ![]() with respect to a triangle
with respect to a triangle ![]() respectively.
respectively.
Let ![]() cross
cross ![]() at
at ![]() and
and ![]() cross
cross ![]() at
at ![]()
Prove that point ![]() is the isogonal conjugate of a point
is the isogonal conjugate of a point ![]() with respect to
with respect to ![]()
Proof
There are two pairs of isogonals ![]() and
and ![]() with respect to the angle
with respect to the angle ![]()
![]() are isogonals with respect to the
are isogonals with respect to the ![]() in accordance with The isogonal theorem.
in accordance with The isogonal theorem.
Similarly ![]() are the isogonals with respect to the
are the isogonals with respect to the ![]()
Therefore the point ![]() is the isogonal conjugate of a point
is the isogonal conjugate of a point ![]() with respect to
with respect to ![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Circles
Let ![]() be the isogonal conjugate of a point
be the isogonal conjugate of a point ![]() with respect to a triangle
with respect to a triangle ![]()
Let ![]() be the circumcenter of
be the circumcenter of ![]()
Let ![]() be the circumcenter of
be the circumcenter of ![]()
Prove that points ![]() and
and ![]() are inverses with respect to the circumcircle of
are inverses with respect to the circumcircle of ![]()
Proof
The circumcenter of ![]() point
point ![]() and points
and points ![]() and
and ![]() lies on the perpendicular bisector of
lies on the perpendicular bisector of ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() Similarly
Similarly ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Equidistant isogonal conjugate points
Let triangle ![]() with incenter
with incenter ![]() be given.
Denote
be given.
Denote ![]()
Let point ![]() be the isogonal conjugate of the point
be the isogonal conjugate of the point ![]() with respect to
with respect to ![]()
Prove that ![]() iff
iff ![]()
Proof
1. Let ![]() WLOG,
WLOG, ![]() Point
Point ![]()
Point ![]() is the isogonal conjugate of the point
is the isogonal conjugate of the point ![]() with respect to
with respect to ![]()
![]() So points
So points ![]() and
and ![]() are concyclic.
are concyclic.
Let ![]() Then
Then ![]() is the center of
is the center of ![]()
![]()
![]()
2. Let ![]()
![]()
Points ![]() and
and ![]() are symmetric with respect
are symmetric with respect ![]()
Suppose that ![]()
Let ![]() be the center of
be the center of ![]() be the center of
be the center of ![]()
It is known that points ![]() and
and ![]() are inverted with respect to the circumcircle of
are inverted with respect to the circumcircle of ![]()
Points ![]() and
and ![]() belong to bisector
belong to bisector ![]()
Therefore ![]() divide
divide ![]() and
and ![]()
WLOG (see diagram) ![]() contradiction.
contradiction.
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
1995 USAMO Problems/Problem 3
Given a nonisosceles, nonright triangle ![]() let
let ![]() denote the center of its circumscribed circle, and let
denote the center of its circumscribed circle, and let ![]() and
and ![]() be the midpoints of sides
be the midpoints of sides ![]() and
and ![]() respectively. Point
respectively. Point ![]() is located on the ray
is located on the ray ![]() so that
so that ![]() is similar to
is similar to ![]() . Points
. Points ![]() and
and ![]() on rays
on rays ![]() and
and ![]() respectively, are defined similarly. Prove that lines
respectively, are defined similarly. Prove that lines ![]() and
and ![]() are concurrent.
are concurrent.
Solution
Let ![]() be the altitude of
be the altitude of ![]()
![]()
![]() Hence
Hence ![]() and
and ![]() are isogonals with respect to the angle
are isogonals with respect to the angle ![]()
![]()
![]() and
and ![]() are isogonals with respect to the angle
are isogonals with respect to the angle ![]()
Similarly ![]() and
and ![]() are isogonals with respect to
are isogonals with respect to ![]()
Similarly ![]() and
and ![]() are isogonals with respect to
are isogonals with respect to ![]()
Let ![]() be the centroid of
be the centroid of ![]()
![]() is the isogonal conjugate of a point
is the isogonal conjugate of a point ![]() with respect to a triangle
with respect to a triangle ![]()
![]()
Corollary
If median and symmedian start from any vertex of the triangle, then the angle formed by the symmedian and the angle side has the same measure as the angle between the median and the other side of the angle.
![]() are medians, therefore
are medians, therefore ![]() are symmedians, so the three symmedians meet at a point which is triangle center called the Lemoine point.
are symmedians, so the three symmedians meet at a point which is triangle center called the Lemoine point.
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
2011 USAMO Problems/Problem 5
Let ![]() be a given point inside quadrilateral
be a given point inside quadrilateral ![]() . Points
. Points ![]() and
and ![]() are located within
are located within ![]() such that
such that ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() .
.
Prove that ![]() if and only if
if and only if ![]() .
.
Solution
Case 1 The lines ![]() and
and ![]() are not parallel. Denote
are not parallel. Denote ![]()
![]() Point
Point ![]() isogonal conjugate of a point
isogonal conjugate of a point ![]() with respect to a triangle
with respect to a triangle ![]()
![]() and
and ![]() are isogonals with respect to
are isogonals with respect to ![]()
Similarly point ![]() isogonal conjugate of a point
isogonal conjugate of a point ![]() with respect to a triangle
with respect to a triangle ![]()
![]() and
and ![]() are isogonals with respect to
are isogonals with respect to ![]()
Therefore points ![]() lies on the isogonal
lies on the isogonal ![]() with respect to
with respect to ![]()
![]() is not parallel to
is not parallel to ![]() or
or ![]()
Case 2 ![]() We use The isogonal theorem in case parallel lines and get
We use The isogonal theorem in case parallel lines and get
![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
2024 Sharygin olimpiad Problem 16
Let ![]() and
and ![]() be the bisectors of a triangle
be the bisectors of a triangle ![]()
The segments ![]() and
and ![]() meet at point
meet at point ![]() Let
Let ![]() be the projection of
be the projection of ![]() to
to ![]()
Points ![]() and
and ![]() on the sides
on the sides ![]() and
and ![]() respectively, are such that
respectively, are such that ![]()
Prove that ![]()
Proof
![]() is the common side)
is the common side) ![]()
![]() is the midpoint
is the midpoint ![]()
Denote ![]() the inradius of
the inradius of ![]() is the base of perpendicular from
is the base of perpendicular from ![]() to
to ![]()
![]() It is known that
It is known that ![]() (see Division of bisector for details.)
(see Division of bisector for details.)
![]() is incenter of
is incenter of ![]()
![]()
![]() is isogonal conjugate of E with respect
is isogonal conjugate of E with respect ![]()
Another solution see 2024.2C_Problem_16
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Simplified distance formula for isogonal points
Let triangle ![]() points
points ![]() and
and ![]() and
and ![]() be given. Let point
be given. Let point ![]() be the isogonal conjugate of a point
be the isogonal conjugate of a point ![]() with respect to a triangle
with respect to a triangle ![]()
![]() Prove that
Prove that ![]()
Proof
![]() and
and ![]() are both subtended by arc
are both subtended by arc ![]()
![]()
![]() Similarly
Similarly ![]() Product of isogonal segments
Product of isogonal segments
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Point on circumcircle
Let triangle ![]() points
points ![]() and
and ![]() be given.
be given.
Denote ![]()
![]() Prove that
Prove that ![]()
Proof
WLOG, the order of the points is ![]() as shown on diagram.
as shown on diagram.
The spiral symilarity centered at ![]() maps
maps ![]() to
to ![]() and point
and point ![]() to point
to point ![]()
![]() is the external angle of
is the external angle of ![]()
![]()
Corollary
![]() is the isogonal conjugate to
is the isogonal conjugate to ![]() with respect
with respect ![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Fixed point on circumcircle
Let triangle ![]() point
point ![]() on circumcircle
on circumcircle ![]() and point
and point ![]() be given.
be given.
Point ![]() lies on
lies on ![]() point
point ![]() be the isogonal conjugate of a point
be the isogonal conjugate of a point ![]() with respect to a triangle
with respect to a triangle ![]()
Prove that ![]() is fixed point and not depends from position of
is fixed point and not depends from position of ![]()
Proof
WLOG, the order of points on sideline is ![]() point
point ![]() is closer to
is closer to ![]() than to
than to ![]()
Denote ![]()
![]()
Spiral similarity centered at ![]() which maps
which maps ![]() into
into ![]() transform point
transform point ![]() into point
into point ![]()
![]()
![]() Points
Points ![]() and
and ![]() are collinear.
are collinear.
It is known ( Ratio of isogonal segments) that ![]()
We use the ratio of the areas and get:
![]()
![]()
![]() Denote
Denote ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() Therefore
Therefore ![]() which means ( Problems | Simple) that
which means ( Problems | Simple) that ![]() is the radical axes of
is the radical axes of ![]() and
and ![]()
![]() and not depends from position of
and not depends from position of ![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Distance formula for isogonal points
Let triangle ![]() and point
and point ![]() be given.
be given.
Let point ![]() be the isogonal conjugate of a point
be the isogonal conjugate of a point ![]() with respect to a triangle
with respect to a triangle ![]()
Let lines ![]() and
and ![]() cross sideline
cross sideline ![]() at
at ![]() and
and ![]() and circumcircle of
and circumcircle of ![]() at
at ![]() and
and ![]() respectively.
respectively.
We apply the Isogonal’s property and get ![]()
![]() We apply the Ptolemy's theorem to
We apply the Ptolemy's theorem to ![]() and get
and get ![]()
We apply the barycentric coordinates and get
![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Miquel point for isogonal conjugate points
Let triangle ![]() points
points ![]() and
and ![]() be given. Let point
be given. Let point ![]() be the isogonal conjugate of a point
be the isogonal conjugate of a point ![]() with respect to a triangle
with respect to a triangle ![]()
![]() Let
Let ![]() be the Miquel point of a complete quadrilateral
be the Miquel point of a complete quadrilateral ![]()
Prove that ![]() lies on the circumcircle of
lies on the circumcircle of ![]()
Proof
Point ![]() is the isogonal conjugate of a point
is the isogonal conjugate of a point ![]() with respect to a triangle
with respect to a triangle ![]() so point
so point ![]() is the isogonal conjugate of a point
is the isogonal conjugate of a point ![]() with respect to a triangle
with respect to a triangle ![]()
Points ![]() and
and ![]() lies on the same line, therefore
lies on the same line, therefore ![]()
![]() Point
Point ![]() lies on circles
lies on circles ![]() and
and ![]() spiral similarity centered at
spiral similarity centered at ![]() transform triangle
transform triangle ![]() to
to ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Point on circumcircle
Let triangle ![]() and points
and points ![]() and
and ![]() be given.
be given.
Let ![]()
Let lines ![]() and
and ![]() be the isogonals with respect to the angle
be the isogonals with respect to the angle ![]()
Let ![]() be an arbitrary point on
be an arbitrary point on ![]()
Prove that ![]() lies on
lies on ![]()
Simplified problem
Let ![]() and points
and points ![]() and
and ![]() be given,
be given, ![]()
Let lines ![]() and
and ![]() be the isogonals with respect to
be the isogonals with respect to ![]()
Prove that ![]()
Proof, Simplified problem
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
points ![]() are concyclic on
are concyclic on ![]()
Proof
Let points ![]() and
and ![]() be the isogonal conjugate of a points
be the isogonal conjugate of a points ![]() and
and ![]() with respect to a triangle
with respect to a triangle ![]()
It is known that ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() points
points ![]() are concyclic on
are concyclic on ![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Isogonal of line BC with respect to angle BAC
Let triangle ![]() be given,
be given, ![]()
Let lines ![]() and
and ![]() be the isogonals with respect to
be the isogonals with respect to ![]()
Prove that ![]() is tangent to
is tangent to ![]()
Proof
Let ![]() and
and ![]() be the circumcenter and the orthocenter of
be the circumcenter and the orthocenter of ![]() respectively.
respectively.
![]()
![]() is isogonal to
is isogonal to ![]() with respect to
with respect to ![]() is tangent to
is tangent to ![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Isogonal bijection lines and points
Let triangle ![]() and line
and line ![]() be given,
be given, ![]()
Define ![]() the point with property
the point with property ![]()
Prove that ![]() is equal the angle
is equal the angle ![]() between
between ![]() and
and ![]()
Proof
WLOG, the configuration is the same as shown on diagram, ![]() is the tangent to
is the tangent to ![]()
![]() is isogonal to
is isogonal to ![]() is isogonal to
is isogonal to ![]() with respect to
with respect to ![]()
![]() A bijection has been established between the set of lines parallel to a given one and the set of points of the circumcircle.
A bijection has been established between the set of lines parallel to a given one and the set of points of the circumcircle.
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Miquel point for two pare isogonal points
Let triangle ![]() and points
and points ![]() and
and ![]() be given.
be given.
Let points ![]() and
and ![]() be the isogonal conjugate of the points
be the isogonal conjugate of the points ![]() and
and ![]() with respect to
with respect to ![]() is the Miquel point of quadrilateral
is the Miquel point of quadrilateral ![]()
Prove that ![]()
Proof
Denote ![]()
Then ![]() is the Miquel point of quadrilateral
is the Miquel point of quadrilateral ![]()
Denote ![]()
Let ![]() be the point with property
be the point with property ![]()
WLOG, configuration is similar as shown in diagram.
![]() ( Isogonal_bijection_lines_and_points).
( Isogonal_bijection_lines_and_points).
![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Isogonic center’s conjugate point
Let triangle ![]() with isogonic center
with isogonic center ![]() or
or ![]() be given. Denote
be given. Denote ![]()
Let line ![]() be the axial symmetry of line
be the axial symmetry of line ![]() according to the sideline
according to the sideline ![]()
Define lines ![]() and
and ![]() similarly.
similarly.
Prove that the lines ![]() and
and ![]() are concurrent.
are concurrent.
Proof
Let ![]() be the incenter of
be the incenter of ![]()
![]() Let
Let ![]() is simmetric to
is simmetric to ![]() with respect
with respect ![]()
The diameter ![]() of
of ![]() lies on
lies on ![]()
Therefore ![]() is the isogonal conjugate of
is the isogonal conjugate of ![]() with respect to
with respect to ![]()
Similarly ![]() and
and ![]() are the isogonal conjugate of
are the isogonal conjugate of ![]() and
and ![]() so point
so point ![]() is the isogonal conjugate of point
is the isogonal conjugate of point ![]() with respect to
with respect to ![]()
The second diagram show construction in the case ![]() The proof is similar.
The proof is similar.
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Three pairs isogonal points
Let a triangle ![]() points
points ![]() and
and ![]() be given,
be given, ![]() Points
Points ![]() and
and ![]() are the isogonal conjugate of the points
are the isogonal conjugate of the points ![]() and
and ![]() respectively, with respect to
respectively, with respect to ![]()
Prove that ![]()
Proof
Denote ![]()
![]() We use isogonal properties and get
We use isogonal properties and get
![]() By applying the Law of Sines, we get
By applying the Law of Sines, we get ![]() Symilarly,
Symilarly, ![]() We multiply these equations and get
We multiply these equations and get
![]() vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Ratio for three pairs of isogonal points
Let a triangle ![]() points
points ![]() and
and ![]() be given,
be given, ![]()
Points ![]() and
and ![]() are the isogonal conjugate of the points
are the isogonal conjugate of the points ![]() and
and ![]() respectively, with respect to
respectively, with respect to ![]()
Denote ![]() and
and ![]() the circumradii of triangles
the circumradii of triangles ![]() and
and ![]() respectively.
respectively.
Prove that ![]()
Proof
Denote ![]()
![]() where
where ![]() is the area of the figure
is the area of the figure ![]()
![]() Similarly,
Similarly, ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() Similarly,
Similarly, ![]() It is known that
It is known that ![]() ( Three pairs isogonal points), therefore
( Three pairs isogonal points), therefore
![]() Comment: The main idea of the proof was found by Leonid Shatunov.
Comment: The main idea of the proof was found by Leonid Shatunov.
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss