Difference between revisions of "2019 AIME II Problems/Problem 15"
m (→Solution 4 (Clean)) |
Mathboy282 (talk | contribs) (→Solution 5) |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
To finish, <cmath>bc= \frac{(b\cos B)(c\cos C)}{\cos B\cos C}=\frac{16\cdot 21}{(2/\sqrt{35})(3/\sqrt{40})}=560\sqrt{14}.</cmath> | To finish, <cmath>bc= \frac{(b\cos B)(c\cos C)}{\cos B\cos C}=\frac{16\cdot 21}{(2/\sqrt{35})(3/\sqrt{40})}=560\sqrt{14}.</cmath> | ||
The requested sum is <math>\boxed{574}</math>. | The requested sum is <math>\boxed{574}</math>. | ||
| + | - crazyeyemoody907 | ||
| − | + | Remark: The proof that <math>a \cos A = PQ</math> can be found here: http://www.irmo.ie/5.Orthic_triangle.pdf | |
==Solution 2== | ==Solution 2== | ||
| Line 104: | Line 105: | ||
and the answer is <math>560 + 14 = \boxed{574}</math>. ~rocketsri | and the answer is <math>560 + 14 = \boxed{574}</math>. ~rocketsri | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Solution 5== | ||
| + | [[File:2019AIMEIIP15Solution.png|900px]] | ||
| + | '''mathboy282''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Video Solution by MOP 2024== | ||
| + | https://youtu.be/aYV09qIwTqs | ||
| + | |||
| + | ~r00tsOfUnity | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
Latest revision as of 02:11, 7 January 2024
Contents
Problem
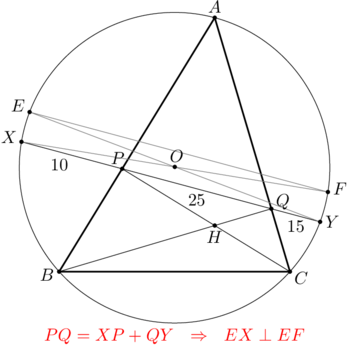
In acute triangle ![]() points
points ![]() and
and ![]() are the feet of the perpendiculars from
are the feet of the perpendiculars from ![]() to
to ![]() and from
and from ![]() to
to ![]() , respectively. Line
, respectively. Line ![]() intersects the circumcircle of
intersects the circumcircle of ![]() in two distinct points,
in two distinct points, ![]() and
and ![]() . Suppose
. Suppose ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() . The value of
. The value of ![]() can be written in the form
can be written in the form ![]() where
where ![]() and
and ![]() are positive integers, and
are positive integers, and ![]() is not divisible by the square of any prime. Find
is not divisible by the square of any prime. Find ![]() .
.
Diagram
![[asy] size(200); defaultpen(linewidth(0.4)+fontsize(10)); pen s = linewidth(0.8)+fontsize(8); pair A,B,C,P,Q,X,Y,O; O = origin; real theta = 32; A = dir(180+theta); B = dir(-theta); C = dir(75); Q = foot(B,A,C); P = foot(C,A,B); path c = circumcircle(A,B,C); X = IP(c, Q--(2*P-Q)); Y = IP(c, P--(2*Q-P)); draw(A--B--C--A, black+0.8); draw(c^^X--Y^^B--Q^^C--P); dot("$A$", A, SW); dot("$B$", B, SE); dot("$C$", C, N); dot("$P$", P, SW); dot("$Q$", Q, W); dot("$X$", X, SE); dot("$Y$", Y, NW); label("$25$", P--Q, SW); label("$15$", Q--Y, SW); label("$10$", X--P, SW); [/asy]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/0/b/9/0b96efb71a1d1aef4a0c2f0c402c8d9d0e29cee0.png)
Solution 1
First we have ![]() , and
, and ![]() by PoP. Similarly,
by PoP. Similarly, ![]() and dividing these each by
and dividing these each by ![]() gives
gives
![]() .
.
It is known that the sides of the orthic triangle are ![]() , and its angles are
, and its angles are ![]() ,
,![]() , and
, and ![]() . We thus have the three sides of the orthic triangle now.
Letting
. We thus have the three sides of the orthic triangle now.
Letting ![]() be the foot of the altitude from
be the foot of the altitude from ![]() , we have, in
, we have, in ![]() ,
,
![]()
![]() similarly, we get
similarly, we get
![]() To finish,
To finish, ![]() The requested sum is
The requested sum is ![]() .
- crazyeyemoody907
.
- crazyeyemoody907
Remark: The proof that ![]() can be found here: http://www.irmo.ie/5.Orthic_triangle.pdf
can be found here: http://www.irmo.ie/5.Orthic_triangle.pdf
Solution 2
Let ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() . Let
. Let ![]() . Then
. Then ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
By Power of a Point theorem,
![]() Thus
Thus ![]() . Then
. Then ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and
![]() Use the Law of Cosines in
Use the Law of Cosines in ![]() to get
to get ![]() , which rearranges to
, which rearranges to ![]() Upon simplification, this reduces to a linear equation in
Upon simplification, this reduces to a linear equation in ![]() , with solution
, with solution ![]() . Then
. Then ![]() So the final answer is
So the final answer is ![]()
By SpecialBeing2017
Solution 3
Let ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() . By Power of a Point,
. By Power of a Point,
![]() Points
Points ![]() and
and ![]() lie on the circle,
lie on the circle, ![]() , with diameter
, with diameter ![]() , and pow
, and pow![]() , so
, so ![]() Use Law of Cosines in
Use Law of Cosines in ![]() to get
to get ![]() ; since
; since ![]() , this simplifies as
, this simplifies as
![]() We get
We get ![]() and thus
and thus
![]() Therefore
Therefore ![]() . So the answer is
. So the answer is ![]()
By asr41
Solution 4 (Clean)
This solution is directly based of @CantonMathGuy's solution. We start off with a key claim.
Claim. ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
Proof.
Let ![]() and
and ![]() denote the reflections of the orthocenter over points
denote the reflections of the orthocenter over points ![]() and
and ![]() , respectively. Since
, respectively. Since ![]() and
and ![]() we have that
we have that ![]() is a rectangle. Then, since
is a rectangle. Then, since ![]() we obtain
we obtain ![]() (which directly follows from
(which directly follows from ![]() being cyclic); hence
being cyclic); hence ![]() , or
, or ![]() .
.
Similarly, we can obtain ![]() .
. ![]()
A direct result of this claim is that ![]() .
.
Thus, we can set ![]() and
and ![]() , then applying Power of a Point on
, then applying Power of a Point on ![]() we get
we get ![]() . Also, we can set
. Also, we can set ![]() and
and ![]() and once again applying Power of a Point (but this time to
and once again applying Power of a Point (but this time to ![]() ) we get
) we get
![]() .
.
Hence,
![]()
and the answer is ![]() . ~rocketsri
. ~rocketsri
Solution 5
Video Solution by MOP 2024
~r00tsOfUnity
See Also
| 2019 AIME II (Problems • Answer Key • Resources) | ||
| Preceded by Problem 14 |
Followed by Last Question | |
| 1 • 2 • 3 • 4 • 5 • 6 • 7 • 8 • 9 • 10 • 11 • 12 • 13 • 14 • 15 | ||
| All AIME Problems and Solutions | ||
The problems on this page are copyrighted by the Mathematical Association of America's American Mathematics Competitions.