Difference between revisions of "2021 AIME II Problems/Problem 8"
(→Solution 4 (Casework)) |
m |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 160: | Line 160: | ||
Our probability is then <math>\frac{176 + 28}{3 \cdot 2^7} = \frac{17}{32}</math>, so the answer is <math>17+32=\boxed{049}</math>. | Our probability is then <math>\frac{176 + 28}{3 \cdot 2^7} = \frac{17}{32}</math>, so the answer is <math>17+32=\boxed{049}</math>. | ||
| − | ==Solution 5 ( | + | ==Solution 5 (One-Variable Recursion and Casework)== |
Let <math>p(n)</math> be the probability that we are on the top when you get to the <math>n</math>th move, and <math>p(n-1)</math> and <math>p(n-2)</math> be the probability that you are on the top when you get to the <math>(n-1)</math>th move and <math>(n-2)</math>th move respectively. | Let <math>p(n)</math> be the probability that we are on the top when you get to the <math>n</math>th move, and <math>p(n-1)</math> and <math>p(n-2)</math> be the probability that you are on the top when you get to the <math>(n-1)</math>th move and <math>(n-2)</math>th move respectively. | ||
| Line 166: | Line 166: | ||
Now you can do some recursion, splitting up into cases: | Now you can do some recursion, splitting up into cases: | ||
| − | Case 1: You are not on the top for the <math>(n-1)</math>th move or the <math>(n-2)</math>th move. In this case, it is a <math>1-p(n-1)</math> chance that you were not on the top for the <math>(n-1)</math>th move, and a <math>1-p(n-2)</math> that you are not on the top for the <math>(n-2)</math>th move. This leads you to a <math>\frac{1}{2} | + | Case 1: You are not on the top for the <math>(n-1)</math>th move or the <math>(n-2)</math>th move. In this case, it is a <math>1-p(n-1)</math> chance that you were not on the top for the <math>(n-1)</math>th move, and a <math>1-p(n-2)</math> that you are not on the top for the <math>(n-2)</math>th move. This leads you to a <math>\frac{1}{2}\cdot(1-p(n-1))\cdot(1-p(n-2))</math> chance for the first case. (The <math>\frac12</math> is there because of the fact that you can go up and you can also stay on the bottom side, as you cannot return.) |
| − | Case 2: You are on the top for the <math>(n-1)</math>th move, but not on the top for the <math>(n-2)</math>th move. This leads you to a <math>p(n-1) | + | Case 2: You are on the top for the <math>(n-1)</math>th move, but not on the top for the <math>(n-2)</math>th move. This leads you to a <math>p(n-1)\cdot(1-p(n-2))</math> probability (no extra components because you cannot return). |
| − | Case 3: You are on top for both the <math>(n-1)</math>th move and the <math>(n-2)</math>th move. This leads to a probability of <math>\frac{1}{2} | + | Case 3: You are on top for both the <math>(n-1)</math>th move and the <math>(n-2)</math>th move. This leads to a probability of <math>\frac{1}{2}\cdot p(n-1)\cdot p(n-2)</math> (adding the extra <math>\frac12</math> because you can either stay on the top or go down. |
| − | As the 4th case requires you to go down then up, but you cannot retrace, there is no | + | As the 4th case requires you to go down then up, but you cannot retrace, there is no <math>4</math>th case. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | These cases, added up, lead you to <cmath>p(n)=\frac{1}{2}\cdot(1-p(n-1))(1-p(n-2))+p(n-1)(1-p(n-2))+\frac{1}{2}\cdot p(n-1)p(n-2).</cmath> This can be further simplified down by expanding and combining like terms to <cmath>p(n)=\frac{1+p(n-1)-p(n-2)}{2}.</cmath> | ||
| + | Then we must find <math>p(1)</math> and <math>p(2)</math>. p(1) is trivially <math>\frac{1}{3}</math>. You can find <math>p(2)</math> using basic probability techniques that is left as an exercise to the reader to get <math>\frac{2}{3}</math>. In the end, you plug in to get | ||
<cmath>p(1)=\frac{1}{3}, | <cmath>p(1)=\frac{1}{3}, | ||
P(2)=\frac{2}{3}, | P(2)=\frac{2}{3}, | ||
| Line 185: | Line 183: | ||
P(6)=\frac{11}{24}, | P(6)=\frac{11}{24}, | ||
P(7)=\frac{25}{48}, | P(7)=\frac{25}{48}, | ||
| − | P(8)=\boxed{\frac{17}{32}}</cmath> | + | P(8)=\boxed{\frac{17}{32}}.</cmath> |
| − | + | Therefore, the answer is <math>17+32=\boxed{049}</math>. | |
| − | <math>17+32=\boxed{049}</math> | ||
| − | + | ~dragoon | |
==Remark (Markov Chain)== | ==Remark (Markov Chain)== | ||
| Line 214: | Line 211: | ||
~Interstigation | ~Interstigation | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Video Solution== | ||
| + | https://youtu.be/4UjQhFEa1ms | ||
| + | |||
| + | ~MathProblemSolvingSkills.com | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
{{AIME box|year=2021|n=II|num-b=7|num-a=9}} | {{AIME box|year=2021|n=II|num-b=7|num-a=9}} | ||
{{MAA Notice}} | {{MAA Notice}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Intermediate Combinatorics Problems]] | ||
Latest revision as of 17:32, 23 January 2023
Contents
Problem
An ant makes a sequence of moves on a cube where a move consists of walking from one vertex to an adjacent vertex along an edge of the cube. Initially the ant is at a vertex of the bottom face of the cube and chooses one of the three adjacent vertices to move to as its first move. For all moves after the first move, the ant does not return to its previous vertex, but chooses to move to one of the other two adjacent vertices. All choices are selected at random so that each of the possible moves is equally likely. The probability that after exactly ![]() moves that ant is at a vertex of the top face on the cube is
moves that ant is at a vertex of the top face on the cube is ![]() , where
, where ![]() and
and ![]() are relatively prime positive integers. Find
are relatively prime positive integers. Find ![]()
Solution 1 (Four-Variable Recursion)
For all positive integers ![]() let
let
 be the number of ways to make a sequence of exactly
be the number of ways to make a sequence of exactly  moves, where the last move is from the bottom face to the bottom face.
moves, where the last move is from the bottom face to the bottom face.
 be the number of ways to make a sequence of exactly
be the number of ways to make a sequence of exactly  moves, where the last move is from the bottom face to the top face.
moves, where the last move is from the bottom face to the top face.
 be the number of ways to make a sequence of exactly
be the number of ways to make a sequence of exactly  moves, where the last move is from the top face to the bottom face.
moves, where the last move is from the top face to the bottom face.
 be the number of ways to make a sequence of exactly
be the number of ways to make a sequence of exactly  moves, where the last move is from the top face to the top face.
moves, where the last move is from the top face to the top face.
The base case occurs at ![]() from which
from which ![]()
Suppose the ant makes exactly ![]() moves for some
moves for some ![]() We perform casework on its last move:
We perform casework on its last move:
- If its last move is from the bottom face to the bottom face, then its next move has
 way to move from the bottom face to the bottom face.
way to move from the bottom face to the bottom face. way to move from the bottom face to the top face.
way to move from the bottom face to the top face.- If its last move is from the bottom face to the top face, then its next move has
 ways to move from the top face to the top face.
ways to move from the top face to the top face. - If its last move is from the top face to the bottom face, then its next move has
 ways to move from the bottom face to the bottom face.
ways to move from the bottom face to the bottom face. - If its last move is from the top face to the top face, then its next move has
 way to move from the top face to the bottom face.
way to move from the top face to the bottom face. way to move from the top face to the top face.
way to move from the top face to the top face.
Alternatively, this recursion argument is illustrated below, where each dashed arrow indicates ![]() way, and each solid arrow indicates
way, and each solid arrow indicates ![]() ways:
ways:
![[asy] /* Made by MRENTHUSIASM */ size(9cm); pair A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, X, Y; A=(0,6); B=(0,4); C=(0,2); D=(0,0); E=(10,6); F=(10,4); G=(10,2); H=(10,0); X=(-1,8); Y=(11,8); label("BB", A, (-2,0)); label("BT", B, (-2,0)); label("TB", C, (-2,0)); label("TT", D, (-2,0)); label("BB", E, (2,0)); label("BT", F, (2,0)); label("TB", G, (2,0)); label("TT", H, (2,0)); label("\textbf{The \boldmath{$k$}th Move}", shift(0.3,0)*X); label("\textbf{The \boldmath{$(k+1)$}th Move}", shift(-0.3,-0.085)*Y); draw(A--E,0.8+black+dashed,EndArrow); draw(A--F,0.8+black+dashed,EndArrow); draw(B--H,0.8+black,EndArrow); draw(C--E,0.8+black,EndArrow); draw(D--G,0.8+black+dashed,EndArrow); draw(D--H,0.8+black+dashed,EndArrow); dot(A^^B^^C^^D^^E^^F^^G^^H, 5+black); [/asy]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/f/d/0/fd0afc8df31f7cd55dacb05b9c7f12a9eb193230.png) Therefore, we have the following relationships:
Therefore, we have the following relationships:
 Using these equations, we recursively fill out the table below:
Using these equations, we recursively fill out the table below:
![\[\begin{array}{c||c|c|c|c|c|c|c|c} \hspace{7mm}&\hspace{6.5mm}&\hspace{6.5mm}&\hspace{6.75mm}&\hspace{6.75mm}&\hspace{6.75mm}&\hspace{6.75mm}&& \\ [-2.5ex] \boldsymbol{k} & \boldsymbol{1} & \boldsymbol{2} & \boldsymbol{3} & \boldsymbol{4} & \boldsymbol{5} & \boldsymbol{6} & \boldsymbol{7} & \boldsymbol{8} \\ \hline \hline &&&&&&&& \\ [-2.25ex] \boldsymbol{N(k,\mathrm{BB})} &2&2&2&6&18&38&66&118 \\ \hline &&&&&&&& \\ [-2.25ex] \boldsymbol{N(k,\mathrm{BT})} &1&2&2&2&6&18&38&66 \\ \hline &&&&&&&& \\ [-2.25ex] \boldsymbol{N(k,\mathrm{TB})} &0&0&2&6&10&14&26&62 \\ \hline &&&&&&&& \\ [-2.25ex] \boldsymbol{N(k,\mathrm{TT})} &0&2&6&10&14&26&62&138 \\ \hline \hline &&&&&&&& \\ [-2.25ex] \textbf{Total}&\boldsymbol{3}&\boldsymbol{6}&\boldsymbol{12}&\boldsymbol{24}&\boldsymbol{48}&\boldsymbol{96}&\boldsymbol{192}&\boldsymbol{384} \end{array}\]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/3/0/c/30cf8611e8e260b65e3a4a055d23b92809e21790.png) By the Multiplication Principle, there are
By the Multiplication Principle, there are ![]() ways to make exactly
ways to make exactly ![]() moves. So, we must get
moves. So, we must get ![]() for all values of
for all values of ![]()
Finally, the requested probability is ![]() from which the answer is
from which the answer is ![]()
~Arcticturn ~MRENTHUSIASM
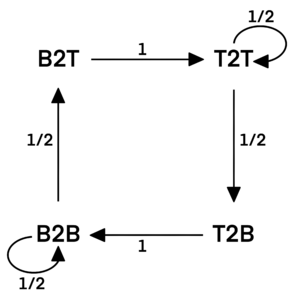
Solution 2 (Markov Chain and Dynamic Programming)
Let the state from bottom to top be ![]() from top to top be
from top to top be ![]() from top to bottom be
from top to bottom be ![]() and from bottom to bottom be
and from bottom to bottom be ![]() We can draw the following State Transition Diagram with Markov Chain. The numbers on the transition arc are the transition probabilities.
We can draw the following State Transition Diagram with Markov Chain. The numbers on the transition arc are the transition probabilities.
The probabilities of being in a state after ![]() steps and after
steps and after ![]() steps has the following relationships:
steps has the following relationships:
 Those probabilities are calculated by Dynamic Programming in the following table:
Those probabilities are calculated by Dynamic Programming in the following table:
![\[\begin{array}{c|cccc} & & & & \\ [-2ex] n & B2T(n) & T2T(n) & T2B(n) & B2B(n) \\ [1ex] \hline & & & & \\ [-1ex] 1 & \frac13 & 0 & 0 & \frac23\\ & & & & \\ 2 & \frac23 \cdot \frac12 = \frac13 & \frac13 & 0 & \frac23 \cdot \frac12 = \frac13 \\ & & & & \\ 3 & \frac13 \cdot \frac12 = \frac16 & \frac13 + \frac13 \cdot \frac12 = \frac12 & \frac13 \cdot \frac12 = \frac16 & \frac13 \cdot \frac12 = \frac16 \\ & & & & \\ 4 & \frac16 \cdot \frac12 = \frac{1}{12} & \frac16 + \frac12 \cdot \frac12 = \frac{5}{12} & \frac12 \cdot \frac12 = \frac14 & \frac16 + \frac16 \cdot \frac12 = \frac14 \\ & & & & \\ 5 & \frac14 \cdot \frac12 = \frac18 & \frac{1}{12} + \frac{5}{12} \cdot \frac{1}{2} = \frac{7}{24} & \frac{5}{12} \cdot \frac12 = \frac{5}{24} & \frac14 + \frac14 \cdot \frac12 = \frac38 \\ & & & & \\ 6 & \frac38 \cdot \frac12 = \frac{3}{16} & \frac18 + \frac{7}{24} \cdot \frac12 = \frac{13}{48} & \frac{7}{24} \cdot \frac12 = \frac{7}{48} & \frac{5}{24} + \frac38 \cdot \frac12 = \frac{19}{48} \\ & & & & \\ 7 & \frac{19}{48} \cdot \frac12 = \frac{19}{96}& \frac{3}{16} + \frac{13}{48} \cdot \frac{1}{2} = \frac{31}{96}& \frac{13}{48} \cdot \frac{1}{2} = \frac{13}{96} & \frac{7}{48} + \frac{19}{48} \cdot \frac12 = \frac{11}{32}\\ & & & & \\ 8 & \frac{11}{32} \cdot \frac{1}{2} = \frac{11}{64} & \frac{19}{96} + \frac{31}{96} \cdot \frac12 = \frac{23}{64} & \frac{31}{96} \cdot \frac12 = \frac{31}{192} & \frac{13}{96} + \frac{11}{32} \cdot \frac12 = \frac{59}{192} \\ [1ex] \end{array}\]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/5/7/5/575e180d64eb37431e0ff565ae56a1e07cce0f5a.png) Finally, the requested probability is
Finally, the requested probability is ![]() from which the answer is
from which the answer is ![]()
Solution 3 (One-Variable Recursion)
Note that we don't care which exact vertex the ant is located at, just which level (either top face or bottom face).
Consider the ant to be on any of the two levels and having moved at least one move. Define ![]() to be the probability that after
to be the probability that after ![]() moves, the ant ends up on the level it started on.
moves, the ant ends up on the level it started on.
On the first move, the ant can stay on the bottom level with ![]() chance and
chance and ![]() moves left. Or, it can move to the top level with
moves left. Or, it can move to the top level with ![]() chance and
chance and ![]() moves left (it has to spend another on the top as it can not return immediately). So the requested probability is
moves left (it has to spend another on the top as it can not return immediately). So the requested probability is ![]() .
.
Consider when the ant has ![]() moves left (and it's not the ant's first move). It can either stay on its current level with
moves left (and it's not the ant's first move). It can either stay on its current level with ![]() chance and
chance and ![]() moves left, or travel to the opposite level with
moves left, or travel to the opposite level with ![]() chance, then move to another vertex on the opposite level, to have
chance, then move to another vertex on the opposite level, to have ![]() moves left. Thus we obtain the recurrence
moves left. Thus we obtain the recurrence
![]()
Computing ![]() with the starting conditions
with the starting conditions ![]() and
and ![]() , we obtain
, we obtain ![]() and
and ![]() . Hence
. Hence ![]() as desired;
as desired; ![]() .
.
~polarity
Solution 4 (Casework)
On each move, we can either stay on the level we previously were (stay on the bottom/top) or switch levels (go from top to bottom and vise versa). Since we start on the bottom, ending on the top means that we will have to switch an odd number of times; since we cannot switch twice in a row, over an eight-move period we can either make one or three switches. Furthermore, once we switch to a level we can choose one of two directions of traveling on that level: clockwise or counterclockwise (since we can't go back to our previous move, our first move on the level after switching determines our direction).
- Case 1: one switch. Our one switch can either happen at the start/end of our moves, or in the middle. There are
 ways to do this, outlined below.
ways to do this, outlined below.
- Subcase 1: switch happens at ends. If our first move is a switch, then there are two ways to determine the direction we travel along the top layer. Multiply by
 to count for symmetry (last move is a switch) so this case yields
to count for symmetry (last move is a switch) so this case yields  possibilities.
possibilities. - Subcase 2: switch happens in the middle. There are six places for the switch to happen; the switch breaks the sequences of moves into two chains, with each having
 ways to choose their direction of travel. This case yields
ways to choose their direction of travel. This case yields  possibilities.
possibilities.
- Subcase 1: switch happens at ends. If our first move is a switch, then there are two ways to determine the direction we travel along the top layer. Multiply by
- Case 2: three switches. Either two, one, or none of our switches occur at the start/end of our moves. There are
 ways to do this, outlined below. (Keep in mind we can't have two switches in a row.)
ways to do this, outlined below. (Keep in mind we can't have two switches in a row.)
- Subcase 1: start and end with a switch. Since our third switch can't be in moves
 or
or  , there are four ways to place our switch, breaking our sequence into two chains. This case yields
, there are four ways to place our switch, breaking our sequence into two chains. This case yields  possibilities.
possibilities. - Subcase 2: one of our switches is at the start/end. WLOG our first move is a switch; moves
 and
and  cannot be switches. We can choose
cannot be switches. We can choose  from any of the remaining
from any of the remaining  moves to be switches, but we have to subtract the
moves to be switches, but we have to subtract the  illegal cases where the two switches are in a row (3-4, 4-5, 5-6, 6-7). These three switches break our sequence into three chains; accounting for symmetry this case yields
illegal cases where the two switches are in a row (3-4, 4-5, 5-6, 6-7). These three switches break our sequence into three chains; accounting for symmetry this case yields  possibilities.
possibilities. - Subcase 3: all our switches are in the middle. We choose
 from any of the
from any of the  middle moves to be our switches, but have to subtract the cases where at least two of them are in a row. If at least two switches are in a row, there are five places for the group of
middle moves to be our switches, but have to subtract the cases where at least two of them are in a row. If at least two switches are in a row, there are five places for the group of  and four places for the third switch; however this overcounts the case where all three are in a row, which has
and four places for the third switch; however this overcounts the case where all three are in a row, which has  possibilities. These three switches break our sequence into four chains, so this case yields
possibilities. These three switches break our sequence into four chains, so this case yields  possibilities.
possibilities.
- Subcase 1: start and end with a switch. Since our third switch can't be in moves
Our probability is then ![]() , so the answer is
, so the answer is ![]() .
.
Solution 5 (One-Variable Recursion and Casework)
Let ![]() be the probability that we are on the top when you get to the
be the probability that we are on the top when you get to the ![]() th move, and
th move, and ![]() and
and ![]() be the probability that you are on the top when you get to the
be the probability that you are on the top when you get to the ![]() th move and
th move and ![]() th move respectively.
th move respectively.
Now you can do some recursion, splitting up into cases:
Case 1: You are not on the top for the ![]() th move or the
th move or the ![]() th move. In this case, it is a
th move. In this case, it is a ![]() chance that you were not on the top for the
chance that you were not on the top for the ![]() th move, and a
th move, and a ![]() that you are not on the top for the
that you are not on the top for the ![]() th move. This leads you to a
th move. This leads you to a ![]() chance for the first case. (The
chance for the first case. (The ![]() is there because of the fact that you can go up and you can also stay on the bottom side, as you cannot return.)
is there because of the fact that you can go up and you can also stay on the bottom side, as you cannot return.)
Case 2: You are on the top for the ![]() th move, but not on the top for the
th move, but not on the top for the ![]() th move. This leads you to a
th move. This leads you to a ![]() probability (no extra components because you cannot return).
probability (no extra components because you cannot return).
Case 3: You are on top for both the ![]() th move and the
th move and the ![]() th move. This leads to a probability of
th move. This leads to a probability of ![]() (adding the extra
(adding the extra ![]() because you can either stay on the top or go down.
because you can either stay on the top or go down.
As the 4th case requires you to go down then up, but you cannot retrace, there is no ![]() th case.
th case.
These cases, added up, lead you to ![]() This can be further simplified down by expanding and combining like terms to
This can be further simplified down by expanding and combining like terms to ![]() Then we must find
Then we must find ![]() and
and ![]() . p(1) is trivially
. p(1) is trivially ![]() . You can find
. You can find ![]() using basic probability techniques that is left as an exercise to the reader to get
using basic probability techniques that is left as an exercise to the reader to get ![]() . In the end, you plug in to get
. In the end, you plug in to get
![]() Therefore, the answer is
Therefore, the answer is ![]() .
.
~dragoon
Remark (Markov Chain)
This problem is similar to the following problems:
They can all be solved by Markov Chain and Dynamic Programming.
Let ![]() be the probability that state
be the probability that state ![]() transits to state
transits to state ![]() on the next step, and
on the next step, and ![]() be the probability of being in state
be the probability of being in state ![]() . It follows that
. It follows that ![]() is the sum of the products of
is the sum of the products of ![]() and
and ![]() of all the previous state
of all the previous state ![]() :
: ![]() This formula can also be applied to solve 2019 AMC10B Problem 22.
This formula can also be applied to solve 2019 AMC10B Problem 22.
Video Solution
~Interstigation
Video Solution
~MathProblemSolvingSkills.com
See Also
| 2021 AIME II (Problems • Answer Key • Resources) | ||
| Preceded by Problem 7 |
Followed by Problem 9 | |
| 1 • 2 • 3 • 4 • 5 • 6 • 7 • 8 • 9 • 10 • 11 • 12 • 13 • 14 • 15 | ||
| All AIME Problems and Solutions | ||
The problems on this page are copyrighted by the Mathematical Association of America's American Mathematics Competitions. 





 possibilities.
possibilities. possibilities.
possibilities.



