Difference between revisions of "2019 AIME II Problems/Problem 11"
(→Solution (Inversion simplified)) |
Faliure167 (talk | contribs) (→Solution 3 (Death By Trig Bash)) |
||
| (32 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) | |||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
label("$C$",C,dir(-75)); | label("$C$",C,dir(-75)); | ||
dot((2.68,2.25)); | dot((2.68,2.25)); | ||
| − | label("$K$",(2.68,2.25), | + | label("$K$",(2.68,2.25),2*down); |
| − | label("$\omega_1$",(- | + | label("$\omega_1$",(-4.5,1)); |
| − | label("$\omega_2$",( | + | label("$\omega_2$",(12.75,6)); |
label("$7$",(A+B)/2,dir(140)); | label("$7$",(A+B)/2,dir(140)); | ||
label("$8$",(B+C)/2,dir(-90)); | label("$8$",(B+C)/2,dir(-90)); | ||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
| − | Note that from the tangency condition that the supplement of <math>\angle CAB</math> with respects to lines <math>AB</math> and <math>AC</math> are equal to <math>\angle AKB</math> and <math>\angle AKC</math>, respectively, so from tangent-chord, <cmath>\angle AKC=\angle AKB=180^{\circ}-\angle BAC</cmath> Also note that <math>\angle ABK=\angle KAC</math>, so <math>\triangle AKB\sim \triangle CKA</math>. Using similarity ratios, we can easily find <cmath>AK^2=BK*KC</cmath> However, since <math>AB=7</math> and <math>CA=9</math>, we can use similarity ratios to get <cmath>BK=\frac{7}{9}AK, CK=\frac{9}{7}AK</cmath> | + | Note that from the tangency condition that the supplement of <math>\angle CAB</math> with respects to lines <math>AB</math> and <math>AC</math> are equal to <math>\angle AKB</math> and <math>\angle AKC</math>, respectively, so from tangent-chord, <cmath>\angle AKC=\angle AKB=180^{\circ}-\angle BAC</cmath> Also note that <math>\angle ABK=\angle KAC</math><math>^{(*)}</math>, so <math>\triangle AKB\sim \triangle CKA</math>. Using similarity ratios, we can easily find <cmath>AK^2=BK*KC</cmath> However, since <math>AB=7</math> and <math>CA=9</math>, we can use similarity ratios to get <cmath>BK=\frac{7}{9}AK, CK=\frac{9}{7}AK</cmath> |
| − | *Now we use Law of Cosines on <math>\triangle AKB</math>: From reverse Law of Cosines, <math>\cos{\angle BAC}=\frac{11}{21}\implies \cos{(180^{\circ}-\angle BAC)}=-\frac{11}{21}</math> | + | *Now we use Law of Cosines on <math>\triangle AKB</math>: From reverse Law of Cosines, <math>\cos{\angle BAC}=\frac{11}{21}\implies \cos{(180^{\circ}-\angle BAC)}=\angle AKB=-\frac{11}{21}</math> |
| − | + | Giving us <cmath>AK^2+\frac{49}{81}AK^2+\frac{22}{27}AK^2=49</cmath> <cmath>\implies \frac{196}{81}AK^2=49</cmath> <cmath>AK=\frac{9}{2}</cmath> so our answer is <math>9+2=\boxed{011}</math>. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <math>^{(*)}</math> Let <math>O</math> be the center of <math>\omega_1</math>. Then <math>\angle KAC = 90 - \angle OAK = 90 - \frac{1}{2}(180 - \angle AOK) = \frac{\angle AOK}{2} = \angle ABK</math>. Thus, <math>\angle ABK = \angle KAC</math> | |
| + | |||
| + | -franchester; <math>^{(*)}</math> by firebolt360 | ||
| + | ===Supplement=== | ||
| + | *In order to get to the Law of Cosines first, we first apply the LOC to <math>\triangle{ABC},</math> obtaining <math>\angle{BAC}.</math> | ||
| + | *We angle chase before applying the law of cosines to <math>\angle{AKB}.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Note that <math>\angle{ABK}=\angle{KAC}</math> and <math>\angle{KCA}=\angle{KAB}</math> from tangent-chord. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Thus, <math>\angle{AKC}=\angle{AKB}=180^{\circ}-(\angle{ABK}+\angle{KAB}).</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | However from our tangent chord, note that: | ||
| + | <cmath>\angle{ABK}+\angle{KAB}=\angle{KAC}+\angle{KAB}=\angle{BAC}.</cmath> | ||
| + | Thus, <math>\angle{AKB}=180^\circ-\angle{BAC}.</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *As an alternative approach, note that the sum of the angles in quadrilateral <math>ABKC</math> is <math>360^{\circ}</math> and we can find <math>\angle{AKB}=\frac12</math> of convex <math>\angle{BKC},</math> which is just: | ||
| + | <cmath>\frac12 \left(360^{\circ}-2(\angle{KAB}+\angle{KBA}\right) = 180^\circ - \angle{BAC}.</cmath> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ~mathboy282 | ||
==Solution 2 (Inversion)== | ==Solution 2 (Inversion)== | ||
Consider an inversion with center <math>A</math> and radius <math>r=AK</math>. Then, we have <math>AB\cdot AB^*=AK^2</math>, or <math>AB^*=\frac{AK^2}{7}</math>. Similarly, <math>AC^*=\frac{AK^2}{9}</math>. Notice that <math>AB^*KC^*</math> is a parallelogram, since <math>\omega_1</math> and <math>\omega_2</math> are tangent to <math>AC</math> and <math>AB</math>, respectively. Thus, <math>AC^*=B^*K</math>. Now, we get that | Consider an inversion with center <math>A</math> and radius <math>r=AK</math>. Then, we have <math>AB\cdot AB^*=AK^2</math>, or <math>AB^*=\frac{AK^2}{7}</math>. Similarly, <math>AC^*=\frac{AK^2}{9}</math>. Notice that <math>AB^*KC^*</math> is a parallelogram, since <math>\omega_1</math> and <math>\omega_2</math> are tangent to <math>AC</math> and <math>AB</math>, respectively. Thus, <math>AC^*=B^*K</math>. Now, we get that | ||
| − | <cmath>\cos(\angle AB^*K)= | + | <cmath>\cos(\angle AB^*K)=\cos(180-\angle BAC)=-\frac{11}{21}</cmath> |
so by Law of Cosines on <math>\triangle AB^*K</math> we have | so by Law of Cosines on <math>\triangle AB^*K</math> we have | ||
<cmath>(AK)^2=(AB^*)2+(B^*K)^2-2\cdot AB^*\cdot B^*K \cdot \cos(\angle AB^*K)</cmath> | <cmath>(AK)^2=(AB^*)2+(B^*K)^2-2\cdot AB^*\cdot B^*K \cdot \cos(\angle AB^*K)</cmath> | ||
| Line 47: | Line 63: | ||
== Solution 3 (Death By Trig Bash) == | == Solution 3 (Death By Trig Bash) == | ||
| − | + | Let the centers of the circles be <math>O_{1}</math> and <math>O_{2}</math> where the <math>O_{1}</math> has the side length <math>7</math> contained in the circle. Now let <math>\angle BAC =x.</math> This implies <cmath>\angle O_{1}AB = \angle O_{1}BA = \angle O_{2}AC = \angle O_{2}CA = 90^{\circ}-x</cmath> by the angle by by tangent. Then we also know that <cmath>\angle AO_{1}B = \angle AO_{2}C = 2x</cmath> Now we first find <math>\cos x.</math> We use law of cosines on <math>\bigtriangleup ABC</math> to obtain <cmath>64 = 81 + 48 - 2 \cdot 9 \cdot 7 \cdot \cos{x}</cmath> <cmath>\implies \cos{x} =\frac{11}{21}</cmath> <cmath>\implies \sin{x} =\frac{8\sqrt{5}}{21}</cmath> Then applying law of sines on <math>\bigtriangleup AO_{1}B</math> we obtain <cmath>\frac{7}{\sin{2x}} =\frac{O_{1}B}{\sin{90^{\circ}-x}}</cmath> <cmath>\implies\frac{7}{2\sin{x}\cos{x}} =\frac{O_{1}B}{\cos{x}}</cmath> <cmath>\implies O_{1}B = O_{1}A=\frac{147}{16\sqrt{5}}</cmath> Using similar logic we obtain <math>O_{2}A =\frac{189}{16\sqrt{5}}.</math> | |
| − | Now we know that <math>\angle O_{1}AO_{2}=180^{\circ}-x.</math> Thus using law of cosines on <math>\bigtriangleup O_{1}AO_{2}</math> yields <cmath>O_{1}O_{2} =\sqrt{\left(\frac{147}{16\sqrt{5}}\right)^2+\left(\frac{189}{16\sqrt{5}}\right)^2-2\:\cdot \left(\frac{147}{16\sqrt{5}}\right)\cdot \frac{189}{16\sqrt{5}}\cdot -\frac{11}{21}}</cmath> While this does look daunting we can write the above expression as <cmath>\sqrt{\left(\frac{189+147}{16\sqrt{5}}\right)^2 - 2\cdot \left(\frac{147}{16\sqrt{5}}\right)\cdot \frac{189}{16\sqrt{5}}\cdot \frac{10}{21}} =\sqrt{\left(\frac{168}{8\sqrt{5}}\right)^2 - \left(\frac{7 \cdot 189 \cdot 5}{8 \sqrt{5} \cdot 8\sqrt{5}}\right)}</cmath> Then factoring yields <cmath>\sqrt{\frac{21^2(8^2-15)}{(8\sqrt{5})^2}} =\frac{147}{8\sqrt{5}}</cmath> The area <cmath>[O_{1}AO_{2}] =\frac{1}{2} \cdot\frac{147}{16\sqrt{5}} \cdot\frac{189}{16\sqrt{5}} \cdot \sin(180^{\circ}-x) =\frac{1}{2} \cdot\frac{147}{16\sqrt{5}} \cdot\frac{189}{16\sqrt{5}} \cdot\frac{8\sqrt{5}}{21}</cmath> Now <math>AK</math> is twice the length of the altitude of <math>\bigtriangleup O_{1}AO_{2}</math> so we let the altitude be <math>h</math> and we have <cmath>\frac{1}{2} \cdot h \cdot\frac{147 | + | Now we know that <math>\angle O_{1}AO_{2}=180^{\circ}-x.</math> Thus using law of cosines on <math>\bigtriangleup O_{1}AO_{2}</math> yields <cmath>O_{1}O_{2} =\sqrt{\left(\frac{147}{16\sqrt{5}}\right)^2+\left(\frac{189}{16\sqrt{5}}\right)^2-2\:\cdot \left(\frac{147}{16\sqrt{5}}\right)\cdot \frac{189}{16\sqrt{5}}\cdot -\frac{11}{21}}</cmath> While this does look daunting we can write the above expression as <cmath>\sqrt{\left(\frac{189+147}{16\sqrt{5}}\right)^2 - 2\cdot \left(\frac{147}{16\sqrt{5}}\right)\cdot \frac{189}{16\sqrt{5}}\cdot \frac{10}{21}} =\sqrt{\left(\frac{168}{8\sqrt{5}}\right)^2 - \left(\frac{7 \cdot 189 \cdot 5}{8 \sqrt{5} \cdot 8\sqrt{5}}\right)}</cmath> Then factoring yields <cmath>\sqrt{\frac{21^2(8^2-15)}{(8\sqrt{5})^2}} =\frac{147}{8\sqrt{5}}</cmath> The area <cmath>[O_{1}AO_{2}] =\frac{1}{2} \cdot\frac{147}{16\sqrt{5}} \cdot\frac{189}{16\sqrt{5}} \cdot \sin(180^{\circ}-x) =\frac{1}{2} \cdot\frac{147}{16\sqrt{5}} \cdot\frac{189}{16\sqrt{5}} \cdot\frac{8\sqrt{5}}{21}</cmath> Now <math>AK</math> is twice the length of the altitude of <math>\bigtriangleup O_{1}AO_{2}</math> so we let the altitude be <math>h</math> and we have <cmath>\frac{1}{2} \cdot h \cdot\frac{147}{8\sqrt{5}} =\frac{1}{2} \cdot\frac{147}{16\sqrt{5}} \cdot\frac{189}{16\sqrt{5}} \cdot\frac{8\sqrt{5}}{21}</cmath> <cmath>\implies h =\frac{9}{4}</cmath> Thus our desired length is <math>\frac{9}{2} \implies m+n = \boxed{11}.</math> |
| + | |||
| + | -minor edits by faliure167 | ||
==Solution 4 (Video)== | ==Solution 4 (Video)== | ||
| Line 60: | Line 78: | ||
<cmath>AK = \frac{AM'}{2} = \frac{AC\cdot AB}{2AM} = \frac{7\cdot 9}{2\sqrt{\frac{9^2\cdot 4 + 7^2\cdot 4 - 4^2\cdot 8}{8}}} = \frac{7\cdot 9}{2\sqrt{49}} = \frac{9}{2}\implies m + n = \boxed{11}.</cmath> | <cmath>AK = \frac{AM'}{2} = \frac{AC\cdot AB}{2AM} = \frac{7\cdot 9}{2\sqrt{\frac{9^2\cdot 4 + 7^2\cdot 4 - 4^2\cdot 8}{8}}} = \frac{7\cdot 9}{2\sqrt{49}} = \frac{9}{2}\implies m + n = \boxed{11}.</cmath> | ||
| − | ==Solution | + | ==Solution 6 (Inversion simplified)== |
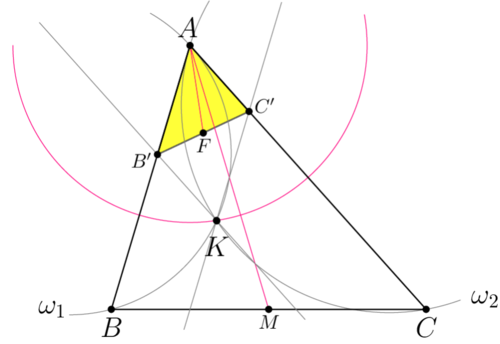
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:AIME-II-2019-11.png|500px|right]] |
| − | The median of <math>\triangle ABC</math> is <math>AM = \sqrt{\frac {AB^2 + AC^2 }{2} – \frac{BC^2}{4}} = 7 | + | The median of <math>\triangle ABC</math> is <math>AM = \sqrt{\frac {AB^2 + AC^2 }{2} – \frac{BC^2}{4}} = 7</math> (via Stewart's Theorem). |
Consider an inversion with center <math>A</math> and radius <math>AK</math> (inversion with respect the red circle). | Consider an inversion with center <math>A</math> and radius <math>AK</math> (inversion with respect the red circle). | ||
| Line 69: | Line 87: | ||
Image of line <math>AB</math> is line <math>AB, B'</math> lies on this line. | Image of line <math>AB</math> is line <math>AB, B'</math> lies on this line. | ||
| − | Image of <math>\omega_2</math> is line <math>KC'||AB</math> (circle <math>\omega_2</math> passes through K, C and is tangent to the line <math>AB</math> at point <math>A.</math> Diagram shows | + | Image of <math>\omega_2</math> is line <math>KC'||AB</math> (circle <math>\omega_2</math> passes through K, C and is tangent to the line <math>AB</math> at point <math>A.</math> Diagram shows circle and its image using same color). |
Similarly, <math>AC||B'K (B'K</math> is the image of the circle <math>\omega_1</math>). | Similarly, <math>AC||B'K (B'K</math> is the image of the circle <math>\omega_1</math>). | ||
| Line 77: | Line 95: | ||
So median <cmath>AF = k AM \implies \frac {AK}{2} = AM \cdot k = 7\cdot \frac{AK^2}{7\cdot 9} \implies AK = \frac{9}{2}.</cmath> | So median <cmath>AF = k AM \implies \frac {AK}{2} = AM \cdot k = 7\cdot \frac{AK^2}{7\cdot 9} \implies AK = \frac{9}{2}.</cmath> | ||
| − | + | '''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | |
| + | |||
| + | == Solution 7 (Heavy Bash) == | ||
| + | We start by assigning coordinates to point <math>A</math>, labeling it <math>(0,0)</math> and point <math>B</math> at <math>(7,0)</math>, and letting point <math>C</math> be above the <math>x</math>-axis. Through an application of the Pythagorean Theorem and dropping an altitude to side <math>AB</math>, it is easy to see that <math>C</math> has coordinates <math>(33/7, 24\sqrt{5}/7)</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Let <math>O1</math> be the center of circle <math>\omega_1</math> and <math>O2</math> be the center of circle <math>\omega_2</math>. Since circle <math>\omega_1</math> contains both points <math>A</math> and <math>B</math>, <math>O1</math> must lie on the perpendicular bisector of line <math>AB</math>, and similarly <math>O2</math> must lie on the perpendicular bisector of line <math>AC</math>. Through some calculations, we find that the perpendicular bisector of <math>AB</math> has equation <math>x = 3.5</math>, and the perpendicular bisector of <math>AC</math> has equation <math>y = {-11\sqrt{5}/40 \cdot x} + 189\sqrt{5}/80</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Since circle <math>\omega_1</math> is tangent to line <math>AC</math> at <math>A</math>, its radius must be perpendicular to <math>AC</math> at <math>A</math>. | ||
| + | Therefore, the radius has equation <math>y = {{-11\cdot\sqrt{5}/40} \cdot x}</math>. Substituting the <math>x</math>-coordinate of <math>O1</math> into this, we find the y-coordinate of <math>O1 = {{-11 \cdot \sqrt{5}/40} \cdot 7/2} = {-77 \cdot \sqrt{5}/80}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Similarly, since circle <math>\omega_2</math> is tangent to line <math>AB</math> at <math>A</math>, its radius must be perpendicular to <math>AB</math> at <math>A</math>. Therefore, the radius has equation <math>x = 0</math> and combining with the previous result for <math>O2</math> we get that the coordinates of <math>O2</math> are <math>(0, 189\sqrt{5}/80)</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | We now find the slope of <math>O1O2</math>, the line joining the centers of circles <math>\omega_1</math> and <math>\omega_2</math>, which turns out to be <math>{({266 \cdot \sqrt{5} / 80}) \cdot -2/7} = {-19 \cdot \sqrt{5}/20}</math>. Since the <math>y</math>-intercept of that line is at <math>O2(0,189\sqrt{5}/80)</math>, the equation is <math>y = {{-19 \cdot \sqrt{5}/20} \cdot x} + {189 \cdot \sqrt{5}/80}</math>. Since circles <math>\omega_1</math> and <math>\omega_2</math> intersect at points <math>A</math> and <math>K</math>, line <math>AK</math> is the radical axis of those circles, and since the radical axis is always perpendicular to the line joining the centers of the circles, <math>AK</math> has slope <math>{4 \cdot \sqrt{5}/19}</math>. Since point <math>A</math> is <math>(0,0)</math>, this line has a <math>y</math>-intercept of <math>0</math>, so it has equation <math>y</math> = <math>{{4 \cdot \sqrt{5}/19} \cdot x}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | We set <math>{{4 \cdot \sqrt{5}/19} \cdot x} = {{-19 \cdot \sqrt{5}/20} \cdot x} + {189 \cdot \sqrt{5}/80}</math> in order to find the intersection <math>I</math> of the radical axis <math>AK</math> and <math>O1O2</math>. Through some moderate bashing, we find that the intersection point is <math>I(57/28, {3 \cdot \sqrt{5}/7})</math>. We know that either intersection point of two circles is the same distance from the intersection of radical axis and line joining the centers of those circles, so reflecting <math>A</math> over <math>I</math> yields <math>K</math> and <math>AK</math> = <math>2AI</math> = (This is the most tedious part of the bash) <math>{2 \cdot \sqrt{(57/28)^2 + ({3 \cdot \sqrt{5}/7)^2)}}} = {2 \cdot \sqrt{3969/784}} = {2 \cdot 63/28} = {2 \cdot 9/4} = 9/2</math>. Therefore the answer is <math>9 + 2 = \boxed{011}.</math> | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
Latest revision as of 18:52, 28 January 2024
Contents
Problem
Triangle ![]() has side lengths
has side lengths ![]() and
and ![]() Circle
Circle ![]() passes through
passes through ![]() and is tangent to line
and is tangent to line ![]() at
at ![]() Circle
Circle ![]() passes through
passes through ![]() and is tangent to line
and is tangent to line ![]() at
at ![]() Let
Let ![]() be the intersection of circles
be the intersection of circles ![]() and
and ![]() not equal to
not equal to ![]() Then
Then ![]() where
where ![]() and
and ![]() are relatively prime positive integers. Find
are relatively prime positive integers. Find ![]()
Solution 1
![[asy] unitsize(20); pair B = (0,0); pair A = (2,sqrt(45)); pair C = (8,0); draw(circumcircle(A,B,(-17/8,0)),rgb(.7,.7,.7)); draw(circumcircle(A,C,(49/8,0)),rgb(.7,.7,.7)); draw(B--A--C--cycle); label("$A$",A,dir(105)); label("$B$",B,dir(-135)); label("$C$",C,dir(-75)); dot((2.68,2.25)); label("$K$",(2.68,2.25),2*down); label("$\omega_1$",(-4.5,1)); label("$\omega_2$",(12.75,6)); label("$7$",(A+B)/2,dir(140)); label("$8$",(B+C)/2,dir(-90)); label("$9$",(A+C)/2,dir(60)); [/asy]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/8/8/b/88be119b0fb37d4a5ccbef2477f35c87890164fa.png) -Diagram by Brendanb4321
-Diagram by Brendanb4321
Note that from the tangency condition that the supplement of ![]() with respects to lines
with respects to lines ![]() and
and ![]() are equal to
are equal to ![]() and
and ![]() , respectively, so from tangent-chord,
, respectively, so from tangent-chord, ![]() Also note that
Also note that ![]()
![]() , so
, so ![]() . Using similarity ratios, we can easily find
. Using similarity ratios, we can easily find ![]() However, since
However, since ![]() and
and ![]() , we can use similarity ratios to get
, we can use similarity ratios to get ![]()
- Now we use Law of Cosines on
 : From reverse Law of Cosines,
: From reverse Law of Cosines, 
Giving us ![]()
![]()
![]() so our answer is
so our answer is ![]() .
.
![]() Let
Let ![]() be the center of
be the center of ![]() . Then
. Then ![]() . Thus,
. Thus, ![]()
-franchester; ![]() by firebolt360
by firebolt360
Supplement
- In order to get to the Law of Cosines first, we first apply the LOC to
 obtaining
obtaining 
- We angle chase before applying the law of cosines to

Note that ![]() and
and ![]() from tangent-chord.
from tangent-chord.
Thus, ![]()
However from our tangent chord, note that:
![]() Thus,
Thus, ![]()
- As an alternative approach, note that the sum of the angles in quadrilateral
 is
is  and we can find
and we can find  of convex
of convex  which is just:
which is just:
![]()
~mathboy282
Solution 2 (Inversion)
Consider an inversion with center ![]() and radius
and radius ![]() . Then, we have
. Then, we have ![]() , or
, or ![]() . Similarly,
. Similarly, ![]() . Notice that
. Notice that ![]() is a parallelogram, since
is a parallelogram, since ![]() and
and ![]() are tangent to
are tangent to ![]() and
and ![]() , respectively. Thus,
, respectively. Thus, ![]() . Now, we get that
. Now, we get that
![]() so by Law of Cosines on
so by Law of Cosines on ![]() we have
we have
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() Then, our answer is
Then, our answer is ![]() .
-brianzjk
.
-brianzjk
Solution 3 (Death By Trig Bash)
Let the centers of the circles be ![]() and
and ![]() where the
where the ![]() has the side length
has the side length ![]() contained in the circle. Now let
contained in the circle. Now let ![]() This implies
This implies ![]() by the angle by by tangent. Then we also know that
by the angle by by tangent. Then we also know that ![]() Now we first find
Now we first find ![]() We use law of cosines on
We use law of cosines on ![]() to obtain
to obtain ![]()
![]()
![]() Then applying law of sines on
Then applying law of sines on ![]() we obtain
we obtain ![]()
![]()
![]() Using similar logic we obtain
Using similar logic we obtain ![]()
Now we know that ![]() Thus using law of cosines on
Thus using law of cosines on ![]() yields
yields ![\[O_{1}O_{2} =\sqrt{\left(\frac{147}{16\sqrt{5}}\right)^2+\left(\frac{189}{16\sqrt{5}}\right)^2-2\:\cdot \left(\frac{147}{16\sqrt{5}}\right)\cdot \frac{189}{16\sqrt{5}}\cdot -\frac{11}{21}}\]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/7/5/e/75eb919ddcf26cbdd728f3334981b8820e6ca652.png) While this does look daunting we can write the above expression as
While this does look daunting we can write the above expression as ![\[\sqrt{\left(\frac{189+147}{16\sqrt{5}}\right)^2 - 2\cdot \left(\frac{147}{16\sqrt{5}}\right)\cdot \frac{189}{16\sqrt{5}}\cdot \frac{10}{21}} =\sqrt{\left(\frac{168}{8\sqrt{5}}\right)^2 - \left(\frac{7 \cdot 189 \cdot 5}{8 \sqrt{5} \cdot 8\sqrt{5}}\right)}\]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/d/1/2/d1287aaea319d3e846f4e6b1ead1d8ef2fca23bb.png) Then factoring yields
Then factoring yields ![\[\sqrt{\frac{21^2(8^2-15)}{(8\sqrt{5})^2}} =\frac{147}{8\sqrt{5}}\]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/a/d/a/ada9f6ae2fa33d8108173f501b684b04e0ce3c0c.png) The area
The area ![]() Now
Now ![]() is twice the length of the altitude of
is twice the length of the altitude of ![]() so we let the altitude be
so we let the altitude be ![]() and we have
and we have ![]()
![]() Thus our desired length is
Thus our desired length is ![]()
-minor edits by faliure167
Solution 4 (Video)
Video Link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nJydO5CLuuI
Solution 5 (Olympiad Geometry)
By the definition of ![]() , it is the spiral center mapping
, it is the spiral center mapping ![]() , which means that it is the midpoint of the
, which means that it is the midpoint of the ![]() -symmedian chord. In particular, if
-symmedian chord. In particular, if ![]() is the midpoint of
is the midpoint of ![]() and
and ![]() is the reflection of
is the reflection of ![]() across
across ![]() , we have
, we have ![]() . By Stewart's Theorem, it then follows that
. By Stewart's Theorem, it then follows that
![\[AK = \frac{AM'}{2} = \frac{AC\cdot AB}{2AM} = \frac{7\cdot 9}{2\sqrt{\frac{9^2\cdot 4 + 7^2\cdot 4 - 4^2\cdot 8}{8}}} = \frac{7\cdot 9}{2\sqrt{49}} = \frac{9}{2}\implies m + n = \boxed{11}.\]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/5/0/6/506edfe22cd2bfc9cad3967090ce0e228c88fab3.png)
Solution 6 (Inversion simplified)
The median of ![]() is
is ![]() (via Stewart's Theorem).
(via Stewart's Theorem).
Consider an inversion with center ![]() and radius
and radius ![]() (inversion with respect the red circle).
Let
(inversion with respect the red circle).
Let ![]() and
and ![]() be inverse points for
be inverse points for ![]() and
and ![]() respectively.
respectively.
Image of line ![]() is line
is line ![]() lies on this line.
lies on this line.
Image of ![]() is line
is line ![]() (circle
(circle ![]() passes through K, C and is tangent to the line
passes through K, C and is tangent to the line ![]() at point
at point ![]() Diagram shows circle and its image using same color).
Diagram shows circle and its image using same color).
Similarly, ![]() is the image of the circle
is the image of the circle ![]() ).
).
Therefore ![]() is a parallelogram,
is a parallelogram, ![]() is median of
is median of ![]() and
and ![]() Then, we have
Then, we have ![]() .
. ![]() with coefficient
with coefficient ![]()
So median ![]() vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Solution 7 (Heavy Bash)
We start by assigning coordinates to point ![]() , labeling it
, labeling it ![]() and point
and point ![]() at
at ![]() , and letting point
, and letting point ![]() be above the
be above the ![]() -axis. Through an application of the Pythagorean Theorem and dropping an altitude to side
-axis. Through an application of the Pythagorean Theorem and dropping an altitude to side ![]() , it is easy to see that
, it is easy to see that ![]() has coordinates
has coordinates ![]() .
.
Let ![]() be the center of circle
be the center of circle ![]() and
and ![]() be the center of circle
be the center of circle ![]() . Since circle
. Since circle ![]() contains both points
contains both points ![]() and
and ![]() ,
, ![]() must lie on the perpendicular bisector of line
must lie on the perpendicular bisector of line ![]() , and similarly
, and similarly ![]() must lie on the perpendicular bisector of line
must lie on the perpendicular bisector of line ![]() . Through some calculations, we find that the perpendicular bisector of
. Through some calculations, we find that the perpendicular bisector of ![]() has equation
has equation ![]() , and the perpendicular bisector of
, and the perpendicular bisector of ![]() has equation
has equation ![]() .
.
Since circle ![]() is tangent to line
is tangent to line ![]() at
at ![]() , its radius must be perpendicular to
, its radius must be perpendicular to ![]() at
at ![]() .
Therefore, the radius has equation
.
Therefore, the radius has equation ![]() . Substituting the
. Substituting the ![]() -coordinate of
-coordinate of ![]() into this, we find the y-coordinate of
into this, we find the y-coordinate of ![]() .
.
Similarly, since circle ![]() is tangent to line
is tangent to line ![]() at
at ![]() , its radius must be perpendicular to
, its radius must be perpendicular to ![]() at
at ![]() . Therefore, the radius has equation
. Therefore, the radius has equation ![]() and combining with the previous result for
and combining with the previous result for ![]() we get that the coordinates of
we get that the coordinates of ![]() are
are ![]() .
.
We now find the slope of ![]() , the line joining the centers of circles
, the line joining the centers of circles ![]() and
and ![]() , which turns out to be
, which turns out to be ![]() . Since the
. Since the ![]() -intercept of that line is at
-intercept of that line is at ![]() , the equation is
, the equation is ![]() . Since circles
. Since circles ![]() and
and ![]() intersect at points
intersect at points ![]() and
and ![]() , line
, line ![]() is the radical axis of those circles, and since the radical axis is always perpendicular to the line joining the centers of the circles,
is the radical axis of those circles, and since the radical axis is always perpendicular to the line joining the centers of the circles, ![]() has slope
has slope ![]() . Since point
. Since point ![]() is
is ![]() , this line has a
, this line has a ![]() -intercept of
-intercept of ![]() , so it has equation
, so it has equation ![]() =
= ![]() .
.
We set ![]() in order to find the intersection
in order to find the intersection ![]() of the radical axis
of the radical axis ![]() and
and ![]() . Through some moderate bashing, we find that the intersection point is
. Through some moderate bashing, we find that the intersection point is ![]() . We know that either intersection point of two circles is the same distance from the intersection of radical axis and line joining the centers of those circles, so reflecting
. We know that either intersection point of two circles is the same distance from the intersection of radical axis and line joining the centers of those circles, so reflecting ![]() over
over ![]() yields
yields ![]() and
and ![]() =
= ![]() = (This is the most tedious part of the bash)
= (This is the most tedious part of the bash) ![]() . Therefore the answer is
. Therefore the answer is ![]()
See Also
| 2019 AIME II (Problems • Answer Key • Resources) | ||
| Preceded by Problem 10 |
Followed by Problem 12 | |
| 1 • 2 • 3 • 4 • 5 • 6 • 7 • 8 • 9 • 10 • 11 • 12 • 13 • 14 • 15 | ||
| All AIME Problems and Solutions | ||
The problems on this page are copyrighted by the Mathematical Association of America's American Mathematics Competitions.