Difference between revisions of "2005 AMC 10A Problems/Problem 17"
(→Solution 2) |
|||
| (13 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
<math> \textbf{(A) } 9\qquad \textbf{(B) } 10\qquad \textbf{(C) } 11\qquad \textbf{(D) } 12\qquad \textbf{(E) } 13 </math> | <math> \textbf{(A) } 9\qquad \textbf{(B) } 10\qquad \textbf{(C) } 11\qquad \textbf{(D) } 12\qquad \textbf{(E) } 13 </math> | ||
| − | ==Solution 1== | + | ==Solution 1 == |
| + | (meta-solving; answer choices imply solution exists) | ||
| + | |||
Each corner <math>(A,B,C,D,E)</math> goes to two sides/numbers. (<math>A</math> goes to <math>AE</math> and <math>AB</math>, <math>D</math> goes to <math>DC</math> and <math>DE</math>). The sum of every term is equal to <math>2(3+5+6+7+9)=60</math> | Each corner <math>(A,B,C,D,E)</math> goes to two sides/numbers. (<math>A</math> goes to <math>AE</math> and <math>AB</math>, <math>D</math> goes to <math>DC</math> and <math>DE</math>). The sum of every term is equal to <math>2(3+5+6+7+9)=60</math> | ||
Since the middle term in an arithmetic sequence is the average of all the terms in the sequence, the middle number is <math>\frac{60}{5}=\boxed{\textbf{(D) }12}</math> | Since the middle term in an arithmetic sequence is the average of all the terms in the sequence, the middle number is <math>\frac{60}{5}=\boxed{\textbf{(D) }12}</math> | ||
| − | ==Solution 2== | + | ==Solution 2 (Doesn't assume a solution exists) == |
| − | We know that the smallest number in | + | We know that the smallest number in the arithmetic sequence must be <math>\geq 3 + 5 = 8</math>, and the largest number must be <math>\leq 7 + 9 = 16</math>. |
| − | + | ||
| + | Since there are <math>5</math> terms in this sequence, the common difference <math>d \leq (16 - 8)/(5-1) = 2</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Since <math>d</math> is an integer (difference of sums of integers), and since exactly 2 of the sums must be odd, <math>d</math> must be odd. Therefore, <math>d=1</math>. | ||
| − | == Video Solution == | + | The middle term must have the majority parity, so it must be even. |
| + | The 2 terms adjacent to the middle are odd, <math>6+a</math> and <math>6+b</math>. <math>a-b = 2d = 2</math>. <math>a</math> and <math>b</math> can't be the smallest (or largest) 2 odd numbers, because that would make it impossible to construct the smallest (or largest) sum from one of the remaining two numbers and one of the odd numbers. Therefore, <math>\{a,b\} = \{5,7\}</math>. The middle sum must then be <math>(6+5) + 1 = (6+7)-1 = \boxed{12}</math>. The remaining edges are <math>\{9,3\}</math> (because <math>\{5,7\}</math> can't be an edge, as that would make a triangle with 6), <math>\{3,7\}</math>, and <math>\{5,9\}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ~oinava | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Solution 3 == | ||
| + | We notice that the average of <math>3,5,6,7</math> and <math>9</math> is <math>6</math>. Now all we have to do is plug <math>6</math> into each value. This results in all the terms being <math>12</math> and since the term we are looking for is the middle term, we know that our answer is <math>12</math>, <math>\boxed{D}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Video Solution by OmegaLearn == | ||
https://youtu.be/tKsYSBdeVuw?t=544 | https://youtu.be/tKsYSBdeVuw?t=544 | ||
| Line 21: | Line 34: | ||
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
| − | + | [[Category:Introductory Algebra Problems]] | |
{{AMC10 box|year=2005|ab=A|num-b=16|num-a=18}} | {{AMC10 box|year=2005|ab=A|num-b=16|num-a=18}} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{{MAA Notice}} | {{MAA Notice}} | ||
Latest revision as of 13:25, 13 October 2024
Contents
Problem
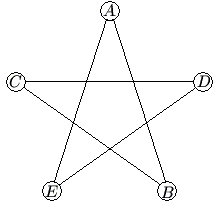
In the five-sided star shown, the letters ![]() and
and ![]() are replaced by the numbers
are replaced by the numbers ![]() and
and ![]() , although not necessarily in this order. The sums of the numbers at the ends of the line segments
, although not necessarily in this order. The sums of the numbers at the ends of the line segments ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() form an arithmetic sequence, although not necessarily in that order. What is the middle term of the arithmetic sequence?
form an arithmetic sequence, although not necessarily in that order. What is the middle term of the arithmetic sequence?
![]()
Solution 1
(meta-solving; answer choices imply solution exists)
Each corner ![]() goes to two sides/numbers. (
goes to two sides/numbers. (![]() goes to
goes to ![]() and
and ![]() ,
, ![]() goes to
goes to ![]() and
and ![]() ). The sum of every term is equal to
). The sum of every term is equal to ![]()
Since the middle term in an arithmetic sequence is the average of all the terms in the sequence, the middle number is ![]()
Solution 2 (Doesn't assume a solution exists)
We know that the smallest number in the arithmetic sequence must be ![]() , and the largest number must be
, and the largest number must be ![]() .
.
Since there are ![]() terms in this sequence, the common difference
terms in this sequence, the common difference ![]() .
.
Since ![]() is an integer (difference of sums of integers), and since exactly 2 of the sums must be odd,
is an integer (difference of sums of integers), and since exactly 2 of the sums must be odd, ![]() must be odd. Therefore,
must be odd. Therefore, ![]() .
.
The middle term must have the majority parity, so it must be even.
The 2 terms adjacent to the middle are odd, ![]() and
and ![]() .
. ![]() .
. ![]() and
and ![]() can't be the smallest (or largest) 2 odd numbers, because that would make it impossible to construct the smallest (or largest) sum from one of the remaining two numbers and one of the odd numbers. Therefore,
can't be the smallest (or largest) 2 odd numbers, because that would make it impossible to construct the smallest (or largest) sum from one of the remaining two numbers and one of the odd numbers. Therefore, ![]() . The middle sum must then be
. The middle sum must then be ![]() . The remaining edges are
. The remaining edges are ![]() (because
(because ![]() can't be an edge, as that would make a triangle with 6),
can't be an edge, as that would make a triangle with 6), ![]() , and
, and ![]() .
.
~oinava
Solution 3
We notice that the average of ![]() and
and ![]() is
is ![]() . Now all we have to do is plug
. Now all we have to do is plug ![]() into each value. This results in all the terms being
into each value. This results in all the terms being ![]() and since the term we are looking for is the middle term, we know that our answer is
and since the term we are looking for is the middle term, we know that our answer is ![]() ,
, ![]() .
.
Video Solution by OmegaLearn
https://youtu.be/tKsYSBdeVuw?t=544
~ pi_is_3.14
See Also
| 2005 AMC 10A (Problems • Answer Key • Resources) | ||
| Preceded by Problem 16 |
Followed by Problem 18 | |
| 1 • 2 • 3 • 4 • 5 • 6 • 7 • 8 • 9 • 10 • 11 • 12 • 13 • 14 • 15 • 16 • 17 • 18 • 19 • 20 • 21 • 22 • 23 • 24 • 25 | ||
| All AMC 10 Problems and Solutions | ||
The problems on this page are copyrighted by the Mathematical Association of America's American Mathematics Competitions.