Difference between revisions of "2021 Fall AMC 10A Problems/Problem 24"
MRENTHUSIASM (talk | contribs) (→Solution 4 (Graph Coloring): As the solutions in this page use CASEWORK throughout, for consistency purposes let's delete the title? Also, I centered all diagrams.) |
Mathboy282 (talk | contribs) (→Case 1) |
||
| (11 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
==Solution 1== | ==Solution 1== | ||
| − | For simplicity | + | For simplicity, we will name this cube <math>ABCDEFGH</math> by vertices, as shown below. |
<asy> | <asy> | ||
/* Made by MRENTHUSIASM */ | /* Made by MRENTHUSIASM */ | ||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
dot("$H$",H,1.5*NW,linewidth(4)); | dot("$H$",H,1.5*NW,linewidth(4)); | ||
</asy> | </asy> | ||
| − | Note that for each face of this cube, two edges are labeled <math>0</math> and two edges are labeled <math>1.</math> For all twelve edges of this cube, we conclude that six edges are labeled <math>0,</math> and six edges are labeled <math>1.</math> | + | Note that for each face of this cube, two edges are labeled <math>0,</math> and two edges are labeled <math>1.</math> For all twelve edges of this cube, we conclude that six edges are labeled <math>0,</math> and six edges are labeled <math>1.</math> |
We apply casework to face <math>ABCD.</math> Recall that there are <math>\binom42=6</math> ways to label its edges: | We apply casework to face <math>ABCD.</math> Recall that there are <math>\binom42=6</math> ways to label its edges: | ||
<ol style="margin-left: 1.5em;"> | <ol style="margin-left: 1.5em;"> | ||
<li><b>Opposite edges have the same label.</b></li><p> | <li><b>Opposite edges have the same label.</b></li><p> | ||
| − | There are <math>2</math> ways to label the edges of <math>ABCD.</math> We will consider one of the ways, then multiply the count by <math>2.</math> Without | + | There are <math>2</math> ways to label the edges of <math>ABCD.</math> We will consider one of the ways, then multiply the count by <math>2.</math> Without loss of generality, we assume that <math>\overline{AB},\overline{BC},\overline{CD},\overline{DA}</math> are labeled <math>1,0,1,0,</math> respectively:<p> |
We apply casework to the label of <math>\overline{AE},</math> as shown below. | We apply casework to the label of <math>\overline{AE},</math> as shown below. | ||
<asy> | <asy> | ||
| Line 116: | Line 116: | ||
We have <math>2\cdot2=4</math> such labelings for this case. | We have <math>2\cdot2=4</math> such labelings for this case. | ||
<li><b>Opposite edges have different labels.</b></li><p> | <li><b>Opposite edges have different labels.</b></li><p> | ||
| − | There are <math>4</math> ways to label the edges of <math>ABCD.</math> We will consider one of the ways, then multiply the count by <math>4.</math> Without | + | There are <math>4</math> ways to label the edges of <math>ABCD.</math> We will consider one of the ways, then multiply the count by <math>4.</math> Without loss of generality, we assume that <math>\overline{AB},\overline{BC},\overline{CD},\overline{DA}</math> are labeled <math>1,1,0,0,</math> respectively:<p> |
We apply casework to the labels of <math>\overline{AE}</math> and <math>\overline{BF},</math> as shown below. | We apply casework to the labels of <math>\overline{AE}</math> and <math>\overline{BF},</math> as shown below. | ||
<asy> | <asy> | ||
| Line 275: | Line 275: | ||
<u><b>Remark</b></u> | <u><b>Remark</b></u> | ||
| − | It is very easy to get disorganized when counting, so when doing this problem, make sure to draw a diagram of the cube. Labeling is a bit harder, since we often confuse one side with another. Try doing the problem by labeling sides on the lines (literally letting the lines pass through your <math>0</math>s and <math>1</math>s.) I found that to be very helpful when solving this problem. | + | It is very easy to get disorganized when counting, resulting in incorrect calculations, so when doing this problem, make sure to draw a diagram of the cube. Labeling is a bit harder, since we often confuse one side with another. Try doing the problem by labeling sides on the lines (literally letting the lines pass through your <math>0</math>s and <math>1</math>s.) I found that to be very helpful when solving this problem. |
~Arcticturn | ~Arcticturn | ||
| Line 369: | Line 369: | ||
We can see that we choose <math>2</math> diametrically opposite vertices to put <math>3</math> <math>1</math>'s on the connecting edges. As a result, this case has <math>\frac{8}{2}=4</math> orientations. | We can see that we choose <math>2</math> diametrically opposite vertices to put <math>3</math> <math>1</math>'s on the connecting edges. As a result, this case has <math>\frac{8}{2}=4</math> orientations. | ||
| + | |||
| + | An alternate way to count would be to realize that you can rotate the configuration four times yielding four different configurations, but when you reflect horizontally and diagonally, you don't get another unique configuration, rather you get the same configuration as if you rotated it. ~mathboy282 | ||
===Case 2=== | ===Case 2=== | ||
| Line 712: | Line 714: | ||
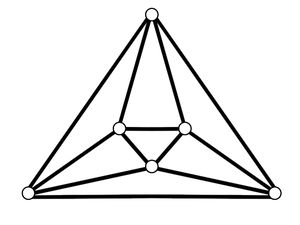
[[File:Graph coloring normal.jpg|300px|center]] | [[File:Graph coloring normal.jpg|300px|center]] | ||
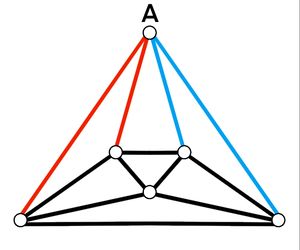
| − | <math>\textbf{Case 1}</math>: | + | <math>\textbf{Case 1}</math>: <math>2</math> adjacent red edges from vertex A. There are <math>4</math> ways to choose <math>2</math> red edges adjacent to each other and connect to <math>2</math> vertices with an edge between them as shown below. |
[[File:Graph coloring 1.jpg|300px|center]] | [[File:Graph coloring 1.jpg|300px|center]] | ||
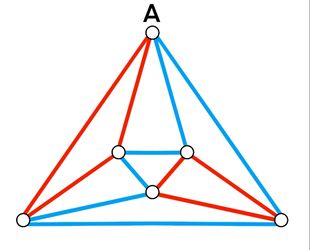
| − | <math>\textbf{Case 1.1}</math>: | + | <math>\textbf{Case 1.1}</math>: <math>2</math> adjacent red edges from vertex <math>A</math> form a closed loop with a third red edge. There is only <math>1</math> case as shown below. |
[[File:Graph coloring case 1.1 .jpg | 310px|center]] | [[File:Graph coloring case 1.1 .jpg | 310px|center]] | ||
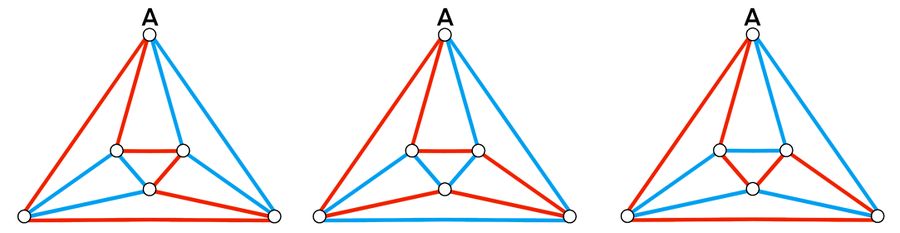
| − | <math>\textbf{Case 1.2}</math>: | + | <math>\textbf{Case 1.2}</math>: <math>2</math> adjacent red edges from vertex <math>A</math> does not form a closed loop with a third red edge. There are <math>3</math> cases as shown below. |
[[File:Graph coloring case 1.2 .jpg | 900px|center]] | [[File:Graph coloring case 1.2 .jpg | 900px|center]] | ||
| Line 726: | Line 728: | ||
In case <math>1</math>, there are total <math>4 \cdot (1 + 3) = 16</math> ways. | In case <math>1</math>, there are total <math>4 \cdot (1 + 3) = 16</math> ways. | ||
| − | <math>\textbf{Case 2}</math>: | + | <math>\textbf{Case 2}</math>: <math>2</math> red edges from vertex <math>A</math> with <math>1</math> blue edge in between. There are <math>2</math> ways to choose <math>2</math> red edges with <math>1</math> blue edge in between. |
[[File:Graph coloring case 2 .jpg | 300px|center]] | [[File:Graph coloring case 2 .jpg | 300px|center]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:13, 13 October 2024
Contents
Problem
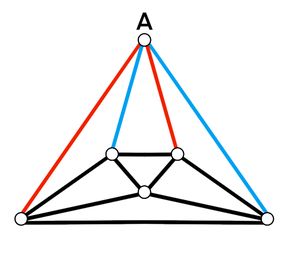
Each of the ![]() edges of a cube is labeled
edges of a cube is labeled ![]() or
or ![]() . Two labelings are considered different even if one can be obtained from the other by a sequence of one or more rotations and/or reflections. For how many such labelings is the sum of the labels on the edges of each of the
. Two labelings are considered different even if one can be obtained from the other by a sequence of one or more rotations and/or reflections. For how many such labelings is the sum of the labels on the edges of each of the ![]() faces of the cube equal to
faces of the cube equal to ![]() ?
?
![]()
Solution 1
For simplicity, we will name this cube ![]() by vertices, as shown below.
by vertices, as shown below.
![[asy] /* Made by MRENTHUSIASM */ size(150); pair A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H; A = (0,1); B = (1,1); C = (1,0); D = (0,0); E = (0.3,1.3); F = (1.3,1.3); G = (1.3,0.3); H = (0.3,0.3); draw(A--B--C--D--cycle^^A--E^^B--F^^C--G^^E--F--G); draw(H--D^^H--E^^H--G,dashed); dot("$A$",A,1.5*W,linewidth(4)); dot("$B$",B,1.5*(1,0),linewidth(4)); dot("$C$",C,1.5*SE,linewidth(4)); dot("$D$",D,1.5*SW,linewidth(4)); dot("$E$",E,1.5*NW,linewidth(4)); dot("$F$",F,1.5*NE,linewidth(4)); dot("$G$",G,1.5*NE,linewidth(4)); dot("$H$",H,1.5*NW,linewidth(4)); [/asy]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/9/4/4/94407de6b1861a30f4b3f566982e93252a7c9ce2.png) Note that for each face of this cube, two edges are labeled
Note that for each face of this cube, two edges are labeled ![]() and two edges are labeled
and two edges are labeled ![]() For all twelve edges of this cube, we conclude that six edges are labeled
For all twelve edges of this cube, we conclude that six edges are labeled ![]() and six edges are labeled
and six edges are labeled ![]()
We apply casework to face ![]() Recall that there are
Recall that there are  ways to label its edges:
ways to label its edges:
- Opposite edges have the same label.
- Opposite edges have different labels.
There are ![]() ways to label the edges of
ways to label the edges of ![]() We will consider one of the ways, then multiply the count by
We will consider one of the ways, then multiply the count by ![]() Without loss of generality, we assume that
Without loss of generality, we assume that ![]() are labeled
are labeled ![]() respectively:
respectively:
We apply casework to the label of ![]() as shown below.
as shown below.
![[asy] /* Made by MRENTHUSIASM */ size(1200,150); pair A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, A1, B1, C1, D1, E1, F1, G1, H1, V; A = (0,1); B = (1,1); C = (1,0); D = (0,0); E = (0.3,1.3); F = (1.3,1.3); G = (1.3,0.3); H = (0.3,0.3); V = (3,0); A1 = A+V; B1 = B+V; C1 = C+V; D1 = D+V; E1 = E+V; F1 = F+V; G1 = G+V; H1 = H+V; draw(A--B--C--D--cycle^^A--E^^B--F^^C--G^^E--F--G); draw(H--D^^H--E^^H--G,dashed); draw(A1--B1--C1--D1--cycle^^A1--E1^^B1--F1^^C1--G1^^E1--F1--G1); draw(H1--D1^^H1--E1^^H1--G1,dashed); dot("$A$",A,1.5*W,linewidth(4)); dot("$B$",B,1.5*(1,0),linewidth(4)); dot("$C$",C,1.5*SE,linewidth(4)); dot("$D$",D,1.5*SW,linewidth(4)); dot("$E$",E,1.5*NW,linewidth(4)); dot("$F$",F,1.5*NE,linewidth(4)); dot("$G$",G,1.5*NE,linewidth(4)); dot("$H$",H,1.5*NW,linewidth(4)); dot("$A$",A1,1.5*W,linewidth(4)); dot("$B$",B1,1.5*(1,0),linewidth(4)); dot("$C$",C1,1.5*SE,linewidth(4)); dot("$D$",D1,1.5*SW,linewidth(4)); dot("$E$",E1,1.5*NW,linewidth(4)); dot("$F$",F1,1.5*NE,linewidth(4)); dot("$G$",G1,1.5*NE,linewidth(4)); dot("$H$",H1,1.5*NW,linewidth(4)); label("$1$",midpoint(A--B),red,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$0$",midpoint(B--C),red,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$1$",midpoint(C--D),red,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$0$",midpoint(D--A),red,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$1$",midpoint(A1--B1),red,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$0$",midpoint(B1--C1),red,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$1$",midpoint(C1--D1),red,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$0$",midpoint(D1--A1),red,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$0$",midpoint(A--E),blue,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$1$",midpoint(E--H),blue,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$1$",midpoint(H--D),blue,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$0$",midpoint(G--C),blue,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$0$",midpoint(G--H),blue,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$1$",midpoint(B--F),blue,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$1$",midpoint(F--G),blue,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$0$",midpoint(E--F),blue,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$1$",midpoint(A1--E1),blue,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$0$",midpoint(E1--F1),blue,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$0$",midpoint(B1--F1),blue,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$1$",midpoint(F1--G1),blue,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$1$",midpoint(G1--C1),blue,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$0$",midpoint(G1--H1),blue,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$0$",midpoint(H1--D1),blue,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$1$",midpoint(E1--H1),blue,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("The label of $\overline{AE}$ is $0.$",(D.x-0.25,D.y-0.5),blue,align=right); label("The label of $\overline{AE}$ is $1.$",(D1.x-0.25,D1.y-0.5),blue,align=right); [/asy]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/b/5/5/b55ae29a7fef005f1a8879199a28b2babb98cbf2.png) We have
We have ![]() such labelings for this case.
such labelings for this case.
There are ![]() ways to label the edges of
ways to label the edges of ![]() We will consider one of the ways, then multiply the count by
We will consider one of the ways, then multiply the count by ![]() Without loss of generality, we assume that
Without loss of generality, we assume that ![]() are labeled
are labeled ![]() respectively:
respectively:
We apply casework to the labels of ![]() and
and ![]() as shown below.
as shown below.
![[asy] /* Made by MRENTHUSIASM */ size(1200,150); pair A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, A1, B1, C1, D1, E1, F1, G1, H1, A2, B2, C2, D2, E2, F2, G2, H2, A3, B3, C3, D3, E3, F3, G3, H3, V; A = (0,1); B = (1,1); C = (1,0); D = (0,0); E = (0.3,1.3); F = (1.3,1.3); G = (1.3,0.3); H = (0.3,0.3); V = (3,0); A1 = A+V; B1 = B+V; C1 = C+V; D1 = D+V; E1 = E+V; F1 = F+V; G1 = G+V; H1 = H+V; A2 = A1+V; B2 = B1+V; C2 = C1+V; D2 = D1+V; E2 = E1+V; F2 = F1+V; G2 = G1+V; H2 = H1+V; A3 = A2+V; B3 = B2+V; C3 = C2+V; D3 = D2+V; E3 = E2+V; F3 = F2+V; G3 = G2+V; H3 = H2+V; draw(A--B--C--D--cycle^^A--E^^B--F^^C--G^^E--F--G); draw(H--D^^H--E^^H--G,dashed); draw(A1--B1--C1--D1--cycle^^A1--E1^^B1--F1^^C1--G1^^E1--F1--G1); draw(H1--D1^^H1--E1^^H1--G1,dashed); draw(A2--B2--C2--D2--cycle^^A2--E2^^B2--F2^^C2--G2^^E2--F2--G2); draw(H2--D2^^H2--E2^^H2--G2,dashed); draw(A3--B3--C3--D3--cycle^^A3--E3^^B3--F3^^C3--G3^^E3--F3--G3); draw(H3--D3^^H3--E3^^H3--G3,dashed); dot("$A$",A,W,linewidth(4)); dot("$B$",B,(1,0),linewidth(4)); dot("$C$",C,SE,linewidth(4)); dot("$D$",D,SW,linewidth(4)); dot("$E$",E,NW,linewidth(4)); dot("$F$",F,NE,linewidth(4)); dot("$G$",G,NE,linewidth(4)); dot("$H$",H,NW,linewidth(4)); dot("$A$",A1,W,linewidth(4)); dot("$B$",B1,(1,0),linewidth(4)); dot("$C$",C1,SE,linewidth(4)); dot("$D$",D1,SW,linewidth(4)); dot("$E$",E1,NW,linewidth(4)); dot("$F$",F1,NE,linewidth(4)); dot("$G$",G1,NE,linewidth(4)); dot("$H$",H1,NW,linewidth(4)); dot("$A$",A2,W,linewidth(4)); dot("$B$",B2,(1,0),linewidth(4)); dot("$C$",C2,SE,linewidth(4)); dot("$D$",D2,SW,linewidth(4)); dot("$E$",E2,NW,linewidth(4)); dot("$F$",F2,NE,linewidth(4)); dot("$G$",G2,NE,linewidth(4)); dot("$H$",H2,NW,linewidth(4)); dot("$A$",A3,W,linewidth(4)); dot("$B$",B3,(1,0),linewidth(4)); dot("$C$",C3,SE,linewidth(4)); dot("$D$",D3,SW,linewidth(4)); dot("$E$",E3,NW,linewidth(4)); dot("$F$",F3,NE,linewidth(4)); dot("$G$",G3,NE,linewidth(4)); dot("$H$",H3,NW,linewidth(4)); label("$1$",midpoint(A--B),red,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$1$",midpoint(B--C),red,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$0$",midpoint(C--D),red,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$0$",midpoint(D--A),red,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$1$",midpoint(A1--B1),red,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$1$",midpoint(B1--C1),red,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$0$",midpoint(C1--D1),red,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$0$",midpoint(D1--A1),red,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$1$",midpoint(A2--B2),red,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$1$",midpoint(B2--C2),red,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$0$",midpoint(C2--D2),red,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$0$",midpoint(D2--A2),red,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$1$",midpoint(A3--B3),red,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$1$",midpoint(B3--C3),red,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$0$",midpoint(C3--D3),red,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$0$",midpoint(D3--A3),red,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$0$",midpoint(A--E),blue,Fill(0,0,white)); label("$0$",midpoint(B--F),blue,Fill(0,0,white)); label("$1$",midpoint(E--F),blue,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$1$",midpoint(E--H),blue,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$1$",midpoint(D--H),blue,Fill(0,0,white)); label("$0$",midpoint(F--G),blue,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$0$",midpoint(G--H),blue,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$1$",midpoint(G--C),blue,Fill(0,0,white)); label("$0$",midpoint(A1--E1),blue,Fill(0,0,white)); label("$1$",midpoint(B1--F1),blue,Fill(0,0,white)); label("$0$",midpoint(E1--F1),blue,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$1$",midpoint(E1--H1),blue,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$1$",midpoint(D1--H1),blue,Fill(0,0,white)); label("$0$",midpoint(F1--G1),blue,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$1$",midpoint(G1--H1),blue,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$0$",midpoint(G1--C1),blue,Fill(0,0,white)); label("$1$",midpoint(A2--E2),blue,Fill(0,0,white)); label("$0$",midpoint(B2--F2),blue,Fill(0,0,white)); label("$0$",midpoint(E2--F2),blue,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$1$",midpoint(E2--H2),blue,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$0$",midpoint(D2--H2),blue,Fill(0,0,white)); label("$0$",midpoint(F2--G2),blue,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$1$",midpoint(G2--H2),blue,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$1$",midpoint(G2--C2),blue,Fill(0,0,white)); label("$1$",midpoint(A3--E3),blue,Fill(0,0,white)); label("$0$",midpoint(B3--F3),blue,Fill(0,0,white)); label("$0$",midpoint(E3--F3),blue,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$0$",midpoint(E3--H3),blue,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$1$",midpoint(D3--H3),blue,Fill(0,0,white)); label("$1$",midpoint(F3--G3),blue,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$1$",midpoint(G3--H3),blue,Fill(1.5,2,white)); label("$0$",midpoint(G3--C3),blue,Fill(0,0,white)); label("The label of $\overline{AE}$ is $0.$",(D.x-0.25,D.y-0.5),blue,align=right); label("The label of $\overline{BF}$ is $0.$",(D.x-0.25,D.y-0.75),blue,align=right); label("The label of $\overline{AE}$ is $0.$",(D1.x-0.25,D1.y-0.5),blue,align=right); label("The label of $\overline{BF}$ is $1.$",(D1.x-0.25,D1.y-0.75),blue,align=right); draw(brace((G3.x+0.25,-0.5),(D2.x-0.25,-0.5),.3),blue); label("The label of $\overline{AE}$ is $1.$",(G2.x-0.25,D2.y-1),blue,align=right); label("The label of $\overline{BF}$ is $0.$",(G2.x-0.25,D2.y-1.25),blue,align=right); [/asy]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/4/6/4/4641d4d5901d2a8b55d4c7ef3b54bb3bf41357db.png) We have
We have ![]() such labelings for this case.
such labelings for this case.
Therefore, we have ![]() such labelings in total.
such labelings in total.
~MRENTHUSIASM
Solution 2
Since we want the sum of the edges of each face to be ![]() , we need there to be two
, we need there to be two ![]() s and two
s and two ![]() s on each face. Through experimentation, we find that either
s on each face. Through experimentation, we find that either ![]() or all of them have
or all of them have ![]() s adjacent to
s adjacent to ![]() s and
s and ![]() s adjacent to
s adjacent to ![]() on each face. WLOG, let the first face (counterclockwise) be
on each face. WLOG, let the first face (counterclockwise) be ![]() . In this case we are trying to have all of them be adjacent to each other. First face:
. In this case we are trying to have all of them be adjacent to each other. First face: ![]() . Second face:
. Second face: ![]() choices:
choices: ![]() or
or ![]() . After that, it is basically forced and everything will fall in to place. Since we assumed WLOG, we need to multiply
. After that, it is basically forced and everything will fall in to place. Since we assumed WLOG, we need to multiply ![]() by
by ![]() to get a total of
to get a total of ![]() different arrangements.
different arrangements.
Secondly, ![]() of the faces have all of them adjacent and
of the faces have all of them adjacent and ![]() of the faces do not: WLOG counting counterclockwise, we have
of the faces do not: WLOG counting counterclockwise, we have ![]() . Then, we choose the other face next to it. There are two cases, which are
. Then, we choose the other face next to it. There are two cases, which are ![]() and
and ![]() . Therefore, this subcase has
. Therefore, this subcase has ![]() different arrangements. Then, we can choose the face at front to be
different arrangements. Then, we can choose the face at front to be ![]() . This has
. This has ![]() cases. The sides can either be
cases. The sides can either be ![]() or
or ![]() . Therefore, we have another
. Therefore, we have another ![]() cases.
cases.
Summing these up, we have ![]() . Therefore, our answer is
. Therefore, our answer is ![]() .
.
Remark
It is very easy to get disorganized when counting, resulting in incorrect calculations, so when doing this problem, make sure to draw a diagram of the cube. Labeling is a bit harder, since we often confuse one side with another. Try doing the problem by labeling sides on the lines (literally letting the lines pass through your ![]() s and
s and ![]() s.) I found that to be very helpful when solving this problem.
s.) I found that to be very helpful when solving this problem.
~Arcticturn
Solution 3
![[asy] pair A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H; A = (0, 0); B = (12.071,0); C = (12.071,12.071); D = (0,12.071); E = (3.536,3.536); F = (8.536,3.536); G = (8.536,8.536); H = (3.536,8.536); draw(A--B--C--D--A--E--F--G--H--E--F--B--C--G--H--D); label("$A$", A, SW); label("$B$", B, SE); label("$C$", C, NE); label("$D$", D, NW); label("$E$", E, NW); label("$F$", F, NE); label("$G$", G, SE); label("$H$", H, SW); [/asy]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/c/a/4/ca48b6c9ba86c93ae29a483d2635045eaf263751.png)
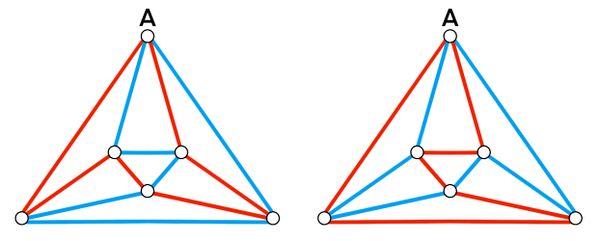
We see that each face has to have 2 1's and 2 0's. We can start with edges connecting to A.
Case 1
![[asy] pair A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H; A = (0, 0); B = (12.071,0); C = (12.071,12.071); D = (0,12.071); E = (3.536,3.536); F = (8.536,3.536); G = (8.536,8.536); H = (3.536,8.536); draw(A--B--C--D--A--E--F--G--H--E--F--B--C--G--H--D); label("$A$", A, SW); label("$B$", B, SE); label("$C$", C, NE); label("$D$", D, NW); label("$E$", E, NW); label("$F$", F, NE); label("$G$", G, SE); label("$H$", H, SW); label("$1$", A--B, S); label("$1$", A--D, W); label("$1$", A--E, NW); [/asy]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/5/b/e/5bec0115d3431ffbf0aa21837677561cb129a053.png)
This goes to:
![[asy] pair A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H; A = (0, 0); B = (12.071,0); C = (12.071,12.071); D = (0,12.071); E = (3.536,3.536); F = (8.536,3.536); G = (8.536,8.536); H = (3.536,8.536); draw(A--B--C--D--A--E--F--G--H--E--F--B--C--G--H--D); label("$A$", A, SW); label("$B$", B, SE); label("$C$", C, NE); label("$D$", D, NW); label("$E$", E, NW); label("$F$", F, NE); label("$G$", G, SE); label("$H$", H, SW); label("$1$", A--B, S); label("$0$", B--C, (1,0)); label("$0$", C--D, N); label("$1$", D--A, W); label("$0$", E--F, S); label("$1$", F--G, (1,0)); label("$1$", G--H, N); label("$0$", H--E, W); label("$1$", A--E, NW); label("$0$", B--F, NE); label("$1$", C--G, SE); label("$0$", D--H, SW); [/asy]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/4/1/6/4163df76ff1a55aab8ed189e1dae20f1c74194cc.png)
We can see that we choose ![]() diametrically opposite vertices to put
diametrically opposite vertices to put ![]()
![]() 's on the connecting edges. As a result, this case has
's on the connecting edges. As a result, this case has ![]() orientations.
orientations.
An alternate way to count would be to realize that you can rotate the configuration four times yielding four different configurations, but when you reflect horizontally and diagonally, you don't get another unique configuration, rather you get the same configuration as if you rotated it. ~mathboy282
Case 2
![[asy] pair A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H; A = (0, 0); B = (12.071,0); C = (12.071,12.071); D = (0,12.071); E = (3.536,3.536); F = (8.536,3.536); G = (8.536,8.536); H = (3.536,8.536); draw(A--B--C--D--A--E--F--G--H--E--F--B--C--G--H--D); label("$A$", A, SW); label("$B$", B, SE); label("$C$", C, NE); label("$D$", D, NW); label("$E$", E, NW); label("$F$", F, NE); label("$G$", G, SE); label("$H$", H, SW); label("$0$", A--B, S); label("$1$", A--D, W); label("$1$", A--E, NW); [/asy]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/7/3/c/73cefeba1494409c3a280a8f0fd5991186407d85.png)
Filling out a bit more, we have:
![[asy] pair A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H; A = (0, 0); B = (12.071,0); C = (12.071,12.071); D = (0,12.071); E = (3.536,3.536); F = (8.536,3.536); G = (8.536,8.536); H = (3.536,8.536); draw(A--B--C--D--A--E--F--G--H--E--F--B--C--G--H--D); label("$A$", A, SW); label("$B$", B, SE); label("$C$", C, NE); label("$D$", D, NW); label("$E$", E, NW); label("$F$", F, NE); label("$G$", G, SE); label("$H$", H, SW); label("$0$", A--B, S); label("$1$", A--D, W); label("$1$", A--E, NW); label("$0$", H--E, W); label("$0$", D--H, SW); [/asy]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/c/7/3/c73cf4315a46f0615275c01c967e3e3cf7cca4f1.png)
Let's try filling out ![]() and
and ![]() first.
first.
Case 2.1
![[asy] pair A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H; A = (0, 0); B = (12.071,0); C = (12.071,12.071); D = (0,12.071); E = (3.536,3.536); F = (8.536,3.536); G = (8.536,8.536); H = (3.536,8.536); draw(A--B--C--D--A--E--F--G--H--E--F--B--C--G--H--D); label("$A$", A, SW); label("$B$", B, SE); label("$C$", C, NE); label("$D$", D, NW); label("$E$", E, NW); label("$F$", F, NE); label("$G$", G, SE); label("$H$", H, SW); label("$0$", A--B, S); label("$$", B--C, (1,0)); label("$$", C--D, N); label("$1$", D--A, W); label("$0$", E--F, S); label("$$", F--G, (1,0)); label("$$", G--H, N); label("$0$", H--E, W); label("$1$", A--E, NW); label("$1$", B--F, NE); label("$$", C--G, SE); label("$0$", D--H, SW); [/asy]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/9/9/b/99b254c16f968297e096d33dd3553471e3ce4a36.png)
This goes to:
![[asy] pair A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H; A = (0, 0); B = (12.071,0); C = (12.071,12.071); D = (0,12.071); E = (3.536,3.536); F = (8.536,3.536); G = (8.536,8.536); H = (3.536,8.536); draw(A--B--C--D--A--E--F--G--H--E--F--B--C--G--H--D); label("$A$", A, SW); label("$B$", B, SE); label("$C$", C, NE); label("$D$", D, NW); label("$E$", E, NW); label("$F$", F, NE); label("$G$", G, SE); label("$H$", H, SW); label("$0$", A--B, S); label("$0$", B--C, (1,0)); label("$1$", C--D, N); label("$1$", D--A, W); label("$0$", E--F, S); label("$1$", F--G, (1,0)); label("$1$", G--H, N); label("$0$", H--E, W); label("$1$", A--E, NW); label("$1$", B--F, NE); label("$0$", C--G, SE); label("$0$", D--H, SW); [/asy]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/5/e/e/5eeaec9af0a5798e48b450af4735370531e01d40.png)
We can see that it consists of chains of three ![]() 's, with the middle of each chain being opposite edges. As a result, this case has
's, with the middle of each chain being opposite edges. As a result, this case has ![]() orientations.
orientations.
Case 2.2
![[asy] pair A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H; A = (0, 0); B = (12.071,0); C = (12.071,12.071); D = (0,12.071); E = (3.536,3.536); F = (8.536,3.536); G = (8.536,8.536); H = (3.536,8.536); draw(A--B--C--D--A--E--F--G--H--E--F--B--C--G--H--D); label("$A$", A, SW); label("$B$", B, SE); label("$C$", C, NE); label("$D$", D, NW); label("$E$", E, NW); label("$F$", F, NE); label("$G$", G, SE); label("$H$", H, SW); label("$0$", A--B, S); label("$$", B--C, (1,0)); label("$$", C--D, N); label("$1$", D--A, W); label("$1$", E--F, S); label("$$", F--G, (1,0)); label("$$", G--H, N); label("$0$", H--E, W); label("$1$", A--E, NW); label("$0$", B--F, NE); label("$$", C--G, SE); label("$0$", D--H, SW); [/asy]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/f/9/a/f9a3d0cc26e64ca1f0bca1bda7b6484f7b5ec4a0.png)
Oh no... We have different ways of filling out ![]() and
and ![]() . More casework!
. More casework!
Case 2.2.1
![[asy] pair A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H; A = (0, 0); B = (12.071,0); C = (12.071,12.071); D = (0,12.071); E = (3.536,3.536); F = (8.536,3.536); G = (8.536,8.536); H = (3.536,8.536); draw(A--B--C--D--A--E--F--G--H--E--F--B--C--G--H--D); label("$A$", A, SW); label("$B$", B, SE); label("$C$", C, NE); label("$D$", D, NW); label("$E$", E, NW); label("$F$", F, NE); label("$G$", G, SE); label("$H$", H, SW); label("$0$", A--B, S); label("$$", B--C, (1,0)); label("$$", C--D, N); label("$1$", D--A, W); label("$1$", E--F, S); label("$1$", F--G, (1,0)); label("$0$", G--H, N); label("$0$", H--E, W); label("$1$", A--E, NW); label("$0$", B--F, NE); label("$$", C--G, SE); label("$0$", D--H, SW); [/asy]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/7/b/a/7ba85f8d05c39427e372d5f5f3d83572f0d7ec1b.png)
This goes to:
![[asy] pair A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H; A = (0, 0); B = (12.071,0); C = (12.071,12.071); D = (0,12.071); E = (3.536,3.536); F = (8.536,3.536); G = (8.536,8.536); H = (3.536,8.536); draw(A--B--C--D--A--E--F--G--H--E--F--B--C--G--H--D); label("$A$", A, SW); label("$B$", B, SE); label("$C$", C, NE); label("$D$", D, NW); label("$E$", E, NW); label("$F$", F, NE); label("$G$", G, SE); label("$H$", H, SW); label("$0$", A--B, S); label("$0$", B--C, (1,0)); label("$1$", C--D, N); label("$1$", D--A, W); label("$1$", E--F, S); label("$1$", F--G, (1,0)); label("$0$", G--H, N); label("$0$", H--E, W); label("$1$", A--E, NW); label("$0$", B--F, NE); label("$1$", C--G, SE); label("$0$", D--H, SW); [/asy]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/1/7/9/179b3faf3d72378ec85d8bb98becded14c7e3718.png)
We can see that this is the inverse of case 1 (Define inverse to mean swapping ![]() 's for
's for ![]() 's and
's and ![]() 's for
's for ![]() 's). Therefore, this should also have
's). Therefore, this should also have ![]() orientations.
orientations.
Case 2.2.2
![[asy] pair A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H; A = (0, 0); B = (12.071,0); C = (12.071,12.071); D = (0,12.071); E = (3.536,3.536); F = (8.536,3.536); G = (8.536,8.536); H = (3.536,8.536); draw(A--B--C--D--A--E--F--G--H--E--F--B--C--G--H--D); label("$A$", A, SW); label("$B$", B, SE); label("$C$", C, NE); label("$D$", D, NW); label("$E$", E, NW); label("$F$", F, NE); label("$G$", G, SE); label("$H$", H, SW); label("$0$", A--B, S); label("$$", B--C, (1,0)); label("$$", C--D, N); label("$1$", D--A, W); label("$1$", E--F, S); label("$0$", F--G, (1,0)); label("$1$", G--H, N); label("$0$", H--E, W); label("$1$", A--E, NW); label("$0$", B--F, NE); label("$$", C--G, SE); label("$0$", D--H, SW); [/asy]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/2/3/9/239244f2a013893f9427e26b2e088f848f198d2b.png)
This goes to:
![[asy] pair A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H; A = (0, 0); B = (12.071,0); C = (12.071,12.071); D = (0,12.071); E = (3.536,3.536); F = (8.536,3.536); G = (8.536,8.536); H = (3.536,8.536); draw(A--B--C--D--A--E--F--G--H--E--F--B--C--G--H--D); label("$A$", A, SW); label("$B$", B, SE); label("$C$", C, NE); label("$D$", D, NW); label("$E$", E, NW); label("$F$", F, NE); label("$G$", G, SE); label("$H$", H, SW); label("$0$", A--B, S); label("$1$", B--C, (1,0)); label("$0$", C--D, N); label("$1$", D--A, W); label("$1$", E--F, S); label("$0$", F--G, (1,0)); label("$1$", G--H, N); label("$0$", H--E, W); label("$1$", A--E, NW); label("$0$", B--F, NE); label("$1$", C--G, SE); label("$0$", D--H, SW); [/asy]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/3/2/c/32c6f62bff10f919433f9339bd966733bef07465.png)
This is the inverse of case 2.1, so this will also have ![]() orientations.
orientations.
Putting Them All Together
We see that if the ![]() edges connecting to
edges connecting to ![]() has two
has two ![]() 's, and one
's, and one ![]() , it would have the same solutions as if it had two
, it would have the same solutions as if it had two ![]() 's, and one
's, and one ![]() . The solutions would just be inverted. As case 2.1 and case 2.2.2 are inverses, and case 2.2.1 has case 1 as an inverse, there would not be any additional solutions.
. The solutions would just be inverted. As case 2.1 and case 2.2.2 are inverses, and case 2.2.1 has case 1 as an inverse, there would not be any additional solutions.
Similarly, if the ![]() edges connecting to
edges connecting to ![]() has three
has three ![]() 's, it would be the same as the inverse of case 1, or case 2.2.1, resulting in no new solutions.
's, it would be the same as the inverse of case 1, or case 2.2.1, resulting in no new solutions.
Putting all the cases together, we have ![]() solutions.
solutions.
~ConcaveTriangle
Solution 4
The problem states the sum of the labels on the edges of each of the ![]() faces of the cube equal to
faces of the cube equal to ![]() . That is, the sum of the labels on the
. That is, the sum of the labels on the ![]() edges of a face is equal to
edges of a face is equal to ![]() . The labels can only be
. The labels can only be ![]() or
or ![]() , meaning
, meaning ![]() edges are labeled
edges are labeled ![]() , the other
, the other ![]() are labeled
are labeled ![]() .
.
This problem can be approached by Graph Coloring of Graph Theory. Note that each face of the cube connects to ![]() other faces, each with a shared edge. We use the following graph to represent the problem. Each vertex represents a face, each edge represent the cube's edge. Each vertex has
other faces, each with a shared edge. We use the following graph to represent the problem. Each vertex represents a face, each edge represent the cube's edge. Each vertex has ![]() edges connecting to
edges connecting to ![]() other vertices. The edges can be colored red or blue, with red as label
other vertices. The edges can be colored red or blue, with red as label ![]() , and blue as label
, and blue as label ![]() . Each vertex must have
. Each vertex must have ![]() red edges and
red edges and ![]() blue edges.
blue edges.
![]() :
: ![]() adjacent red edges from vertex A. There are
adjacent red edges from vertex A. There are ![]() ways to choose
ways to choose ![]() red edges adjacent to each other and connect to
red edges adjacent to each other and connect to ![]() vertices with an edge between them as shown below.
vertices with an edge between them as shown below.
![]() :
: ![]() adjacent red edges from vertex
adjacent red edges from vertex ![]() form a closed loop with a third red edge. There is only
form a closed loop with a third red edge. There is only ![]() case as shown below.
case as shown below.
![]() :
: ![]() adjacent red edges from vertex
adjacent red edges from vertex ![]() does not form a closed loop with a third red edge. There are
does not form a closed loop with a third red edge. There are ![]() cases as shown below.
cases as shown below.
In case ![]() , there are total
, there are total ![]() ways.
ways.
![]() :
: ![]() red edges from vertex
red edges from vertex ![]() with
with ![]() blue edge in between. There are
blue edge in between. There are ![]() ways to choose
ways to choose ![]() red edges with
red edges with ![]() blue edge in between.
blue edge in between.
There are only ![]() cases as shown below.
cases as shown below.
In case ![]() , there are total
, there are total ![]() ways.
ways.
From both case ![]() and case
and case ![]() , there are
, there are ![]() ways in total.
ways in total.
See Also
| 2021 Fall AMC 10A (Problems • Answer Key • Resources) | ||
| Preceded by Problem 23 |
Followed by Problem 25 | |
| 1 • 2 • 3 • 4 • 5 • 6 • 7 • 8 • 9 • 10 • 11 • 12 • 13 • 14 • 15 • 16 • 17 • 18 • 19 • 20 • 21 • 22 • 23 • 24 • 25 | ||
| All AMC 10 Problems and Solutions | ||
The problems on this page are copyrighted by the Mathematical Association of America's American Mathematics Competitions.