Difference between revisions of "Circumradius"
(→Theorem) |
|||
| (62 intermediate revisions by 31 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | The '''circumradius''' of a [[cyclic]] [[polygon]] is the radius of the circumscribed circle of that polygon. For a triangle, it is the measure of the [[radius]] of the [[circle]] that [[circumscribe]]s the triangle. Since every triangle is [[cyclic]], every triangle has a circumscribed circle, or a [[circumcircle]]. | |
| − | + | ==Formula for a Triangle== | |
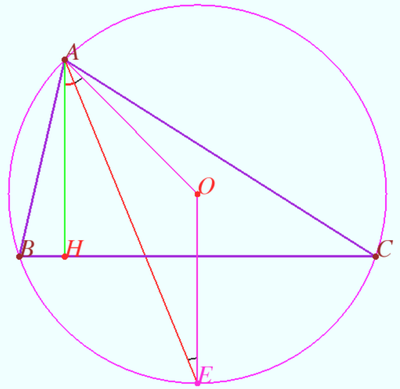
| + | Let <math>a, b</math> and <math>c</math> denote the triangle's three sides and let <math>A</math> denote the area of the triangle. Then, the measure of the circumradius of the triangle is simply <math>R=\frac{abc}{4A}</math>. This can be rewritten as <math>A=\frac{abc}{4R}</math>. | ||
| − | ==Formula== | + | == Proof == |
| − | + | <asy> | |
| + | pair O, A, B, C, D; | ||
| + | O=(0,0); | ||
| + | A=(-5,1); | ||
| + | B=(1,5); | ||
| + | C=(5,1); | ||
| + | dot(O); dot (A); dot (B); dot (C); | ||
| + | draw(circle(O, sqrt(26))); | ||
| + | draw(A--B--C--cycle); | ||
| + | D=-B; dot (D); | ||
| + | draw(B--D--A); | ||
| + | label("$A$", A, W); | ||
| + | label("$B$", B, N); | ||
| + | label("$C$", C, E); | ||
| + | label("$D$", D, S); | ||
| + | label("$O$", O, W); | ||
| + | pair E; | ||
| + | E=foot(B,A,C); | ||
| + | draw(B--E); | ||
| + | dot(E); | ||
| + | label("$E$", E, S); | ||
| + | draw(rightanglemark(B,A,D,20)); | ||
| + | draw(rightanglemark(B,E,C,20)); | ||
| + | </asy> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | We let <math>AB=c</math>, <math>BC=a</math>, <math>AC=b</math>, <math>BE=h</math>, and <math>BO=R</math>. We know that <math>\angle BAD</math> is a right angle because <math>BD</math> is the diameter. Also, <math>\angle ADB = \angle BCA</math> because they both subtend arc <math>AB</math>. Therefore, <math>\triangle BAD \sim \triangle BEC</math> by AA similarity, so we have | ||
| + | <cmath>\frac{BD}{BA} = \frac{BC}{BE},</cmath> or <cmath> \frac {2R} c = \frac ah.</cmath> | ||
| + | However, remember that <math>[ABC] = \frac {bh} 2\implies h=\frac{2 \times [ABC]}b</math>. Substituting this in gives us | ||
| + | <cmath> \frac {2R} c = \frac a{\frac{2 \times [ABC]}b},</cmath> and then simplifying to get | ||
| + | <cmath> R=\frac{abc}{4\times [ABC]}\text{ or }[ABC]=\frac{abc}{4R}</cmath> | ||
| + | and we are done. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Formula for Circumradius== | ||
| + | <math>R = \frac{abc}{4rs}</math> | ||
| + | Where <math>R</math> is the circumradius, <math>r</math> is the inradius, and <math>a</math>, <math>b</math>, and <math>c</math> are the respective sides of the triangle and <math>s = (a+b+c)/2</math> is the semiperimeter. Note that this is similar to the previously mentioned formula; the reason being that <math>A = rs</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | But, if you don't know the inradius, you can find the area of the triangle by [[Heron's Formula|Heron’s Formula]]: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>A=\sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}</math> | ||
| + | ==Circumradius, bisector and altitude== | ||
| + | [[File:R H L angles.png|400px|right]] | ||
| + | Circumradius and altitude are isogonals with respect bisector and vertex of triangle. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Euler's Theorem for a Triangle== | ||
| + | Let <math>\triangle ABC</math> have circumcenter <math>O</math> and incenter <math>I</math>.Then <cmath>OI^2=R(R-2r) \implies R \geq 2r</cmath> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Proof== | ||
| + | |||
| + | See https://www.cut-the-knot.org/triangle/EulerIO.shtml | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Right triangles == | ||
| + | The hypotenuse of the triangle is the diameter of its circumcircle, and the circumcenter is its midpoint, so the circumradius is equal to half of the hypotenuse of the right triangle. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <asy> | ||
| + | pair A,B,C,I; | ||
| + | A=(0,0); | ||
| + | B=(0,3); | ||
| + | C=(4,0); | ||
| + | draw(A--B--C--cycle); | ||
| + | I=circumcenter(A,B,C); | ||
| + | draw(I--A,gray); | ||
| + | label("$r$",(I+A)/2,NW,gray); | ||
| + | draw(circumcircle(A,B,C)); | ||
| + | label("$C$",I,N); | ||
| + | dot(I); | ||
| + | draw(rightanglemark(B,A,C,10)); | ||
| + | </asy> | ||
| + | |||
| + | This results in a well-known theorem: | ||
| + | ===Theorem=== | ||
| + | The midpoint of the hypotenuse is equidistant from the vertices of the right triangle. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Equilateral triangles == | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>R=\frac{s}{\sqrt3}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | where <math>s</math> is the length of a side of the triangle. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <asy> | ||
| + | pair A,B,C,I; | ||
| + | A=(0,0); | ||
| + | B=(1,0); | ||
| + | C=intersectionpoint(arc(A,1,0,90),arc(B,1,90,180)); | ||
| + | draw(A--B--C--cycle); | ||
| + | I=circumcenter(A,B,C); | ||
| + | draw(circumcircle(A,B,C)); | ||
| + | label("$C$",I,E); | ||
| + | dot(I); | ||
| + | label("$s$",A--B,S); | ||
| + | label("$s$",A--C,N); | ||
| + | label("$s$",B--C,N); | ||
| + | </asy> | ||
| + | |||
| + | == If all three sides are known == | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>R=\frac{abc}{\sqrt{(a+b+c)(-a+b+c)(a-b+c)(a+b-c)}}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Which follows from the Heron's Formula and <math>R=\frac{abc}{4A}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == If you know just one side and its opposite angle == | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>2R=\frac{a}{\sin{A}}</math> by the [[Law of Sines]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | (Extended Law of Sines) | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
| − | * [[ | + | * [[Inradius]] |
| − | * [[ | + | * [[Semiperimeter]] |
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Geometry]] | ||
Latest revision as of 18:27, 17 September 2024
The circumradius of a cyclic polygon is the radius of the circumscribed circle of that polygon. For a triangle, it is the measure of the radius of the circle that circumscribes the triangle. Since every triangle is cyclic, every triangle has a circumscribed circle, or a circumcircle.
Contents
Formula for a Triangle
Let ![]() and
and ![]() denote the triangle's three sides and let
denote the triangle's three sides and let ![]() denote the area of the triangle. Then, the measure of the circumradius of the triangle is simply
denote the area of the triangle. Then, the measure of the circumradius of the triangle is simply ![]() . This can be rewritten as
. This can be rewritten as ![]() .
.
Proof
![[asy] pair O, A, B, C, D; O=(0,0); A=(-5,1); B=(1,5); C=(5,1); dot(O); dot (A); dot (B); dot (C); draw(circle(O, sqrt(26))); draw(A--B--C--cycle); D=-B; dot (D); draw(B--D--A); label("$A$", A, W); label("$B$", B, N); label("$C$", C, E); label("$D$", D, S); label("$O$", O, W); pair E; E=foot(B,A,C); draw(B--E); dot(E); label("$E$", E, S); draw(rightanglemark(B,A,D,20)); draw(rightanglemark(B,E,C,20)); [/asy]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/3/a/d/3ad58f915ab8e62f7ffd12a4d01aa92205a280f7.png)
We let ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() . We know that
. We know that ![]() is a right angle because
is a right angle because ![]() is the diameter. Also,
is the diameter. Also, ![]() because they both subtend arc
because they both subtend arc ![]() . Therefore,
. Therefore, ![]() by AA similarity, so we have
by AA similarity, so we have
![]() or
or ![]() However, remember that
However, remember that ![]() . Substituting this in gives us
. Substituting this in gives us
![]() and then simplifying to get
and then simplifying to get
![]() and we are done.
and we are done.
Formula for Circumradius
![]() Where
Where ![]() is the circumradius,
is the circumradius, ![]() is the inradius, and
is the inradius, and ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() are the respective sides of the triangle and
are the respective sides of the triangle and ![]() is the semiperimeter. Note that this is similar to the previously mentioned formula; the reason being that
is the semiperimeter. Note that this is similar to the previously mentioned formula; the reason being that ![]() .
.
But, if you don't know the inradius, you can find the area of the triangle by Heron’s Formula:
![]()
Circumradius, bisector and altitude
Circumradius and altitude are isogonals with respect bisector and vertex of triangle.
Euler's Theorem for a Triangle
Let ![]() have circumcenter
have circumcenter ![]() and incenter
and incenter ![]() .Then
.Then ![]()
Proof
See https://www.cut-the-knot.org/triangle/EulerIO.shtml
Right triangles
The hypotenuse of the triangle is the diameter of its circumcircle, and the circumcenter is its midpoint, so the circumradius is equal to half of the hypotenuse of the right triangle.
![[asy] pair A,B,C,I; A=(0,0); B=(0,3); C=(4,0); draw(A--B--C--cycle); I=circumcenter(A,B,C); draw(I--A,gray); label("$r$",(I+A)/2,NW,gray); draw(circumcircle(A,B,C)); label("$C$",I,N); dot(I); draw(rightanglemark(B,A,C,10)); [/asy]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/7/f/a/7fa53fd535608055e8b16af17f60b76d0766a768.png)
This results in a well-known theorem:
Theorem
The midpoint of the hypotenuse is equidistant from the vertices of the right triangle.
Equilateral triangles
![]()
where ![]() is the length of a side of the triangle.
is the length of a side of the triangle.
![[asy] pair A,B,C,I; A=(0,0); B=(1,0); C=intersectionpoint(arc(A,1,0,90),arc(B,1,90,180)); draw(A--B--C--cycle); I=circumcenter(A,B,C); draw(circumcircle(A,B,C)); label("$C$",I,E); dot(I); label("$s$",A--B,S); label("$s$",A--C,N); label("$s$",B--C,N); [/asy]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/c/a/1/ca10ddc9a1840bd3a175658125dfc16d353a3b39.png)
If all three sides are known
![]()
Which follows from the Heron's Formula and ![]() .
.
If you know just one side and its opposite angle
![]() by the Law of Sines.
by the Law of Sines.
(Extended Law of Sines)