Difference between revisions of "1990 AIME Problems/Problem 14"
m (→See also: 3d asy needed ..) |
(replace with 3D asymptote .. draw sphere?) |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
== Solution == | == Solution == | ||
=== Solution 1 === | === Solution 1 === | ||
| − | + | <center><asy> | |
| + | import three; pointpen = black; pathpen = black+linewidth(0.7); pen small = fontsize(9); | ||
| + | currentprojection = perspective(20,-20,12); | ||
| + | triple O=(0,0,0),A=(0,399^.5,0),D=(108^.5,0,0),C=(-108^.5,0,0); | ||
| + | pair CENTER=circumcenter((A.x,A.y),(C.x,C.y),(D.x,D.y)); | ||
| + | triple P=(CENTER.x,CENTER.y,99/133^.5); /*, Pa=(P.x,P.y,0); | ||
| + | D(P--Pa--A);D(C--Pa--D); */ | ||
| + | D((C+D)/2--A--C--D--P--C--P--A--D); | ||
| + | MP("A",A,NE);MP("P",P,N);MP("C",C);MP("D",D); | ||
| + | MP("13\sqrt{3}",(A+D)/2,E,small);MP("13\sqrt{3}",(A+C)/2,N,small);MP("12\sqrt{3}",(C+D)/2,SW,small); | ||
| + | </asy></center> <!-- Asymptote replacement for Image:1990_AIME-14b.png by azjps --> | ||
| − | Our triangular pyramid has base <math>12\sqrt{3} - 13\sqrt{3} - 13\sqrt{3} \triangle</math>. The area of this isosceles triangle is easy to find by <math>\frac{1}{2}bh</math>, where we can find <math> | + | Our triangular pyramid has base <math>12\sqrt{3} - 13\sqrt{3} - 13\sqrt{3} \triangle</math>. The area of this isosceles triangle is easy to find by <math>[ACD] = \frac{1}{2}bh</math>, where we can find <math>h_{ACD}</math> to be <math>\sqrt{399}</math> by the [[Pythagorean Theorem]]. Thus <math>A = \frac 12(12\sqrt{3})\sqrt{399} = 18\sqrt{133}</math>. |
| − | + | <center><asy> | |
| + | size(280); | ||
| + | import three; pointpen = black; pathpen = black+linewidth(0.7); pen small = fontsize(9); | ||
| + | real h=169/2*(3/133)^.5; currentprojection = perspective(20,-20,12); | ||
| + | triple O=(0,0,0),A=(0,399^.5,0),D=(108^.5,0,0),C=(-108^.5,0,0); | ||
| + | pair CENTER=circumcenter((A.x,A.y),(C.x,C.y),(D.x,D.y)); | ||
| + | triple P=(CENTER.x,CENTER.y,99/133^.5), Pa=(P.x,P.y,0); | ||
| + | D(A--C--D--P--C--P--A--D); | ||
| + | D(P--Pa--A);D(C--Pa--D);D(circle(Pa,h)); | ||
| + | MP("A",A,NE);MP("C",C,NW);MP("D",D);MP("P",P,N);MP("P'",Pa,SW); | ||
| + | MP("13\sqrt{3}",(A+D)/2,E,small);MP("13\sqrt{3}",(A+C)/2,NW,small);MP("12\sqrt{3}",(C+D)/2,SW,small); | ||
| + | MP("h",(P--Pa)/2,W);MP("\frac{\sqrt{939}}2",(C+P)/2,NW); | ||
| + | </asy></center> <!-- Asymptote replacement for Image:1990_AIME-14c.png by azjps --> | ||
| − | To find the volume, we want to use the equation <math>\frac 13Bh = 6\sqrt{133}h</math>, so we need to find the height of the [[tetrahedron]]. By the Pythagorean Theorem, <math>AP = CP = DP = \frac{\sqrt{939}}{2}</math>. If we let <math>P</math> be the center of a [[sphere]] with radius <math>\frac{\sqrt{939}}{2}</math>, then <math>A,C,D</math> lie on the sphere. The cross section of the sphere is a circle, and the center of that circle is the foot of the [[perpendicular]] from the center of the sphere. Hence the foot of the height we want to find occurs at the [[circumcenter]] of <math>\triangle ACD</math>. | + | To find the volume, we want to use the equation <math>\frac 13Bh = 6\sqrt{133}h</math>, so we need to find the height of the [[tetrahedron]]. By the Pythagorean Theorem, <math>AP = CP = DP = \frac{\sqrt{939}}{2}</math>. If we let <math>P</math> be the center of a [[sphere]] with radius <math>\frac{\sqrt{939}}{2}</math>, then <math>A,C,D</math> lie on the sphere. The cross section of the sphere that contains <math>A,C,D</math> is a circle, and the center of that circle is the foot of the [[perpendicular]] from the center of the sphere. Hence the foot of the height we want to find occurs at the [[circumcenter]] of <math>\triangle ACD</math>. |
| − | From here we just need to perform some brutish calculations. Using the formula <math>A = 18\sqrt{133} = \frac{abc}{4R}</math> (<math>R</math> | + | From here we just need to perform some brutish calculations. Using the formula <math>A = 18\sqrt{133} = \frac{abc}{4R}</math> (where <math>R</math> is the [[circumradius]]), we find <math>R = \frac{12\sqrt{3} \cdot (13\sqrt{3})^2}{4\cdot 18\sqrt{133}} = \frac{13^2\sqrt{3}}{2\sqrt{133}}</math> (there are slightly [[Law of Sines|simpler ways]] to calculate <math>R</math> since we have an isosceles triangle). By the Pythagorean Theorem, |
| − | < | + | <center><math>\begin{align*}h^2 &= PA^2 - R^2 \\ |
| − | &= | + | &= \left(\frac{\sqrt{939}}{2}\right)^2 - \left(\frac{13^2\sqrt{3}}{2\sqrt{133}}\right)^2\\ |
| − | &= | + | &= \frac{939 \cdot 133 - 13^4 \cdot 3}{4 \cdot 133} = \frac{13068 \cdot 3}{4 \cdot 133} = \frac{99^2}{133}\\ |
| − | + | h &= \frac{99}{\sqrt{133}} | |
| − | h &= | + | \end{align*}</math></center> |
| − | \end{ | ||
Finally, we substitute <math>h</math> into the volume equation to find <math>V = 6\sqrt{133}\left(\frac{99}{\sqrt{133}}\right) = \boxed{594}</math>. | Finally, we substitute <math>h</math> into the volume equation to find <math>V = 6\sqrt{133}\left(\frac{99}{\sqrt{133}}\right) = \boxed{594}</math>. | ||
| Line 29: | Line 50: | ||
Let <math>\triangle{ABC}</math> (or the triangle with sides <math>12\sqrt {3}</math>, <math>13\sqrt {3}</math>, <math>13\sqrt {3}</math>) be the base of our tetrahedron. We set points <math>B</math> and <math>C</math> as <math>(6\sqrt {3}, 0, 0)</math> and <math>( - 6\sqrt {3}, 0, 0)</math>, respectively. Using Pythagoras, we find <math>A</math> as <math>(0, \sqrt {399}, 0)</math>. We know that the [[vertex]] of the tetrahedron (<math>D</math>) has to be of the form <math>(x, y, z)</math>, where <math>z</math> is the [[altitude]] of the tetrahedron. Since the distance from <math>D</math> to points <math>A</math>, <math>B</math>, and <math>C</math> is <math>\frac {\sqrt {939}}{2}</math>, we can write three equations using the [[distance formula]]: | Let <math>\triangle{ABC}</math> (or the triangle with sides <math>12\sqrt {3}</math>, <math>13\sqrt {3}</math>, <math>13\sqrt {3}</math>) be the base of our tetrahedron. We set points <math>B</math> and <math>C</math> as <math>(6\sqrt {3}, 0, 0)</math> and <math>( - 6\sqrt {3}, 0, 0)</math>, respectively. Using Pythagoras, we find <math>A</math> as <math>(0, \sqrt {399}, 0)</math>. We know that the [[vertex]] of the tetrahedron (<math>D</math>) has to be of the form <math>(x, y, z)</math>, where <math>z</math> is the [[altitude]] of the tetrahedron. Since the distance from <math>D</math> to points <math>A</math>, <math>B</math>, and <math>C</math> is <math>\frac {\sqrt {939}}{2}</math>, we can write three equations using the [[distance formula]]: | ||
| − | < | + | <center><math>\begin{eqnarray*} |
x^{2} + (y - \sqrt {399})^{2} + z^{2} &=& \frac {939}{4}\\ | x^{2} + (y - \sqrt {399})^{2} + z^{2} &=& \frac {939}{4}\\ | ||
(x - 6\sqrt {3})^{2} + y^{2} + z^{2} &=& \frac {939}{4}\\ | (x - 6\sqrt {3})^{2} + y^{2} + z^{2} &=& \frac {939}{4}\\ | ||
(x + 6\sqrt {3})^{2} + y^{2} + z^{2} &=& \frac {939}{4} | (x + 6\sqrt {3})^{2} + y^{2} + z^{2} &=& \frac {939}{4} | ||
| − | \end{eqnarray*}</ | + | \end{eqnarray*}</math></center> |
Subtracting the last two equations, we get <math>x = 0</math>. Solving for <math>y,z</math> with a bit of effort, we eventually get <math>x = 0</math>, <math>y = \frac {291}{2\sqrt {399}}</math>, <math>z = \frac {99}{\sqrt {133}}</math>. | Subtracting the last two equations, we get <math>x = 0</math>. Solving for <math>y,z</math> with a bit of effort, we eventually get <math>x = 0</math>, <math>y = \frac {291}{2\sqrt {399}}</math>, <math>z = \frac {99}{\sqrt {133}}</math>. | ||
Revision as of 20:47, 24 April 2008
Problem
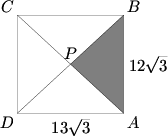
The rectangle ![]() below has dimensions
below has dimensions ![]() and
and ![]() . Diagonals
. Diagonals ![]() and
and ![]() intersect at
intersect at ![]() . If triangle
. If triangle ![]() is cut out and removed, edges
is cut out and removed, edges ![]() and
and ![]() are joined, and the figure is then creased along segments
are joined, and the figure is then creased along segments ![]() and
and ![]() , we obtain a triangular pyramid, all four of whose faces are isosceles triangles. Find the volume of this pyramid.
, we obtain a triangular pyramid, all four of whose faces are isosceles triangles. Find the volume of this pyramid.
Solution
Solution 1
import three; pointpen = black; pathpen = black+linewidth(0.7); pen small = fontsize(9);
currentprojection = perspective(20,-20,12);
triple O=(0,0,0),A=(0,399^.5,0),D=(108^.5,0,0),C=(-108^.5,0,0);
pair CENTER=circumcenter((A.x,A.y),(C.x,C.y),(D.x,D.y));
triple P=(CENTER.x,CENTER.y,99/133^.5); /*, Pa=(P.x,P.y,0);
D(P--Pa--A);D(C--Pa--D); */
D((C+D)/2--A--C--D--P--C--P--A--D);
MP("A",A,NE);MP("P",P,N);MP("C",C);MP("D",D);
MP("13\sqrt{3}",(A+D)/2,E,small);MP("13\sqrt{3}",(A+C)/2,N,small);MP("12\sqrt{3}",(C+D)/2,SW,small);
(Error making remote request. Unknown error_msg)Our triangular pyramid has base ![]() . The area of this isosceles triangle is easy to find by
. The area of this isosceles triangle is easy to find by ![]() , where we can find
, where we can find ![]() to be
to be ![]() by the Pythagorean Theorem. Thus
by the Pythagorean Theorem. Thus ![]() .
.
size(280);
import three; pointpen = black; pathpen = black+linewidth(0.7); pen small = fontsize(9);
real h=169/2*(3/133)^.5; currentprojection = perspective(20,-20,12);
triple O=(0,0,0),A=(0,399^.5,0),D=(108^.5,0,0),C=(-108^.5,0,0);
pair CENTER=circumcenter((A.x,A.y),(C.x,C.y),(D.x,D.y));
triple P=(CENTER.x,CENTER.y,99/133^.5), Pa=(P.x,P.y,0);
D(A--C--D--P--C--P--A--D);
D(P--Pa--A);D(C--Pa--D);D(circle(Pa,h));
MP("A",A,NE);MP("C",C,NW);MP("D",D);MP("P",P,N);MP("P'",Pa,SW);
MP("13\sqrt{3}",(A+D)/2,E,small);MP("13\sqrt{3}",(A+C)/2,NW,small);MP("12\sqrt{3}",(C+D)/2,SW,small);
MP("h",(P--Pa)/2,W);MP("\frac{\sqrt{939}}2",(C+P)/2,NW);
(Error making remote request. Unknown error_msg)To find the volume, we want to use the equation ![]() , so we need to find the height of the tetrahedron. By the Pythagorean Theorem,
, so we need to find the height of the tetrahedron. By the Pythagorean Theorem, ![]() . If we let
. If we let ![]() be the center of a sphere with radius
be the center of a sphere with radius ![]() , then
, then ![]() lie on the sphere. The cross section of the sphere that contains
lie on the sphere. The cross section of the sphere that contains ![]() is a circle, and the center of that circle is the foot of the perpendicular from the center of the sphere. Hence the foot of the height we want to find occurs at the circumcenter of
is a circle, and the center of that circle is the foot of the perpendicular from the center of the sphere. Hence the foot of the height we want to find occurs at the circumcenter of ![]() .
.
From here we just need to perform some brutish calculations. Using the formula ![]() (where
(where ![]() is the circumradius), we find
is the circumradius), we find ![]() (there are slightly simpler ways to calculate
(there are slightly simpler ways to calculate ![]() since we have an isosceles triangle). By the Pythagorean Theorem,
since we have an isosceles triangle). By the Pythagorean Theorem,
&= \left(\frac{\sqrt{939}}{2}\right)^2 - \left(\frac{13^2\sqrt{3}}{2\sqrt{133}}\right)^2\\ &= \frac{939 \cdot 133 - 13^4 \cdot 3}{4 \cdot 133} = \frac{13068 \cdot 3}{4 \cdot 133} = \frac{99^2}{133}\\ h &= \frac{99}{\sqrt{133}}
\end{align*}$ (Error compiling LaTeX. Unknown error_msg)Finally, we substitute ![]() into the volume equation to find
into the volume equation to find ![]() .
.
Solution 2
Let ![]() (or the triangle with sides
(or the triangle with sides ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ) be the base of our tetrahedron. We set points
) be the base of our tetrahedron. We set points ![]() and
and ![]() as
as ![]() and
and ![]() , respectively. Using Pythagoras, we find
, respectively. Using Pythagoras, we find ![]() as
as ![]() . We know that the vertex of the tetrahedron (
. We know that the vertex of the tetrahedron (![]() ) has to be of the form
) has to be of the form ![]() , where
, where ![]() is the altitude of the tetrahedron. Since the distance from
is the altitude of the tetrahedron. Since the distance from ![]() to points
to points ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() is
is ![]() , we can write three equations using the distance formula:
, we can write three equations using the distance formula:
x^{2} + (y - \sqrt {399})^{2} + z^{2} &=& \frac {939}{4}\\ (x - 6\sqrt {3})^{2} + y^{2} + z^{2} &=& \frac {939}{4}\\ (x + 6\sqrt {3})^{2} + y^{2} + z^{2} &=& \frac {939}{4}
\end{eqnarray*}$ (Error compiling LaTeX. Unknown error_msg)Subtracting the last two equations, we get ![]() . Solving for
. Solving for ![]() with a bit of effort, we eventually get
with a bit of effort, we eventually get ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() .
Since the area of a triangle is
.
Since the area of a triangle is ![]() , we have the base area as
, we have the base area as ![]() . Thus, the volume is
. Thus, the volume is ![]() .
.
See also
| 1990 AIME (Problems • Answer Key • Resources) | ||
| Preceded by Problem 13 |
Followed by Problem 15 | |
| 1 • 2 • 3 • 4 • 5 • 6 • 7 • 8 • 9 • 10 • 11 • 12 • 13 • 14 • 15 | ||
| All AIME Problems and Solutions | ||