Difference between revisions of "2016 AIME II Problems/Problem 10"
(→Solution) |
Wuwang2002 (talk | contribs) (→fixing "fixed" latex) |
||
| (33 intermediate revisions by 18 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | ==Problem== | ||
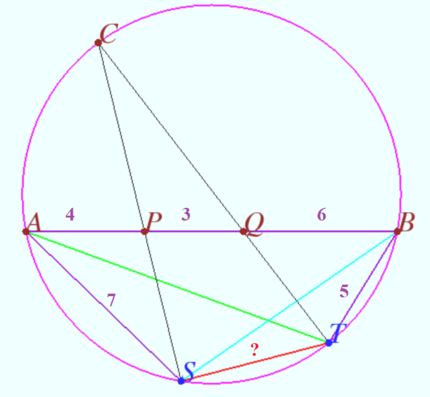
Triangle <math>ABC</math> is inscribed in circle <math>\omega</math>. Points <math>P</math> and <math>Q</math> are on side <math>\overline{AB}</math> with <math>AP<AQ</math>. Rays <math>CP</math> and <math>CQ</math> meet <math>\omega</math> again at <math>S</math> and <math>T</math> (other than <math>C</math>), respectively. If <math>AP=4,PQ=3,QB=6,BT=5,</math> and <math>AS=7</math>, then <math>ST=\frac{m}{n}</math>, where <math>m</math> and <math>n</math> are relatively prime positive integers. Find <math>m+n</math>. | Triangle <math>ABC</math> is inscribed in circle <math>\omega</math>. Points <math>P</math> and <math>Q</math> are on side <math>\overline{AB}</math> with <math>AP<AQ</math>. Rays <math>CP</math> and <math>CQ</math> meet <math>\omega</math> again at <math>S</math> and <math>T</math> (other than <math>C</math>), respectively. If <math>AP=4,PQ=3,QB=6,BT=5,</math> and <math>AS=7</math>, then <math>ST=\frac{m}{n}</math>, where <math>m</math> and <math>n</math> are relatively prime positive integers. Find <math>m+n</math>. | ||
| − | ==Solution== | + | |
| + | ==Solution 1== | ||
<asy> | <asy> | ||
import cse5; | import cse5; | ||
| Line 35: | Line 37: | ||
Now Law of Sines on <math>\triangle ACS</math>, <math>\triangle SCT</math>, and <math>\triangle TCB</math> yields <cmath>\dfrac{AS}{\sin\alpha}=\dfrac{ST}{\sin\beta}=\dfrac{TB}{\sin\gamma}.</cmath>Hence <cmath>\dfrac{ST^2}{\sin^2\beta}=\dfrac{TB\cdot AS}{\sin\alpha\sin\gamma},</cmath>so <cmath>TS^2=TB\cdot AS\left(\dfrac{\sin\beta}{\sin\alpha}\dfrac{\sin\beta}{\sin\gamma}\right)=\dfrac{15\cdot 21}{24^2}\cdot 5\cdot 7=\dfrac{35^2}{8^2}.</cmath>Hence <math>ST=\tfrac{35}8</math> and the requested answer is <math>35+8=\boxed{43}</math>. | Now Law of Sines on <math>\triangle ACS</math>, <math>\triangle SCT</math>, and <math>\triangle TCB</math> yields <cmath>\dfrac{AS}{\sin\alpha}=\dfrac{ST}{\sin\beta}=\dfrac{TB}{\sin\gamma}.</cmath>Hence <cmath>\dfrac{ST^2}{\sin^2\beta}=\dfrac{TB\cdot AS}{\sin\alpha\sin\gamma},</cmath>so <cmath>TS^2=TB\cdot AS\left(\dfrac{\sin\beta}{\sin\alpha}\dfrac{\sin\beta}{\sin\gamma}\right)=\dfrac{15\cdot 21}{24^2}\cdot 5\cdot 7=\dfrac{35^2}{8^2}.</cmath>Hence <math>ST=\tfrac{35}8</math> and the requested answer is <math>35+8=\boxed{43}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Edit: Note that the finish is much simpler. Once you get <math>\dfrac{AS}{\sin\alpha}=\dfrac{ST}{\sin\beta}</math>, you can solve quickly from there getting <math>ST=\dfrac{AS \sin(\beta)}{\sin(\alpha)}=7\cdot \dfrac{15}{24}=\dfrac{35}{8}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Solution 2 (Projective Geometry)== | ||
| + | [[File:2016 AIME II 10c.png|400px|right]] | ||
| + | Projecting through <math>C</math> we have <cmath>\frac{3}{4}\times \frac{13}{6}=(A,Q;P,B)\stackrel{C}{=}(A,T;S,B)=\frac{ST}{7}\times \frac{13}{5}</cmath> which easily gives <math>ST=\frac{35}{8}\Longrightarrow 35+8=\boxed{043}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Solution 3== | ||
| + | By Ptolemy's Theorem applied to quadrilateral <math>ASTB</math>, we find | ||
| + | <cmath>5\cdot 7+13\cdot ST=AT\cdot BS.</cmath> | ||
| + | Therefore, in order to find <math>ST</math>, it suffices to find <math>AT\cdot BS</math>. We do this using similar triangles, which can be found by using Power of a Point theorem. | ||
| + | |||
| + | As <math>\triangle APS\sim \triangle CPB</math>, we find | ||
| + | <cmath>\frac{4}{PC}=\frac{7}{BC}.</cmath> | ||
| + | Therefore, <math>\frac{BC}{PC}=\frac{7}{4}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | As <math>\triangle BQT\sim\triangle CQA</math>, we find | ||
| + | <cmath>\frac{6}{CQ}=\frac{5}{AC}.</cmath> | ||
| + | Therefore, <math>\frac{AC}{CQ}=\frac{5}{6}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | As <math>\triangle ATQ\sim\triangle CBQ</math>, we find | ||
| + | <cmath>\frac{AT}{BC}=\frac{7}{CQ}.</cmath> | ||
| + | Therefore, <math>AT=\frac{7\cdot BC}{CQ}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | As <math>\triangle BPS\sim \triangle CPA</math>, we find | ||
| + | <cmath>\frac{9}{PC}=\frac{BS}{AC}.</cmath> | ||
| + | Therefore, <math>BS=\frac{9\cdot AC}{PC}</math>. Thus we find | ||
| + | <cmath>AT\cdot BS=\left(\frac{7\cdot BC}{CQ}\right)\left(\frac{9\cdot AC}{PC}\right).</cmath> | ||
| + | But now we can substitute in our previously found values for <math>\frac{BC}{PC}</math> and <math>\frac{AC}{CQ}</math>, finding | ||
| + | <cmath>AT\cdot BS=63\cdot \frac{7}{4}\cdot \frac{5}{6}=\frac{21\cdot 35}{8}.</cmath> | ||
| + | Substituting this into our original expression from Ptolemy's Theorem, we find | ||
| + | <cmath>\begin{align*}35+13ST&=\frac{21\cdot 35}{8}\\13ST&=\frac{13\cdot 35}{8}\\ST&=\frac{35}{8}.\end{align*}</cmath> | ||
| + | Thus the answer is <math>\boxed{43}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Solution 4 == | ||
| + | Extend <math>\overline{AB}</math> past <math>B</math> to point <math>X</math> so that <math>CPTX</math> is cyclic. Then, by Power of a Point on <math>CPTX</math>, <math>(CQ)(QT) = (PQ)(QX)</math>. By Power of a Point on <math>CATB</math>, <math>(CQ)(QT) = (AQ)(QB) = 42</math>. Thus, <math>(PQ)(QX) = 42</math>, so <math>BX = 8</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | By the Inscribed Angle Theorem on <math>CPTX</math>, <math>\angle SCT = \angle BXT</math>. By the Inscribed Angle Theorem on <math>ASTC</math>, <math>\angle SCT = \angle SAT</math>, so <math>\angle BXT = \angle SAT</math>. Since <math>ASTB</math> is cyclic, <math>\angle AST = \angle TBX</math>. Thus, <math>\triangle AST \sim \triangle XBT</math>, so <math>AS/XB = ST/BT</math>. Solving for <math>ST</math> yields <math>ST = \frac{35}{8}</math>, for a final answer of <math>35+8 = \boxed{043}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ~ Leo.Euler | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Solution 5 (5 = 2 + 3)== | ||
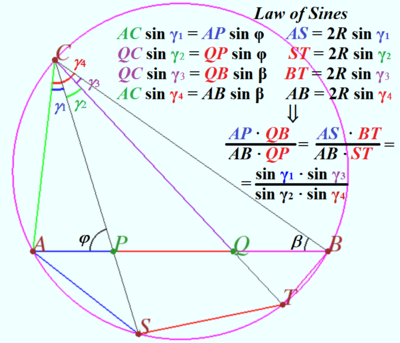
| + | [[File:2016 AIME II 10.png|430px|right]] | ||
| + | By Ptolemy's Theorem applied to quadrilateral <math>ASTB</math>, we find | ||
| + | <cmath>AS\cdot BT+AB\cdot ST=AT\cdot BS.</cmath> | ||
| + | Projecting through <math>C</math> we have | ||
| + | <cmath>\frac{AQ \cdot PB}{PQ \cdot AB} = (A,Q; P,B)\stackrel{C}{=}(A,T; S,B)=\frac{AT \cdot BS}{ST \cdot AB}. </cmath> | ||
| + | Therefore <cmath>AT \cdot BS = \frac {AQ \cdot PB}{PQ} \times ST \implies</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>\left(\frac {AQ \cdot PB}{PQ} - AB\right)\times ST = AS \cdot BT \implies</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>ST = \frac {AS \cdot BT \cdot PQ}{AQ \cdot PB – AB \cdot PQ}</cmath> | ||
| + | <cmath>ST = \frac {7\cdot 5 \cdot 3}{7\cdot 9 – 13 \cdot 3 } = \frac {35}{8} \implies 35 + 8 = \boxed {43}.</cmath> | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Solution 6== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Connect <math>AT</math> and <math>\angle{SCT}=\angle{SAT}, \angle{ACS}=\angle{ATS}, \frac{ST}{\sin \angle{SAT}}=\frac{AS}{\sin \angle{ATS}}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | So we need to get the ratio of <math>\frac{\sin \angle{ACS}}{\sin \angle{SCT}}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | By clear observation <math>\triangle{CAQ}\sim \triangle{BTQ}</math>, we have <math>\frac{CQ}{AC}=\frac{6}{5}</math>, LOS tells <math>\frac{AC}{\sin \angle{CPA}}=\frac{4}{\sin \angle{ACS}}; \frac{CQ}{\sin \angle{CPQ}}=\frac{3}{\sin \angle{PCQ}}</math> so we get <math>\frac{\sin \angle{PCQ}}{\sin \angle{ACS}}=\frac{5}{8}</math>, the desired answer is <math>7\cdot \frac{\sin \angle{SAT}}{\sin \angle{ATS}}=\frac{35}{8}</math> leads to <math>\boxed{043}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ~blusoul | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Solution 7 (no trig or projections)== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Note that since <math>\triangle SAP~\triangle BCP</math>, <math>\frac{9}{SP}=\frac{BC}{7}=\frac{PC}{4}</math>. Furthermore, since <math>\triangle ACQ~\triangle TBQ</math>, we have <math>\frac{7}{TQ}=\frac{AC}{5}=\frac{QC}{6}</math>. From Stewart's on triangle <math>BCP</math>, we have <math>25CQ+BC^2\cdot TQ=TQ\cdot CQ\cdot TC+36TC</math>, and since <math>TQ\cdot CQ=6\cdot7=42</math> by power of a point, this simplifies to <math>25CQ+BC^2\cdot TQ=78TC</math>. Similarly, <math>49CP+AC^2\cdot SP=52SC</math>. Finally, using Ptolemy's on quadrilateral <math>ACBS</math> yields <math>13SC=7BC+SB\cdot AC</math>, and using Ptolemy's on quadrilateral <math>ACBT</math> yields <math>13TC=5AC+TA\cdot BC</math>. From Ptolemy's on <math>ABTS</math>, we find <math>SB\cdot TA=13ST+35</math>, which is nice because it contains <math>ST</math>. | ||
| + | We return to our first Stewart's equation: <math>25CQ+BC^2\cdot TQ=78TC</math>, and we notice that <math>CQ</math> and <math>TQ</math> can be related to <math>AC</math> using our similar triangle conditions. Substituting gives us <math>30AC+\frac{35BC^2}{AC}=78TC</math>, which by four times our first Ptolemy's equation also equals <math>30AC+6TA\cdot BC</math>. Thus, <math>\frac{35BC^2}{AC}=6TA\cdot BC</math> and <math>TA=\frac{35}{6}\cdot\frac{BC}{AC}</math>. Similarly, from our other Stewart's equation, we find <math>28BC+\frac{63AC^2}{BC}=52SC=28BC+4SB\cdot AC</math>, or <math>SB=\frac{63}{4}\cdot\frac{AC}{BC}</math>. Plugging this into our final Ptolemy's equation, we find <cmath>SB\cdot TA=13ST+35\Longrightarrow\frac{35\cdot63}{6\cdot4}=13ST+35\Longrightarrow ST=\frac{\frac{35\cdot21}{8}-35}{13}=\frac{35\cdot\frac{13}{8}}{13}=\frac{35}{8},</cmath>giving us our final answer of <math>\boxed{043}</math>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ~wuwang2002 | ||
| + | |||
| + | == See also == | ||
| + | {{AIME box|year=2016|n=II|num-b=9|num-a=11}} | ||
| + | {{MAA Notice}} | ||
Latest revision as of 22:49, 22 November 2024
Contents
Problem
Triangle ![]() is inscribed in circle
is inscribed in circle ![]() . Points
. Points ![]() and
and ![]() are on side
are on side ![]() with
with ![]() . Rays
. Rays ![]() and
and ![]() meet
meet ![]() again at
again at ![]() and
and ![]() (other than
(other than ![]() ), respectively. If
), respectively. If ![]() and
and ![]() , then
, then ![]() , where
, where ![]() and
and ![]() are relatively prime positive integers. Find
are relatively prime positive integers. Find ![]() .
.
Solution 1
![[asy] import cse5; pathpen = black; pointpen = black; pointfontsize = 9; size(8cm); pair A = origin, B = (13,0), P = (4,0), Q = (7,0), T = B + 5 dir(220), C = IP(circumcircle(A,B,T),Line(T,Q,-0.1,10)), S = IP(circumcircle(A,B,C),Line(C,P,-0.1,10)); Drawing(A--B--C--cycle); D(circumcircle(A,B,C),rgb(0,0.6,1)); DrawPathArray(C--S^^C--T,rgb(1,0.4,0.1)); DrawPathArray(A--S^^B--T,rgb(0,0.4,0)); D(S--T,rgb(1,0.2,0.4)); D("A",A,dir(215)); D("B",B,dir(330)); D("P",P,dir(240)); D("Q",Q,dir(240)); D("T",T,dir(290)); D("C",C,dir(120)); D("S",S,dir(250)); MP("4",(A+P)/2,dir(90)); MP("3",(P+Q)/2,dir(90)); MP("6",(Q+B)/2,dir(90)); MP("5",(B+T)/2,dir(140)); MP("7",(A+S)/2,dir(40)); [/asy]](http://latex.artofproblemsolving.com/f/6/0/f603df291461fa6afd0563d94abdc2644aeb97ec.png) Let
Let ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() . Note that since
. Note that since ![]() we have
we have ![]() , so by the Ratio Lemma
, so by the Ratio Lemma ![]() Similarly, we can deduce
Similarly, we can deduce ![]() and hence
and hence ![]() .
.
Now Law of Sines on ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() yields
yields ![]() Hence
Hence ![]() so
so ![]() Hence
Hence ![]() and the requested answer is
and the requested answer is ![]() .
.
Edit: Note that the finish is much simpler. Once you get ![]() , you can solve quickly from there getting
, you can solve quickly from there getting ![]() .
.
Solution 2 (Projective Geometry)
Projecting through ![]() we have
we have ![]() which easily gives
which easily gives ![]() .
.
Solution 3
By Ptolemy's Theorem applied to quadrilateral ![]() , we find
, we find
![]() Therefore, in order to find
Therefore, in order to find ![]() , it suffices to find
, it suffices to find ![]() . We do this using similar triangles, which can be found by using Power of a Point theorem.
. We do this using similar triangles, which can be found by using Power of a Point theorem.
As ![]() , we find
, we find
![]() Therefore,
Therefore, ![]() .
.
As ![]() , we find
, we find
![]() Therefore,
Therefore, ![]() .
.
As ![]() , we find
, we find
![]() Therefore,
Therefore, ![]() .
.
As ![]() , we find
, we find
![]() Therefore,
Therefore, ![]() . Thus we find
. Thus we find
![]() But now we can substitute in our previously found values for
But now we can substitute in our previously found values for ![]() and
and ![]() , finding
, finding
![]() Substituting this into our original expression from Ptolemy's Theorem, we find
Substituting this into our original expression from Ptolemy's Theorem, we find
 Thus the answer is
Thus the answer is ![]() .
.
Solution 4
Extend ![]() past
past ![]() to point
to point ![]() so that
so that ![]() is cyclic. Then, by Power of a Point on
is cyclic. Then, by Power of a Point on ![]() ,
, ![]() . By Power of a Point on
. By Power of a Point on ![]() ,
, ![]() . Thus,
. Thus, ![]() , so
, so ![]() .
.
By the Inscribed Angle Theorem on ![]() ,
, ![]() . By the Inscribed Angle Theorem on
. By the Inscribed Angle Theorem on ![]() ,
, ![]() , so
, so ![]() . Since
. Since ![]() is cyclic,
is cyclic, ![]() . Thus,
. Thus, ![]() , so
, so ![]() . Solving for
. Solving for ![]() yields
yields ![]() , for a final answer of
, for a final answer of ![]() .
.
~ Leo.Euler
Solution 5 (5 = 2 + 3)
By Ptolemy's Theorem applied to quadrilateral ![]() , we find
, we find
![]() Projecting through
Projecting through ![]() we have
we have
![]() Therefore
Therefore ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
vladimir.shelomovskii@gmail.com, vvsss
Solution 6
Connect ![]() and
and ![]()
So we need to get the ratio of ![]()
By clear observation ![]() , we have
, we have ![]() , LOS tells
, LOS tells ![]() so we get
so we get ![]() , the desired answer is
, the desired answer is ![]() leads to
leads to ![]()
~blusoul
Solution 7 (no trig or projections)
Note that since ![]() ,
, ![]() . Furthermore, since
. Furthermore, since ![]() , we have
, we have ![]() . From Stewart's on triangle
. From Stewart's on triangle ![]() , we have
, we have ![]() , and since
, and since ![]() by power of a point, this simplifies to
by power of a point, this simplifies to ![]() . Similarly,
. Similarly, ![]() . Finally, using Ptolemy's on quadrilateral
. Finally, using Ptolemy's on quadrilateral ![]() yields
yields ![]() , and using Ptolemy's on quadrilateral
, and using Ptolemy's on quadrilateral ![]() yields
yields ![]() . From Ptolemy's on
. From Ptolemy's on ![]() , we find
, we find ![]() , which is nice because it contains
, which is nice because it contains ![]() .
We return to our first Stewart's equation:
.
We return to our first Stewart's equation: ![]() , and we notice that
, and we notice that ![]() and
and ![]() can be related to
can be related to ![]() using our similar triangle conditions. Substituting gives us
using our similar triangle conditions. Substituting gives us ![]() , which by four times our first Ptolemy's equation also equals
, which by four times our first Ptolemy's equation also equals ![]() . Thus,
. Thus, ![]() and
and ![]() . Similarly, from our other Stewart's equation, we find
. Similarly, from our other Stewart's equation, we find ![]() , or
, or ![]() . Plugging this into our final Ptolemy's equation, we find
. Plugging this into our final Ptolemy's equation, we find ![]() giving us our final answer of
giving us our final answer of ![]() .
.
~wuwang2002
See also
| 2016 AIME II (Problems • Answer Key • Resources) | ||
| Preceded by Problem 9 |
Followed by Problem 11 | |
| 1 • 2 • 3 • 4 • 5 • 6 • 7 • 8 • 9 • 10 • 11 • 12 • 13 • 14 • 15 | ||
| All AIME Problems and Solutions | ||
The problems on this page are copyrighted by the Mathematical Association of America's American Mathematics Competitions.