Difference between revisions of "Pentagon"
Jbatterson (talk | contribs) (→The Golden Ratio) |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
# <math>AGHIJ</math> is a regular pentagon. | # <math>AGHIJ</math> is a regular pentagon. | ||
| − | ==The Golden Ratio | + | ==The Golden Ratio== |
| − | The pentagon is closely associated with the [[Golden Ratio]]. More specifically, the ratio of a diagonal to an edge is <math>\frac{1+\sqrt{5}}{2}</math>. | + | The pentagon is closely associated with the [[Golden Ratio]]. More specifically, the ratio of a diagonal to an edge is <math>\frac{1+\sqrt{5}}{2}</math>. |
== See Also == | == See Also == | ||
Latest revision as of 08:59, 6 June 2022
In geometry, a pentagon is a polygon with 5 sides. Each angle of a regular pentagon is ![]() . The sum of the internal angles of any pentagon is
. The sum of the internal angles of any pentagon is ![]() .
.
Construction
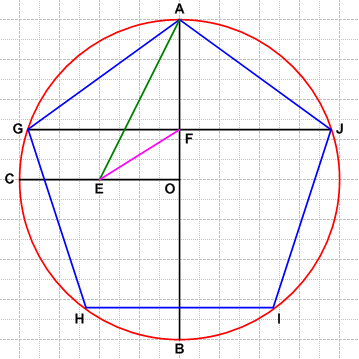
It is possible to construct a regular pentagon with compass and straightedge:
- Draw circle
 (red).
(red). - Draw diameter
 and construct a perpendicular radius through
and construct a perpendicular radius through  .
. - Construct the midpoint of
 , and label it
, and label it  .
. - Draw
 (green).
(green). - Construct the angle bisector of
 , and label its intersection with
, and label its intersection with  as
as  (pink).
(pink). - Construct a perpendicular to
 at
at  .
. - Adjust your compass to length
 , and mark off points
, and mark off points  ,
,  and
and  on circle
on circle  .
.  is a regular pentagon.
is a regular pentagon.
The Golden Ratio
The pentagon is closely associated with the Golden Ratio. More specifically, the ratio of a diagonal to an edge is ![]() .
.
See Also
This article is a stub. Help us out by expanding it.