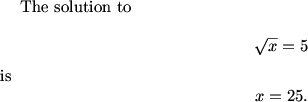Difference between revisions of "LaTeX:Math"
(→Display Style (\displaystyle)) |
(→Equation Arrays (\eqnarray)) |
||
| Line 93: | Line 93: | ||
== Equation Arrays (\eqnarray) == | == Equation Arrays (\eqnarray) == | ||
| + | One very useful tool in displaying equations well is eqnarray, which allows you to neatly align a string of equations: | ||
| + | <pre><nowiki> | ||
| + | \documentclass{article} | ||
| + | \begin{document} | ||
| + | \begin{eqnarray*} | ||
| + | 2x^2 + 3(x-1)(x-2)&=&2x^2 + 3(x^2-3x+2)\\ | ||
| + | &=& 2x^2 + 3x^2 - 9x + 6\\ | ||
| + | &=& 5x^2 - 9x + 6 | ||
| + | \end{eqnarray*} | ||
| + | \end{document} | ||
| + | </nowiki></pre> | ||
| + | Compiling this should give: | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Mathsamp5.gif]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | There are a few things to notice here. First, the * after eqnarray prevents line numbers from popping up after each line - try removing both of the *s from the source file and compile to see equation numbers. Next, notice that each line is of the form | ||
| + | |||
| + | Math stuff & more math stuff & more math stuff\\ | ||
| + | |||
| + | The & symbols separate the columns. There must be three columns (i.e. two & symbols). The \\ tells LaTeX that you are finished with this line and are on to the next. Notice that there's no \\ on the last line; the \end{eqnarray*} tells LaTeX that you're finished. As you see above, you can leave some columns blank. As a style issue, notice that we start a new line in our source file after each \\. We could run all the lines together, but that makes editing very difficult. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Usually, we only use relational symbols like =, >, or < in the middle column; eqnarray aligns these symbols as you see above. That's why we like eqnarray. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Finally, notice that there are no <nowiki>$</nowiki> symbols or \[..\], yet everything is rendered in math mode. This happens because eqnarray automatically puts everything in math mode - you don't need <nowiki>$</nowiki>...<nowiki>$</nowiki> or \[...\]. | ||
==Additional Packages== | ==Additional Packages== | ||
Revision as of 17:49, 10 July 2007
| LaTeX |
| About - Getting Started - Diagrams - Symbols - Downloads - Basics - Math - Examples - Pictures - Layout - Commands - Packages - Help |
This article will detail how to work with math mode in LaTeX and how to display equations, formulas, and mathematical expressions in general.
Contents
Math Mode
LaTeX uses a special math mode to display mathematics. To place something written in TeX in math mode, use $ signs to enclose the math you want to display. For example, open a new source file in TeXnicCenter and type or copy/paste the following:
For example, look at the following segment of code:
\documentclass{article}
\begin{document}
The solution to $\sqrt{x} = 5$ is $x=25$.
\end{document}
Save the document (press Ctrl-S or click File, then Save) as 'mymath' (don't include the quote marks in the name) in a folder of your choice. The file will appear in your folder as 'mymath.tex.'
Compile the document just as you compiled your first document. When you view the output file, you should see
If you remove the $ symbols from your source file then try to compile, you should get 'Missing $ inserted' error messages in the Output window of TeXnicCenter (try it and see - you may have to scroll up in the Output window to see the errors).
Nearly all mathematical items, such as variables, expressions, equations, etc., should be written in math mode. In fact, most math will generate errors if you don't remember to put it in math mode.
Display Math
As we saw above, when using $math stuff here$ to typeset math, the resulting math expression appears right in the test at the location of the $...$. Sometimes we want to break some of the math out out of the text and give it its own special line. To do so, we use $$math stuff here$$ or \[math stuff here\] to put the math text in math mode:
\documentclass{article}
\begin{document}
The solution to \[\sqrt{x} = 5\] is \[x=25.\]
\end{document}
After you compile this and view it, you should see:
Notice that the equations are on their own lines and are centered. As a matter of style, usually we put this display math on their own lines in the source file, like this:
\documentclass{article}
\begin{document}
The solution to
\[\sqrt{x} = 5\]
is
\[x=25.\]
\end{document}
We can also use
\begin{equation} math \end{equation}
to display mathematics. This approach also creates a label, which we can refer to later if we like. Make sure you read our notes about referencing before using these labels for references - it's much better to use \label and \ref than to refer to the equations by number in your source file.
\documentclass{article}
\begin{document}
\begin{equation}
2+2=4
\end{equation}
\end{document}
Notice the (1) out to the right when you compile the above. Once again, rather than typing (1) in your source file to refer to this equation, use LaTeX referencing commands.
Generally, you'll only use \begin{equation} when you need the label.
Display Style (\displaystyle)
Sometimes we have complicated expressions that we don't want to put on their own lines, but that don't render well with $...$ mode. For example:
\documentclass{article}
\begin{document}
Evaluate the sum $\sum_{i=0}^n i^3$.
\end{document}
gives us
That summation symbol is a little ugly. We can make it prettier by using \displaystyle:
\documentclass{article}
\begin{document}
Evaluate the sum $\displaystyle\sum_{i=0}^n i^3$.
\end{document}
This gives us:
Notice that the summation symbol looks much nicer now - adding the \displaystyle at the beginning of your math (inside the $...$) will often make complicated math render more nicely.
Equation Arrays (\eqnarray)
One very useful tool in displaying equations well is eqnarray, which allows you to neatly align a string of equations:
\documentclass{article}
\begin{document}
\begin{eqnarray*}
2x^2 + 3(x-1)(x-2)&=&2x^2 + 3(x^2-3x+2)\\
&=& 2x^2 + 3x^2 - 9x + 6\\
&=& 5x^2 - 9x + 6
\end{eqnarray*}
\end{document}
Compiling this should give:
There are a few things to notice here. First, the * after eqnarray prevents line numbers from popping up after each line - try removing both of the *s from the source file and compile to see equation numbers. Next, notice that each line is of the form
Math stuff & more math stuff & more math stuff\\
The & symbols separate the columns. There must be three columns (i.e. two & symbols). The \\ tells LaTeX that you are finished with this line and are on to the next. Notice that there's no \\ on the last line; the \end{eqnarray*} tells LaTeX that you're finished. As you see above, you can leave some columns blank. As a style issue, notice that we start a new line in our source file after each \\. We could run all the lines together, but that makes editing very difficult.
Usually, we only use relational symbols like =, >, or < in the middle column; eqnarray aligns these symbols as you see above. That's why we like eqnarray.
Finally, notice that there are no $ symbols or \[..\], yet everything is rendered in math mode. This happens because eqnarray automatically puts everything in math mode - you don't need $...$ or \[...\].