Difference between revisions of "2003 AMC 10A Problems/Problem 19"
(added problem and solution) |
(added pic) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Problem == | == Problem == | ||
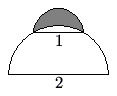
A semicircle of diameter <math>1</math> sits at the top of a semicircle of diameter <math>2</math>, as shown. The shaded area inside the smaller semicircle and outside the larger semicircle is called a ''lune''. Determine the area of this lune. | A semicircle of diameter <math>1</math> sits at the top of a semicircle of diameter <math>2</math>, as shown. The shaded area inside the smaller semicircle and outside the larger semicircle is called a ''lune''. Determine the area of this lune. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:2003amc10a19.gif]] | ||
<math> \mathrm{(A) \ } \frac{1}{6}\pi-\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4}\qquad \mathrm{(B) \ } \frac{\sqrt{3}}{4}-\frac{1}{12}\pi\qquad \mathrm{(C) \ } \frac{\sqrt{3}}{4}-\frac{1}{24}\pi\qquad \mathrm{(D) \ } \frac{\sqrt{3}}{4}+\frac{1}{24}\pi\qquad \mathrm{(E) \ } \frac{\sqrt{3}}{4}+\frac{1}{12}\pi </math> | <math> \mathrm{(A) \ } \frac{1}{6}\pi-\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4}\qquad \mathrm{(B) \ } \frac{\sqrt{3}}{4}-\frac{1}{12}\pi\qquad \mathrm{(C) \ } \frac{\sqrt{3}}{4}-\frac{1}{24}\pi\qquad \mathrm{(D) \ } \frac{\sqrt{3}}{4}+\frac{1}{24}\pi\qquad \mathrm{(E) \ } \frac{\sqrt{3}}{4}+\frac{1}{12}\pi </math> | ||
== Solution == | == Solution == | ||
| + | [[Image:2003amc10a19solution.gif]] | ||
| + | |||
The shaded area is equal to the area of the smaller semicircle minus the area of a sector of the larger circle plus the area of a triangle formed by two radii of the larger semicircle and the diameter of the smaller semicircle. | The shaded area is equal to the area of the smaller semicircle minus the area of a sector of the larger circle plus the area of a triangle formed by two radii of the larger semicircle and the diameter of the smaller semicircle. | ||
Revision as of 20:18, 4 November 2006
Problem
A semicircle of diameter ![]() sits at the top of a semicircle of diameter
sits at the top of a semicircle of diameter ![]() , as shown. The shaded area inside the smaller semicircle and outside the larger semicircle is called a lune. Determine the area of this lune.
, as shown. The shaded area inside the smaller semicircle and outside the larger semicircle is called a lune. Determine the area of this lune.
![]()
Solution
The shaded area is equal to the area of the smaller semicircle minus the area of a sector of the larger circle plus the area of a triangle formed by two radii of the larger semicircle and the diameter of the smaller semicircle.
The area of the smaller semicircle is ![]() .
.
Since the radius of the larger semicircle is equal to the diameter of the smaller semicircle, the triangle is an equilateral triangle and the sector measures ![]() .
.
The area of the ![]() sector of the larger semicircle is
sector of the larger semicircle is ![]() .
.
The area of the triangle is ![]()
So the shaded area is ![]()